![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common protozoan parasite in industrialized countries?
|
tichomonas vaginalis
|
|
|
What are the HPV diagnostic techniques?
On histo what do you look for? |
DNA detection is very sensitive detects 13 high risk types
- look for koilocytes |
|
|
Which types of HPV represent 90% of genital warts?
Which two mc cause cancer? |
6 and 11
16 and 18 MCC cancer |
|
|
What kind of pathogenesis does HPV have?
|
non-lytic replication causes cell proliferation via E6 and E7
|
|
|
Where do the high risk types of HPV usually infect?
What are the two vaccines? |
cervical transformation zone
Gardasil (HPV6,11,16,18) and Cervarix (16 and 18) |
|
|
Vesicular labial lesions that are painful and cervical ulcerations associated with?
|
HSV- dsDNA replicates in nucleus (enveloped virus)
|
|
|
HSV transmitted how?
MC result of infection? |
direct skin to skin contact and has latency and then reactivation in ganglia
- asymptomatic infection if symptomatic usually bilateral erythematous papules/ vesicles on genitalia |
|
|
Why are HSV carriers at greater risk of HIV?
|
CD4+ T cells recruited to sites of HSV and allow direct access to mucosal tissues which allow portal entry for HIV
|
|
|
Tests for dx of HSV?
|
1. PCR- most sensitive/ rapid
2. Antibody test- a-HSV glycoprotein G, HSV Ag detection 3. |
|
|
A 23 year old female presents with fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain and vomiting of 3 days duration. She hasn’t felt well for several weeks, with general malaise, anorexia and nausea. She denies recent IV drug use. A urine specimen is brownish in color, and a physical exam revealed hepatomegaly and slight yellowing of the skin. What should you order and why?
|
Hep screenings
1. a-HAV--> possible vaccine against Hep A 2. a-HAV IgM- recent infection 3. HBsAg- Hep B is present 4. a- HBs- 5. a-HBc IgM- accute and infectious 6. a-HCV- hep c |
|
|
Type of genome for hepatitis B virus?
What is unique about it? |
circular DNA makes nucleocapsid (HBeAg)
- partially dsDNA peplicates an RNA intermediate... it is a retrovirus |
|
|
Main areas of Hepatitis B virus?
|
High- blood, serum, wound exudates
Moderate- semen, vaginal fluid, saliva low- urine, sweat, tears, breast milk |
|
|
Types of diagnosis stuff for HBV...
HBsAg, HBs GO BACK |
HBsAg: General marker of infection -HBs: Recovery and/or immunity to HBV infection
i.e. Vaccination OR natural infection -HBc IgM: Marker of acute infection -HBc (Total): Past or chronic infection HBeAg: Active replication of virus and infectiveness -HBe: Virus no longer replicating HBV-DNA: Active replication of virus- (More accurate than HBeAg Used to monitor response to therapy) |
|
|
testing for karposi?
|
Also detecting presence of KSHV in the lesion itself
PCR testing to pick up KSHV DNA |
|
|
type of HIV virus?
|
enveloped ssRNA infects CD4 + Tcells and kills them
|
|
|
What does HIV need to infect someone?
What are the strain types |
CD4 and (CCR5 (R5) or CXCR4 (X4))
|
|
|
What are the envelope proteins targeted in drugs of HIV?
|
gp120, CCR5
|
|
|
Name the 4 main stages of HIV infection
Where does it replicate during the 8-10 yr latent phase? |
1. Flulike (acute)
2. Feeling fine (latent) 3. Falling count 4. Final crisis - latent phase it replicates in lymph nodes |
|
|
What type of virus is HCV?
Major rx factor of HCV? What causes the liver damage in HCV infections? |
enveloped ssRNA from flavivirus
- drug use IV use -- Liver injury due to inflammatory cells and cytokines |
|
|
How do you diagnose HCV?
|
One of the three
1. Antibodies to hepatitis C virus (a-HCV) via EIA 2. HCV Recombinant Immunoblot Assay (HCV RIBA) 3. Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) for HCV RNA (incl. genotype) (most sensitive) AND --> is negative for IgM against HAV and HBV |
|
|
What are the 8 bacterias that cause discharge STI's? Which is the MC?
|
CC- GH- MN- TU
– Candida albicans – **Chlamydia trachomatis– - Gardnerella vaginalis – Herpes simplex virus – Mycoplasma hominis– -Neisseria gonorrhoeae– -Trichomonas vaginalis – Ureaplasma urealyticum |
|
|
What are the types of ulcerative both painless and painful bacterial causes of STI's?
|
Painless-
a. HPV b. K. granulomatis c. LGV d. Treponema pallidum Painful- a. haemophilus ducreyi (you do cry) b. HSV |
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae...
a. shape/gramstain b. test c. motile or not? (presentation?) d. virulence factors |
a. microaerophilic gram (-) diplococci
b. oxidase positive, isolated on thayer martin (chocolate agar + vanc, colistin, nystatin) c. nonmotile- purulent creamy disharge d. pili, LOS, IgA1 protease, iron scavenging, surface proteins attach to PMNS |
|
|
What bacterias can cause PID (pelvic inflammatory disease?
What is an emerging cause of it? |
New emerging cause= mycoplasma genitalum
Anaerobic bacteria (bacteroides) Falcultative Gram neg rods (ie E. coli) C. trachomatis Mycoplasma hominis |
|
|
Describe the symptomatic manifestations of DGI (disseminated gonococcal infection)
|
1. low grade fever
2. migratory polyarthralgias involving large joints (septic arthritis)- pain and swelling, w/ purulent synovial fluids, and joint destruction 3. skin rashes- pustules on the back of hang |
|
|
What strains of n. Gonorrhoeae are resistant to bactericidal effect of serum?
What are the Antigen detection and nucleic acid techniques for n. gonorrhoeae? |
AHU- (arginine, hypoxanthine and uracil
- GEN- PROBE: rapid DNA probe system |
|
|
What is found on laparoscopic examination in pelvic inflamatory disorder?
|
swollen pus-filled fallopian tubes,
- purulent exudate in the cul-de-sac |
|
|
MC bacterial STD in the US?
|
Chlamydia
|
|
|
What are the many things that chlamydia can cause?
|
NGU (non-gonococcal urethritis)
Cervicitis Salpingitis Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Infertility Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) Neonatal- respiratory/ocular |
|
|
Describe the following for chlamydia... General type of organism?
a. gram stain c. how does it infect? |
a. gram negative cell wall without peptidoglycan
c. elementary body (infectious unit) enters cell via endocytosis and reticulate body (reproductive unit) replicates by fission |
|
|
1. Which serotypes of chlamydia trachomatis cause blindness/ eye infections? why?
|
A-C due to folliular conjunctivitis in Africa (remember ABC= Africa/Blindness/Conjunctivitis)
|
|
|
1. Which serotypes of chlamydia trachomatis cause genital infections?
1. Which serotypes of c. trachomatis cause ulcerative genital infections? |
D-K
- L1-3 cause LGV lymphogranuloma venereum |
|
|
What are the main virulence factors of chlamydiae? (5)
|
1. MOMP- major outer membrane protein (ompA gene)
2. POMP- polymorphic outer membrane proteins (pmp gene) 3. Chlamydial type III secretion system (TTSS) 4. Putative chlamydial cytotoxin 5. LPS: 'rough' type... lipid A penta-acylated |
|
|
What is the gold standard for diagnosis of C.trachomatis?
|
NAAT- nucleic acid amplification, PCR and other methods
Chlamydia rapid testing: immunoassay based- rapid and less expensive test for monoclonal Ab binding of chlamydial Ag from vaginal swab |
|
|
For tissue cultures of c. trachomatis what type of stains and what would you look for?
|
McCoy cells
look for intracytoplasmic inclusions with (giemsa (iodine and immunofluorescence staining) |
|
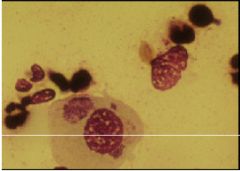
What do we have here?
|
chlamydia inclusion bodies on giemsa stain
|
|
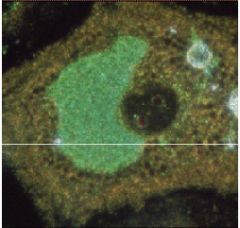
what do we have here?
|
chlamydia inclusion surrounding host cells nucleus on acridine orange stain
|
|
|
What is the most common women's health problem?
|
bacterial vaginitis
|
|
|
What are the main bacterial causes of vaginosis?
|
1. garnerella vaginalis
2. Mycoplasma hominis 3. ureaplasma urealyticum 4. Tons of anaerobes |
|
|
What are the similar clinical manifestations of bacterial vaginosis?
|
1. homogenous and thin abnormal vaginal discharge- normally white or gray with a milk-like consistency
2. vaginal mal odor 3. often vaginal itching or burning, lower abdominal pain, burning on urination |
|
|
For diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis what must there be?
|
3 of the following 4...
1. thin/homogenous discharge 2. pH of discharge greater than 4.5 3. clue cells, 4. fishy amine odor |
|
|
First AID pneumonic for memorizing gardnerella vaginalis and what to look for?
|
"I don't have a Clue why I smell Fish in the Vagina Garden"
|
|
|
Describe how a vaginitis infection occurs...
|
loss of lactobacilli (which produce hydrogen-peroxide to prevent anaerobic overgrowth) --> pH rises--> overgrowth of vaginal anaerobes
|
|
|
For garderella vaginalis what is...
a. gram stain? b. color and on what agar? c. viral factors? |
a. facultative gram-positive bacilli but does not stain consistently
b. grey colonies on chocolate agar c. adhesins and biofilm production |
|
|
Mycoplasm hominis is unique in a few ways... why?
WHAT is mycoplasms characteristic growth on agar |
smallest free living and self-replicating organsm in nature
- no CELL WALL, it contains STEROLS --> center of the colony embedded beneath the surface with a "fried egg" appearance |
|
|
what is the most common protozoal urogenital tract infection?
What is treatment? |
trichomonas vaginalis
- metronidazole |
|
|
Trichomonas vaginalis...
a. clinical presentation b. dx? |
a. foul smelling green or yellow creamy discharge, that itches and burns
b. Trophozoites (mobile w/flagella) on wet mount--- "pear shaped" |
|
|
Vulvovaginal candidiasis features?
|
d/t to overgrowth of dimorphic fungus
mycotic vuvovaginitis, itching and burning pain - white, thick discharge, "curd like", with white spots on the vagina |
|
|
What does candida albicans look like at 20 degrees?
at 37? |
20- pseudohyphae and budding yeasts
37- germ tubes - use KOH prep of vag. secretions, can also culture on Sabouraud's medium |
|
|
1. What is the bug that causes syphilis?
2. What is the shape and description of syphilis? 3. What do you use to visualize? 4. What are the major virulence factors? |
1. treponema pallidum
2. delicate and highly motile corkscrew-shaped spirochetes 3. darkfield microscopy technically gram-neg but doesnt gram stain 4. motility, the slow growth allows immune evasion |
|
|
Describe the following types of syphilis...
a. primary b. secondary c. latent d. tertiary |
a. presents with painless chancre regional lymphadenopathy
b. disseminated rash, condylomatas and generalized lymphadenopathy (secondary means systemic) c. recurrence of secondary in 25% d. Gumma (chronic granulomas), cardiovascular aortitis, argyll robertson pupil and tabes dorsalis |
|
|
How do you identify t. pallidum non-blood wise?
|
1. Direct exam w/ physcial lesions
a. Darkfield microscopy b.. direct fluorescent Ab test for T. pallidum (DFA-TP) 2. Preliminary serologic tests- |
|
|
What are the preliminary serologic tests for syphilis?
What is the go-to confirmatory test for syphilis? |
1. nontreponemal Ag tests (to r/o syphilis)- measure IgG and IgM directed against a lipoidal material released from damaged cells
2. VDRL- confirm with Fluorescent Ab absorption (FTA-ABS) 3. TRUST 4. RPR |
|
|
What could cause a false positive syphilis test? (VDRL)
|
VDRL-
1. Virus (mono, hepatitis) 2. Drugs 3. Rheumatic fever 4. Lupus and leprosy - also pregnancy, malignant neoplasms |
|
|
1. What causes Chancroid? How does it present?
2. What is slightly unique about its composition? 3. What kind of agar? |
Haemophilus ducreyi (H. ducreyi is so painful you "do cry")
- presents with a painful genital ulcer and inguinal adenopathy - oxidase positive 3. Mueller- Hinton agar (cohesive colony morphology, hemin requirement, oxidase positive) |
|
|
Donovanosis (granuloma inguinale)... describe the lesion
a. causative agent? b. type of gram pic? c. type of stain? d. where is it MC seen? |
rolled border on a large red, cobblestone base
a. klebsiella (Calymmatobacterium) granulomatis b. encapsulated gram (-) short rod c. giemsa stain- safety pin appearance (bipolar stained bacilli within mononuclear cells) d. tropics |
|
|
How does a dumbass make a diagnosis of donovanosis?
|
"donovan bodies" precence of mononuclear cells with intra-cytoplasmic vacuoles of bacteria
|
|
|
Lymohogranuloma venereum (LGV)
describe the lesion a. causative agent? b. type of gram pic? c. type of stain/dx? d. where is it MC seen? |
Rectal strictures, lymphadenopathy, genital ulcers
a. chlamydia trachomatis L1-3 b. c. serology for increased Ab titer: tissue culture (McCoy cells)- LGV complement fixation tests (LGV-CFT) d. Tropical africa and Asia |

