![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a hernia?
|
"Rupture" of anatomical structures through a defect in the surrounding walls. Can occur all over the body. 3rd most common reason for bowel obstruction.
|
|
|
How are hernias named?
|
They are generally named for the anatomical site.
|
|
|
List common abdominal and pelvic hernias.
|
Incisional hernias
Ventral hernias Umbilical hernias Inguinal hernias Femoral hernias Epigastric hernias |
|
|
What is a reducible hernia?
|
Contents of hernia can be replaced in the surrounding structures.
|
|
|
What is a nonreducible hernia?
|
Contents of hernia cannot be replaced.
|
|
|
What is a incarcerated hernia?
|
Nonreducible hernia with subsequent bowel obstruction.
|
|
|
What is a strangulated hernia?
|
Nonreducible hernia with obstruction of blood flow, with resultant gangrene (necrosis).
|
|
|
What type of hernia has the highest incidence?
|
Inguinal
70% of all hernias are inguinal; two thirds of those are indirect, one third are direct. It is the most common type of hernias for both men and women. |
|
|
What are the next 3 (2nd-4th) highest occurring hernias?
|
15% of all hernias are incisional
10% of all hernias are ventral or umbilical 5% are femoral and others |
|
|
Who is more likely to have an inguinal hernia, men or women?
|
Men, they are 25X more likely to have inguinal hernias than women.
|
|
|
Who is more likely to have a femoral hernia, men or women?
|
Women, they are 10X times more likely to have them than men.
|
|
|
Who is more likely to have an umbilical or incisional hernia, men or women?
|
Women; umbilical and incisional hernias are 2X more prevalent in women.
|
|
|
What factors affect the prevalence of hernias?
|
Age and obesity
Prevalence of all hernias increase with age Prevalence of strangulation increases with age Prevalence of all hernias increases with obesity |
|
|
What is an indirect inguinal hernia?
|
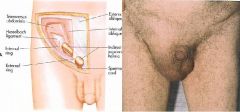
Herniating sac enters the internal inguinal ring, passes through the inguinal canal, an out the external inguinal ring and into scrotum. Most common on the right side (left more protected by tamponading effect of sigmoid colon).
|
|
|
What is a direct inguinal hernia?
|
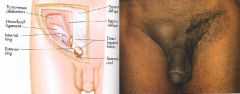
Herniating sac protrudes medial to the inguinal canal and through the external inguinal ring. Rarely extends into scrotum.
|
|
|
What is the difference in how indirect and direct hernias are managed?
|
None, they are managed the same.
|
|
|
What is a femoral hernia?
|
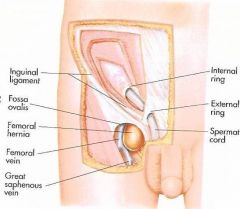
Sac herniates through the femoral canal. More common on the right due to the tamponading effect of the sigmoid colon on the left femoral canal.
|
|
|
What percentage of femoral hernias strangulate?
|
20-25%, thus repair is more common with fermoral hernias.
|
|
|
How are femoral hernias diagnosed?
|
With CT scan.
|
|
|
What is an umbilical hernia? Who is more common in?
|
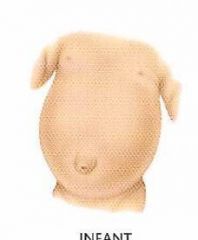
Sac herniates through defective umbilical ring; usually closes spontaneously in infants. More common in infants or adults who are obese.
|
|
|
What is an epigastric (ventral) hernia?
|
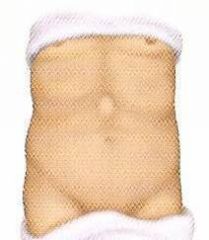
Sac herniates through defect in the linea alba, between the xyphoid process and the umbilicus.
|
|
|
What is an incisional (ventral) hernia?
|
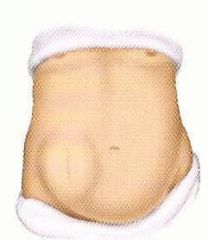
Herniating sac protrudes through operative scar. More common in obesity, post-op infection. Results from tension on one side or another of the scar. Smaller defect more dangerous (high rate of strangulation).
|
|
|
What is a diastasis recti?
|
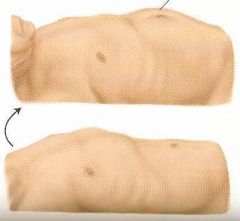
Separation of the two rectus abdominus muscles. Only visible upon increased intra-abdominal pressure (when patient sits up) causing midline ridge. Increased with pregnancies, obesity. No consequences
|
|
|
How are inguinal hernias evaluated or screened?
|
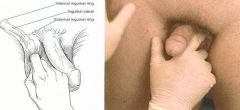
Patient must be evaluated supine and standing, or valsalva maneuver. Finger is inserted into scrotum to palpate inguinal canal.
Direct vs. indirect not important. Differential diagnosis includes all pelvic tumors, and lymph nodes, as well as testicular pathology. US and CT useful in diagnosis. |
|
|
When is surgery indicated for hernias?
|
Strangulation or possibility of (high rate) strangulation, or pain.
|
|
|
How useful are trusses?
|
Trusses generally not effective (cannot fix or prevent hernias), but sometimes helps symptoms.
|
|
|
What do all surgical techniques involve?
|
"Tension free" (mesh) repair. However, there is risk of infection.
|

