![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does GMAW stand for? |
Gas Metal Arc Welding |
|
|
MIG, Microwire, and CO2 welding are slang for what welding process? |
GMAW |
|
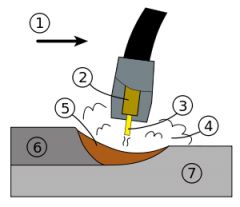
What is #1? |
The nozzel. |
|
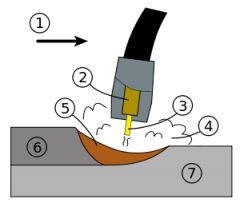
What is #2? |
The guide tube |
|
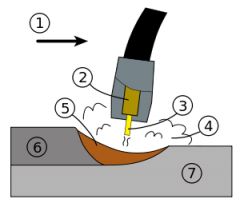
What is #3 |
The electrode |
|
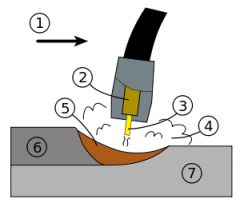
What is #4? |
The shielding gas |
|
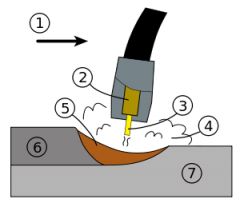
What is #5? |
molten weld metal |
|
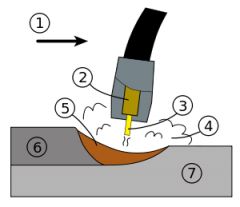
What is #6? |
solidified weld metal |
|
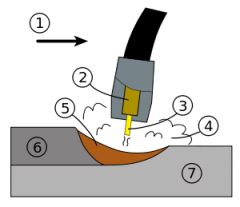
What is #7? |
The base metal |
|
|
What should you do if there is too much spatter? |
Reduce the voltage |
|
|
What is a sign of too low a voltage? |
Weld is too narrow, no penetration. |
|
|
What is a good stickout distance? |
1/4"-3/8" |
|
|
What is the correct work angle? |
90 degrees |
|
|
What is the correct travel angle? |
15 degrees |
|
|
what are the three types of GMAW application? |
manual, fixed/mechanized, automatic/robotic |
|
|
11 advantages of GMAW |
- it is the only process that can be used on most commercial metals and alloys - little spatter - continuous wire feed means little time spent changing electrodes - it can be used in all positions - the arc and weld pool are visible - little or no slag is produced - he relatively small diameter electrode allows for higher current densities - a high percentage of filler metal ends up in the weld - travel speed and deposit rates are faster than SMAW - light weight power sources can be carried to work - when using spray transfer, deeper penetration is possible compared with SMAW |
|
|
4 limitations of GMAW |
- complex, costly equipment - no wind - larger welding gun must be closer to the work for the shielding gas to work - hot and large arc |
|
|
Does GMAW require constant voltage or constant current? |
trick question: either, though constant voltage is often prefered. |
|
|
what is the purpose of the fixed voltage slope? |
to reduce short circuiting. |
|
|
steeper volt/amp curves lower what two things? |
pinch force and short-circuit current |
|
|
high short-circuit and pinch forces caused by a flat volt/amp slope causes what? |
spatter |
|
|
a very low short circuit current and pinch force caused by a steep volt/amp slope cause what? |
The electrode wire to freeze in the puddle. |
|
|
define pinch force |
the force that causes the molten drop of electrode to seperate from the solid wire electrode. |
|
|
in what system would you use a voltage sensing wire feeder? |
constant current |
|
|
how are wire feed speed and supplied current linked? |
conjunctly (both go up/down with the other) |
|
|
in which power system does the wire feed at a fixed speed? |
constant voltage |
|
|
four modes of GMAW |
short-circuit, spray, globular, and pulsed |
|
|
Which mode produces the least spatter? |
spray transfer |
|
|
what force is used in globular transfer to detach the molten electrode from the end of the solid wire? |
gravity |
|
|
"a short circuit creates a rise in current until the molten globule is pinched off" describes what welding mode? |
short circuit |
|
|
the arc is extinguished and reignited constantly in what welding mode? |
short-circuit |
|
|
which welding modes work well for lover voltages? |
short-circuit and globular |
|
|
why can't one use globular welding out of position or overhead? |
the globule will fall away from the piece or into the gun |
|
|
how stable is the arc in globular? |
not very stable |
|
|
in which mode are the molten globules smaller in diameter than the electrode? |
spray transfer |
|
|
in which mode are the molten globules larger in diameter than the electrode? |
globular |
|
|
which welding mode uses two simultaneous currents, one to maintain the arc, and the other in bursts that melt off the filler? |
Pulse |
|
|
most common power source voltages for welding |
200, 230, 460, or 575 volt |
|
|
what does a duty cycle of 60% indicate? |
the machine can weld 6 out of every 10 minutes. |
|
|
what is duty cycle? |
the percentage of time that a power supply welding machine can operate constantly |
|
|
what kind of current does most GMAW use? |
steady direct current |
|
|
what are the two ways current can be connected? |
electrode positive (reverse polarity) and electrode negative (straight polarity) |
|
|
what is the practical difference between straight and reverse polarity? |
reverse provides more penetration |
|
|
what is the more common type of polarity used in GMAW? |
reverse polarity |

