![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
At the keystone area of the nose, which of the following most accurately describes the anatomic position of the upper lateral cartilage in relation to the nasal bones? A) Anterior to the nasal bones B) Caudal to the nasal bones with a 1 to 2 mm fibrous gap C) Edge to edge with the nasal bones with no overlap D) Posterior to the nasal bones
|
D) Posterior to the nasal bones The keystone area of the nose is where the nasal bones overlap the upper lateral cartilages. This is usually the widest part of the nasal dorsum. At the dorsal keystone area, the nasal bones overlap the upper lateral cartilages for a distance of 4 to 14 mm. |
|
|
|
Internal nasal valve borders: lateral and superior? |
The internal nasal valve, formed at the junction of the septum (medially), the nasal floor (inferiorly), the inferior turbinate (laterally), and the caudal border of the upper lateral cartilages (superiorly), accounts for a significant amount of airway resistance. |
|
|
|
A 22-year-old woman is evaluated for revision rhinoplasty. A closed approach is planned. The alar margin is in an appropriate position. On lateral view, excessive columellar show is noted. Which of the following incisions is most appropriate for management of this deformity? A) Alar rim B) Intercartilaginous C) Intracartilaginous D) Killian E) Transfixion |
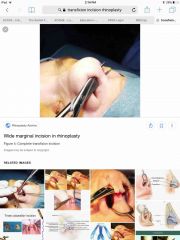
Transfixion |
|
|
|
35-year-old woman is scheduled to undergo functional septorhinoplasty for nasal airway obstruction. In this patient, perioperative administration of corticosteroids is most likely to have which effect on edema and ecchymosis? |
Decrease both |
|
|
|
The first suture for a broad, bulbous tip is the _____ suture. This suture will narrow the dome and narrow the convexity of the lateral crus with mild increased tip projection. |
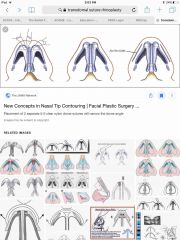
The first suture for a broad, bulbous tip is the transdomal suture. This suture will narrow the dome and narrow the convexity of the lateral crus with mild increased tip projection. |
|
|
|
A 25-year-old man undergoes a submucous resection of the septum for airway obstruction. While the surgeon is scoring the remaining L-strut, the cartilage fractures along the dorsal strut. Reconstruction with which of the available grafts is the most appropriate next step in management? |
When an L-strut fracture occurs, it should be repaired to avoid middle-third nasal collapse. The strut tends to rotate posteriorly, creating a saddle-nose deformity. Spreader grafts secured with sutures will act like a batten graft and secure the L-strut in place. |
|
|
|
The _____ muscle dilates the nares. Paralysis of the muscle allows for collapse of the external valve resulting in airway obstruction. |
The levator labii superioris muscle dilates the nares. Paralysis of the muscle allows for collapse of the external valve resulting in airway obstruction. |
Lip muscle |
|
|
The angle of divergence of the nasal tip is determined using which of the following structures of the lower cartilages? A ) Middle and lateral crura B ) Middle and medial crura C ) Right and left foot plates D ) Right and left lateral crura E ) Right and left middle crura |
E ) Right and left middle crura
The correct response is Option E. |
|
|
|
A 35-year-old man comes to the office for a consultation because he is dissatisfied with the result of a rhinoplasty performed 2 years ago. The patient reports that his nasal openings collapse on deep inspiration and his nasal tip is deformed. Physical examination shows collapse of the external nasal valve on deep inspiration and bilateral asymmetric alar rim collapse with alar retraction of 1 to 2 mm. Revision rhinoplasty is planned. Which graft is most appropriate to correct these conditions? |
Lateral crural strut. strip of septal cartilage that (if available for harvest) is sutured to the underside of the lower lateral cartilage and provides increased support and position control. It is a very powerful graft that can reposition lower lateral cartilages, correct alar retraction, and correct external valve collapse. |
|
|
|
During secondary open rhinoplasty through an existing transcolumellar incision, division of which of the following arteries is most likely to result in vascular ischemia of the nasal tip? A) Anterior ethmoid B) Columellar C) Dorsal nasal D) External nasal E) Lateral nasal |
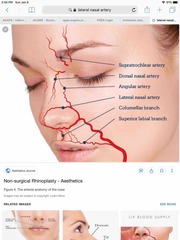
E) lateral nasal While contributions from the ophthalmic circulation's anterior ethmoid, dorsal nasal, and external nasal arteries are present, the dominant supply is derived from branches of the facial artery. Its branches, the columellar artery (present in 68.2% of cadavers in one study) and the lateral nasal artery (present in 100% of cadavers), are more likely to provide the nasal tip with inflow even if the ophthalmic arterial branches are sacrificed during the dissection. |
|
|
|
Which type of graft can be used to correct a pinched nasal deformity? |
Subdomal grafts can be used to correct a pinched nasal tip deformity as well as asymmetry of the domes. The subdomal graft is bar shaped, spanning beneath both domes, controlling the horizontal and vertical orientation of the domes.
|
|
|
|
The intercartilaginous incision in rhinoplasty follows the caudal border of which of the following? A) Alar lateral crus B) Caudal septum C) Lower lateral cartilage D) Middle crus E) Upper lateral cartilage |
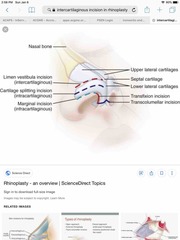
E) Upper lateral cartilage |
|
|
|
30-year-old woman wants improvement of the bulbous tip of her nose. Open rhinoplasty and thinning of the tip is planned. Intraoperative examination shows the cause of the bulbous tip is widely convex lower lateral cartilages that are thick and relatively inflexible. The domal width is greater than 6 mm. The angle of divergence is normal. Which of the following surgical maneuvers is most likely to correct the deformity?
A) Alar rim grafting B) Cephalic trimming of the lower lateral cartilage C) Crural spanning sutures D) Lateral crural strut grafting E) Subdomal spreader grafting |
D) Lateral crural strut grafting A bulbous/boxy tip can be caused by a convex lower lateral cartilage with a wide domal width (less than 4 mm), widened angle of divergence (less than 30 degrees), or a combination of both. This patient's deformity is a widely convex lower lateral cartilage. The best choice is a lateral crural strut graft. This graft is usually harvested from the septum and sutured to the undersurface of the lower lateral cartilage. These grafts are strong and can reshape a thick inflexible lower lateral cartilage. Crural spanning sutures can straighten the convexity of these cartilages if the cartilages are flexible; however, in this patient it would unlikely be successful. |
|

