![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Middle course
|
U shaped valley
Smaller material Wide and deep channel Faster flowing |
|
|
Upper course
|
Steep gradient
V shaped valley Narrow and shallow Large rocks |
|
|
Lower course
|
Broad and deep
Fast flowing Mostly deposition Gentle gradient |
|
|
Change between source to mouth
|
Width, depth, velocity, discharge increases
|
|
|
How is a waterfall formed
|
Softer rock is cut back leaving an overhang of hard rock. In time the overhang with fall. As water splashes from plunge pool, hydraulic action occurs. Eventually a gorge will occur
|
|
|
Flood plain
|
Wide flat area of land on either side of the lower course
|
|
|
Levee
|
Naturally raised bank that extends along a river bank
|
|
|
How is a levee formed
|
Meandering channels deposit sediment on inside and deposit on outside, widening the flood plain. It floods the surrounding land. As water moves away it becomes shallower, more friction and deposition. It drops the largest material close to the river to form a levee
|
|
|
Diagram of levee
|
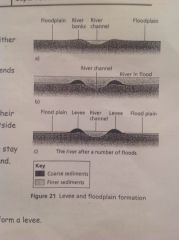
|
|
|
Diagram of waterfall
|
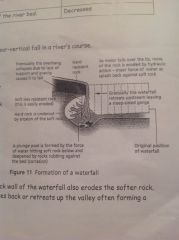
|
|
|
Source
|
Start of river
|
|
|
Watershed
|
The boundary of a river basin
|
|
|
Mouth
|
Where river meets the sea
|
|
|
Confluence
|
The point where two rivers meet
|
|
|
Tributary
|
A stream that joins a larger river
|
|
|
Freeze thaw |
water freezes in a crack widening it |
|
|
Meanders |
Bend in a river (horseshoe shape) |
|
|
Slip off slope |
Inner bend of a river where deposition occurs |
|
|
Oxbow lake |
The neck of the meander join together over time |
|
|
Why do rivers flood? Physical |
Rain fall (soil infiltration) Geology (unable to percolate) Drainage basin (enters system quicker) Snow melt(more water) |
|
|
Why do rivers floor? Human |
Deforestation (decrease of interception storage) Climate change(ice melt) Urbanisation(impermeable) |
|
|
Cumbria river flood |
6 killed 140 properties destroyed |
|
|
Effects of river flooding |
Loss of goods Wildlife destroyed |
|
|
Management schemes |
Water blocking windows Flood wall Washlands |
|
|
Reducing impact of flooding |
Build on stilts Sandbags High sockets Pppe |
|
|
Flood soft engineering |
Afforestation Land use zoning Wash lands |
|
|
Wash lands |
Cheap Industry can't use jt |
|
|
Wash lands |
Cheap Industry can't use jt |
|
|
Land use zoning |
Safer Planning problems |
|
|
Hard engineering |
Channelisation Flood relief channels Embankments |
|
|
Embankments |
Adding levees |
|
|
Hard engineering |
Channelisation Flood relief channels Embankments |
|
|
Embankments |
Adding levees |
|
|
Land use zoning |
Safer Planning problems |
|
|
Channelisation |
Deepening or widening a channel |
|
|
Wash lands |
Cheap Industry can't use jt |
|
|
Land use zoning |
Safer Planning problems |
|
|
Hard engineering |
Channelisation Flood relief channels Embankments |
|
|
Embankments |
Adding levees |
|
|
Channelisation |
Deepening or widening a channel |
|
|
Management at cocker mouth |
Floodgates flood wall River is dredged Embankments |

