![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ways to diagnosis abdominal pain
|
- location
- quality - severity - timing/duration - context - modifying factors - associated signs and symptoms |
|
|
Pain vs. Tenderness
|
Pain is a symptom
Tenderness is a sign where you have the pain and where you have the tenderness can be different |
|
|
Cholecystitis
|
Epigastric pain
Can occur with aching, burn, or hynger can be severe can increase with smoking can occur with nausea |
|
|
Peptic Ulcer Disease
|
Epigastric pain
can occur with aching, burn, or hunger can be mildly severe can occur for an extended period of time can be constant, or decrease at night modifying factor - milk, alkylating agent associated with nausea |
|
|
Bowel Obstruction
|
Can be painful
Can be associated with nausea |
|
|
Pancreatitis
|
Epigastric Pain that radiates to the back
Associated with nausea |
|
|
GERD
|
Can be associated with epigastric pain, an aching, burning, or hunger pain, can be relatively severe.
Can be constant and decrease at hight can increase with smoking can be decreased with milk can be associated with nausea |
|
|
IBD
|
Includes Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease
|
|
|
History point most specific to IBD
|
Family member with MS
|
|
|
Abdominal Exam Pearls
|
- Epithelium = Epithelium (skin can reflect mucosa)
- Imaging/labs are very important - Rectal & Pelvic = only direct access |
|
|
Blue Rubber Bled Nevus Syndrome
|
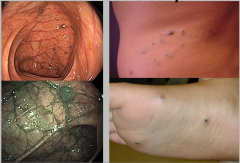
Congenital
Most common place on feet |
|
|
Management of ruptured aneurysm
|
-- diagnose with CT angiography of abdomen
STAT vascular surgery consult Type and cross for blood Maintain bp and urine output |
|
|
Flow of which blood vessel would be affected by a graft that is used to fix an infrarenal aneurysm
|
Inferior mesenteric artery
|
|
|
What is supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery?
|
Descending colon
|
|
|
Catastrophic causes of abdominal pain
|
Sudden onset
Ill appearing Unstable -- ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm -- mesenteric ischemia -- perforation of GI tract --- Ulcer, small bowel, appendix -- ruptured ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
|
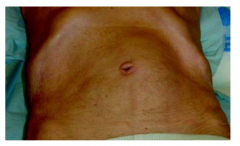
- Dilatation of the abdominal aorta > 3cm in diameter
- Common cause of sudden death - Most are asymptomatic until they rupture - High mortality rate -- most die before getting to the hospital - Size remains the best indicator of risk of rupture |
|
|
Survival - Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
|
No survival advantage with surgery if < 5.5 cm in diameter
- surveillance by ultrasonography is safe |
|
|
Treatment for Aortic Aneurysm
|
- Open surgical repair
- Endovascular repair --- lower morbidity and a faster rehabilitation |
|
|
Risk factors for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
|
- Age
- Male - Smoking - Hypertension - Aneurysm Diameter - Atherosclerosis - Genetic Factors |
|
|
Marfan Syndrome: Genetics
|
- Hereditary
- Autosomal Dominant - Defective FBN1 gene: Marfan syndrome type 1 - Defects in TGFBR2 gene = Marfan syndrome type 2 |
|
|
Marfan Syndrome: CV
|
CV complications are a major cause of mortality
Valvular heart disease is common Multiple CV processes in same patient Many pts experience a second or third aortic event CV abn: -- aortic root and ascending aorta dilation -- aortic aneurysms (thoracic and abdominal) -- aortic dissection |

