![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
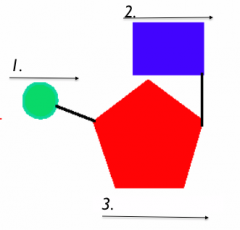
RNA |
1. Phosphate 2. Nitrogen Base 3. Five Carbon Sugar |
|
|
RNA |
- Ribonucleic acid -Single stranded -Found inside and on the outside of a nucleus - RNA is a macromolecule (nucleic acid) |
|
|
RNA Nitrogen Bases |
- Adenine -Uracyl -Cystosine -Guanine |
|
|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
-Carries info from DNA in the Nucleus to Ribosomes in the Cytoplasm -mRNA is a cop of a section of DNA -Contains genetic info |
|
|
Codon |
-a Codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides in mRNA and codes for one amino acid |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
-Transports amino acids from cytoplasm to ribosomes during protein synthesis |
|
|
Anticodon |
sequence of three nucleotides on the tRNA (tRNA anticodon matches mRNA codon) |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
-Ribosome are made of this - mRNA brings the message from DNA to the ribosome (rRNA) and the tRNA brings the corresponding amino acids - Allows mRNA and tRNA to work together |
|
|
How do cells make a protein? |
Joining together amino acids |
|
|
Protein Synthesis |
Transcription and Translation |
|
|
Transcription |
The process of making messenger RNA from the DNA template |
|
|
Transcription Process |
1. DNA unzips and the RNA bases attach to the exposed bases making a strand of mRNA 2. mRNA separate from DNA template 3. mRNA leaves nucleus to go to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm (basically mRNA is made in the nucleus using the DNA as a template and then the mRNA leaves the nucleus to the ribosomes to make proteins) |
|
|
Translation Steps |
1. mRNA goes from nucleus to ribosomes 2. tRNA picks up free amino acids from cytoplasm and brings them to the ribosome 3. The tRNA anticodon attaches to the mRNA codon and releases the amino acid 4. More tRNA brings amino acid and a chain of amino acids begin to form 5. Eventually a STOP codon appears in the mRNA marking the end of the protein |
|
|
Gene |
a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein |
|
|
Gene Mutations |
Mutations that produce changes in a single gene 1. Point Mutations 2. Frameshift Mutations |
|
|
Chromosomal mutations |
change in the number or structure of chromosomes |
|
|
Point Mutation |
Change in one or fewer bases: -Substitution- |
|
|
Frameshift Mutations |
These mutations occur when a base is inserted or deleted. Shifts codon |
|
|
Deletion |
A piece of a chromosome is lost |
|
|
Duplication |
a piece of a chromosome is duplicated |
|
|
Inversion |

a piece of chromosome is reversed or flipped around |
|
|
Translocation |
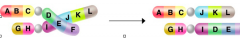
a piece of chromosome breaks off and attaches to another |
|
|
Mutagens |
natural or human-made element that can change a structure or sequence or DNA ex. Chemicals, Radiation |
|
|
Cutting DNA |
We cut DNA into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes.Restriction enzymes cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence. They are very specific.We obtain restriction enzymes from bacteria |
|
|
Making Recombinant DNA |
1. Restriction enzymes recognize specific DNA sequences 2. Restriction enzyme cuts DNA producing sticky ends 3. DNA fragment from other source is added; fragments stick together by base pairing 4. DNA ligase seals the strands |
|
|
Transgenic |
organism that contains DNA from other species |
|
|
Plasmid |
circular DNA molecules found n the cytoplasm of bacteria in addition to regular DNA |
|
|
Polymerase Chain reaction (PCR) |
Makes more copies of DNA 1. DNA fragment heated 2. 2 strands separate 3. Solution cools and DNA polymerase attaches to free nucleates to the open strands 4. TWO DNA MOLECULES |
|
|
Separating of DNA |
1. mixture of fragments placed at the end of a gel 2. electric voltage applied 3. DNA - charged so moves toward + 4. When current is turned off molecules are arrayed in bands along a law according to size |
|
|
Chromosones |
Made of DNA pieces coiled around histones |
|
|
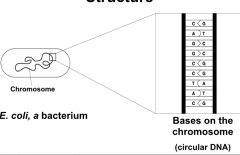
Prokaryotic Chromosome Structure |
|
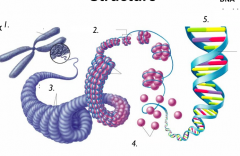
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure |
1. Chromosome 2. Nucleosomes 3. Supercoils 4. Histones 5. Double Helix |
|
|
Nucleotides |
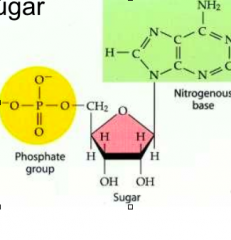
Made of Phosphate, Deoxryribose sugar, Nitrogen base: ADENINE, GUANINE, CYTOSINE, THYMINE |
|
|
Side of Ladder-like structure |
the sides of a DNA strand are made up of sugar and phosphate molecules bonded by covalent bonds. |
|
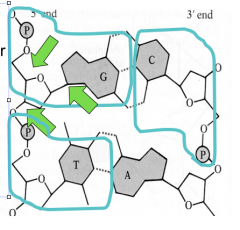
|
phosphate and sugar covalent bonds |
|
|
Rungs of ladder |
Nitrogenous bases joined by hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Complementary Base Pairing |
A=T C=G |
|
|
Erwin Chargaff |
1949 Discovers rules of base pairing |
|
|
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins |
1952 Determined that the DNA molecule was a coiled spiral. They used a technique called X-ray diffraction. |
|
|
James Watson and Francis Crick |
1953 Determined the exact structure of DNA |
|
|
DNA REPLICATION |
-occurs during interphase -takes six hours -Nucleus(eukaryotes) Cytoplasm (prokaryotes) |
|
|
Steps of Replication |
1. Enzymes unwind DNA double helix- helices breaks H-bonds 2. DNA Polymerase brings complementary nucleotides and attaches them t the matching nucleotides in the open strands 3. Continues until completely unzipped 4. DNA polymerase proofreads DNA |
|
|
Two Original Strands of DNA |
Templates |
|
|
New Formed Strands |
Complementary |
|
|
Semi-conservative |
Each replicated DNA molecule consists of old and new strands |
|
|
Pyrimadine |
nitrogen bases in DNA composed of a single ring: Thymine and Cytosine |
|
|
Purine |
Nitrogen bases in DNA composed of two rings: Adenine and Guanine |
|
|
Griffith |
First experimented with mice and discovered strains of bacteria would be changed from one form to another |
|
|
Avery |
Second Used enzymes to test lipids, carbs, and nucleic acids and discovered that nucleic acid DNA is what stores and transmits genetic info from one generation to the next. |
|
|
Hershey and Chase |
Third Worked with bacteriophages and concluded that genetic material of bacteriophages was DNA, not protein |
|
|
Ligase |
enzyme that glues pieces of DNA together once replicated |
|
|
Helicase |
Enzyme that unzips DNA strands and breaks hydrogen binds |
|
|
Peptide Bond |
bond holding together amino acids |
|
|
Polypeptide |
Chains of amino acids |

