![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acurracy of automatic bending equipment |
+- 0.005" |
|
|
Applying force great enough to go beyond elastic limit but not so far as to exceed the ultimate strength |
Plastic deformation |
|
|
Critical mechanical property when selecting material to bend |
% of ductility |
|
|
Bending on easy plane is |
Bending on narrower plane or dimension |
|
|
Bending on hard plane |
Bend on wider plane or dimension |
|
|
If tube is bent too close to the end |
Edge distortion on pipe |
|
|
Recommended min. Radius when bending round tubing |
2.5x outside diameter |
|
|
Min bend radius when bending square tube |
4x OD |
|
|
Stretch out length for pipe bending calculated on 90° bend by |
1.57 x mean bend die radius |
|
|
Most versatile and accurate method of Bending |
Draw bending |
|
|
Obtains 2 simultanious compression bends with each bend being .5 of desired bend angle |
Press bending |
|
|
Workpiece clamped against bending die, die and clamp rotated moving workpiece through a pressure tool. Uses mandrel |
Draw bending |
|
|
Tube is clamped to a stationary bending form and wrapped around it |
Compression bending |
|
|
Similar to plate rolling. Limited to heavy wall tube |
Roll bending |
|
|
Tube stretched longitudinally past elastic limit by pulling both ends then wrapping tube around a form. Used for irregular shapes |
Stretch bending |
|
|
Primary tool around which workpiece is formed |
Bend die |
|
|
Matching half of bend die to form true circle when closed |
Clamp die |
|
|
Contains tube in bend die groove during bend cycle |
Pressure die |
|
|
Prevents flattening, wrinkling or tube collapse during bending |
Mandrel |
|
|
4 factors to consider when selecting bending lubricant |
•Provide physical barrier to protect mandrel and inside of tube • Lube film must remain intact and not dry from heat of forming • Overcome frictional drag of tube over mandrel • Compatible with tooling and workpiece material |
|
|
Ability of material to deform plastically without fracture |
Ductility |
|
|
Line between compression and tensile forces |
Neutral axis |
|
|
Material length should extend how far past bend to prevent distortion |
2x diameter |
|
|
Type of bender capable of both draw and compression bends |
Hossfield benders |
|
|
What are diacro benders |
Compression benders |
|
|
Type of tube bending produces full circles and coils |
Roll bending |
|
|
Inserted into tube to prevent collapse |
Mandrel |
|
|
3 common types of mandrel |
Plug, form and ball |
|

|
3 roll pinch type |
|
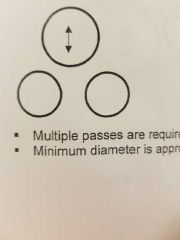
|
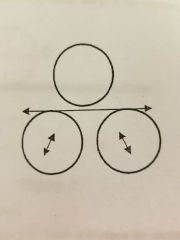
3 roll pyramid type |
|
|
2 roll machine |
|
|
3 types of rolls for sheet metal |
3 roll pinch, 3 roll pyramid, 2 roll |
|
|
3 roll pinch pyramid type |
|
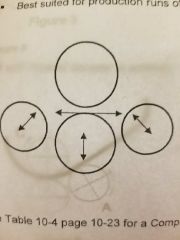
|
Double pinch four roll |
|
|
Types of rolls for plate rolling |
3 roll pinch, 3 roll pinch pyramid, double pinch 4 roll |
|
|
Min diameter achievable with 3 roll pyramid style |
Top roll diameter plus 2 inches |
|
|
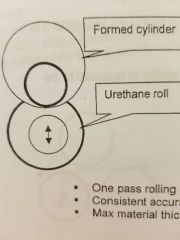
Max material thickness for 2 roll urethane rolls |
1/4" |
|
|
Plate roller choice of most fabricators and produces most accurate curvatures |
3 roll pinch |
|
|
Signed for 1 entry 1 pass forming |
Double pinch 4 roll |
|
|
When pipe bending round or square tubing, how is lube used |
Square tubing lubricated forming die. Round tubing never lubricated forming die |

