![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
216 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CNS consists of |
Brain and spinal chord |
|
|
PNS consists of |
All other nerves within the body |
|
|
3 functions of nervous system |
Detects stimuli(external and internal) Brain processes stimuli Produces a response |
|
|
3 basic parts of the Neuron |
Cell body Axons Dendrons |
|
|
Axon hillock is |
Where the cell body attaches to the axon |
|
|
Axon hillock is |
Where the cell body attaches to the axon |
|
|
Myelin sheath |
Increases the speed of the nerve impulse Made of lipoprotein Composed of Schwann cells (white) |
|
|
Axon hillock is |
Where the cell body attaches to the axon |
|
|
Myelin sheath |
Increases the speed of the nerve impulse Made of lipoprotein Composed of Schwann cells (white) |
|
|
Node of Ranvier |
Allows oxygen and nutrients to pass to the Axon |
|
|
Neuromuscular junction |
Where the Axon meets the muscle fibre |
|
|
A synapse is |
The junction between the processes of 2 neutrons,or between a neutron and an efferent organ |
|
|
Each axon terminates at a synapse. As the nerve impulse travels down the Axon it moves towards the : |
Pre synaptic membrane |
|
|
The impulse reaching theory synaptic membrane causes the release of 2 transmitter chemicals: |
Acetylcholine and Epinephrine |
|
|
The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse rapidly across the --------- ---- and bind with specific receptors on the ---- --------- --------- |
Synaptic cleft Post synaptic membrane |
|
|
NT chemicals make the post synaptic membrane -------------- and allow the nerve impulse to continue on down the ------ ----- |
Excitable Nerve fibre |
|
|
The synaptic effect is stopped by the release of ------------ which destroys any acetylcholine that may remain in the synaptic cleft . |
Cholinesterone |
|
|
A particular neuron will always transmit with the same speed. The different effects of the nervous system depends on: (3) |
The number of nerve impulses transmitted The number of neutrons activated The type of neurons stimulated |
|
|
Cranial Eye Nerves : (4) |
II: Optic III: Oculomotor IV: Trochlear VI: Abducens |
|
|
Cranial mouth/tongue nerves: (2) |
IX: Glossopharyngeal XII: Hypoglossal |
|
|
Cranial Smell nerve |
I: Olfactory |
|
|
Cranial Thorax/organs nerve |
X: Vagus |
|
|
Cranial Pharynx nerve |
V: Trigeminal |
|
|
Cranial Neck nerve |
XI: Accessory |
|
|
Cranial face nerve |
VII: Facial |
|
|
Cranial Hearing and Balance nerve |
VIII: Vestibulocochlear |
|
|
Cranial sensory nerves: (3) |
Olfactory (I) Optic (II) Vestibulocochlear (VIII) |
|
|
Cranial Motor nerves (6) |
Oculomotor (III) Trochlear (IV) Abducens (VI) Facial (VII) Accessory (XI) Hypoglossal (XII) |
|
|
Cranial mixed nerves (3) |
Trigeminal (V) Glossopharyngeal (IX) Vagus (X) |
|
|
Cranial parasympathetic nerves (4) |
Oculomotor (III) Facial (VII) Glossopharyngeal (IX) Vagus (X) |
|
|
The brain controls |
The voluntary and involuntary activities of the body |
|
|
The brain controls |
The voluntary and involuntary activities of the body |
|
|
Structures that surround and protect the brain are (2) |
The skull The meninges |
|
|
Meninges (outer, middle and inner) |
Dura mater: outer Arachnoid mater: middle Pis mater: inner |
|
|
Samples of CSF are collected from the --------- ------ between the ----------- and --------- ---------- |
Back (Definition) Cisterna magna Cerebellum and medulla oblongata |
|
|
Functions of CSF (2) |
Protect the CNS from damage by movement or knocks Provides nutrients to the nervous system |
|
|
Brain is divided into 3 parts |
Forebrain midbrain and hindbrain |
|
|
Largest part of theforebrain is the |
Cerebral hemispheres , which consist of nerve cells and nerve fibres |
|
|
The series of folds in brain tissue are called |
Sulci and Gyri |
|
|
4 lobes of the cerebral hemispheres |
Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal |
|
|
Bulk of cerebral hemisphere consists of ----- matter and composed of nerve fibre tracts called ------------ ------ |
White Myelinated fibres |
|
|
White matter provides links for transfer of information between |
Areas of the brain and the spinal chord |
|
|
White mater is covered by a thin layer of ---- -------- which is composed of ---- ------- |
Grey matter Cell bodies |
|
|
Grey matter is |
Non myelinated |
|
|
The olfactory bulb is concerned with |
Transmitting the impulse of smell from the nasal passages to the cerebral hemispheres where they can be interpreted |
|
|
The --------------- controls the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
The -------- is composed of grey matter and provides communication between the cerebral hemispheres a specific area of the brain |
Thalamus |
|
|
The ----------- ----- is an endocrine gland located below and attached to the hypothalamus via a stalk |
Pituitary gland |
|
|
The ------ ------- is the place where the optic nerves cross over to allow impulses from both eyes to reach the brain to give a binocular image |
Optic chiasm |
|
|
The forebrain is concerned with (8) |
Vision Hearing Olfaction Taste Pain Personality Learning Memory |
|
|
The --- ----- is situated within the cerebral hemispheres and is hidden |
Mid Brain |
|
|
The mid brain connects the forebrain with |
The rest of the brain |
|
|
The roof of the midbrain is called the ------ which passes visual and auditory reflexes to the forebrain |
Tectum |
|
|
The midbrain controls |
The movement of the head to focus objects and to locate the source of sounds . |
|
|
The midbrain controls |
The movement of the head to focus objects and to locate the source of sounds . |
|
|
The floor of the midbrain is concerned with |
Subconscious muscular movements such as bending and rotation |
|
|
The midbrain controls |
The movement of the head to focus objects and to locate the source of sounds . |
|
|
The floor of the midbrain is concerned with |
Subconscious muscular movements such as bending and rotation |
|
|
The midbrain maintains |
Consciousness |
|
|
Endocrine glands release hormones through..... Existing glands release hormones through... |
Endocrine = bloodstream (ductless) Exocrine= ducts |
|
|
Hormones may be (3) |
Steroids proteins or amines (derived from amino acids) |
|
|
7 glands |
Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Pancreas Ovaries Testes Adrenal |
|
|
Secretion of a hormone occurs |
In response to a specific stimuli |
|
|
Stimuli to the Endocrine system may be (4) |
1. Nerve impulses: eg adrenaline being released in response to sympathetic nervous system 2. Stimulating/releasing hormone : eg TSH from anterior Pituitary gland activates the Thyroid gland 3. Levels of chemicals in the blood: eg raised glucose levels stimulating release of insulin from Pancreas 4. Feedback loops preventing over secretion or reduce secretion once effect is achieved : eg oestrogen from ovarian follicles prevent secretion of FSH from anterior Pituitary gland, preventing further Follicle development |
|
|
Some hormones are released by |
Tissue from a other organ |
|
|
Organ tissue hormone secretions (4) |
1. Gastrin - produced by wall of stomach, starts digestion when food enters 2. Secretin - produced by wall of small intestine, continues digestion 3. Chorionic gonadotrophin - produced during pregnancy, helps to maintain corpus luteum in ovary throughout gestation 4. Erythropoetin / ESF - produced by kidney in response to low blood oxygen, stimulates production of erythrocytes/ RBC |
|
|
Position of glands |
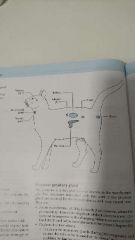
|
|
|
Anterior Pituitary gland also known as |
Adenohypophysis |
|
|
Anterior Pituitary produces : (7) |
TSH Somatotrophin ACTH- adrenocorticotrophic hormone Prolactin FSH Luteinising hormone ICSH - Interstitial cell stimulating hormone |
|
|
Posterior Pituitary gland produces (2) |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin |
|
|
Diabetes insipidus presents as: |
PU PD Polyphagia Urine SG 1.00 (normal = 1.018 - 1.045) |
|
|
TSH stimulates |
The Thyroid gland |
|
|
Somatotrophin stimulates |
Rate of growth in young animals Controls from epiphyses of bones Protein production from amino acids Regulatng use of energy during periods of poor food supply. Conserves glucose for nervous system and fat broken down as source of energy for body |
|
|
ACTH stimulates |
Adrenal cortex - over secretion may cause symptoms of Cushings disease |
|
|
Prolactin stimulates |
Secretion of milk Development of mammary glands |
|
|
Thyroid secretes 3 hormones |
Thyroxine (t4) Tri iodothyronine (t3) Calcitonin |
|
|
Parathyroid gland |
Secretes parathormone Responds to lowered blood calcium levels Stimulates calcium reabsorption from bones, promotes calcium uptake from intestines |
|
|
Adrenal cortex secretes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - in response to ACTH, in order to raise blood glucose levels and reduce inflammatory response |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
Adrenal cortex secretes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -(2) in response to status of ECF and plasma |
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone and sex hormones) |
|
|
Adrenal medulla secretes - - - - - - - . & - - - - - - - - - - - - in response to the sympathetic nervous system to action the fight flight fear responses |
Adrenaline and noradrenaline |
|
|
Calcitonin (3 things ) |
Secreted by the Pancreas Responds to raised blood calcium levels Decreases resorption of calcium from the bones |
|
|
Process of control of blood calcium |
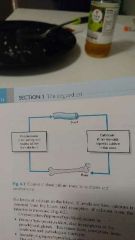
|
|
|
Process of control of blood glucose |
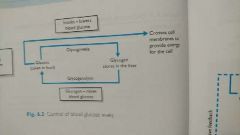
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system |
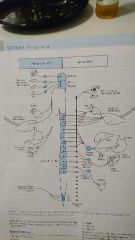
|
|
|
Reflex arc is |
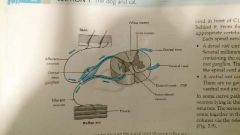
|
|
|
The dorsal root carries sensory fibres - - - - - the spinal chord |
Towards |
|
|
The small swelling containing cell bodies of sensory neurons is |
The dorsal root ganglion |
|
|
The ventral root carries motor fibres - - - - - - - - - - - - the spinal chord |
Away from |
|
|
There are - cervical nerves but - cervical vertebrae |
8 nerves 7 vertebrae |
|
|
In some pathways there may be one or more - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - lying in the grey natter between the sensory and motor neurons |
Intercalated neurons |
|
|
3 types of neuron |
Bipolar (interneuron) Unipolar (sensory) Multipolar (motoneuron) |
|
|
3 types of neuron |
Bipolar (interneuron) Unipolar (sensory) Multipolar (motoneuron) |
|
|
The ---- relays impulses to the cerebellum |
Pons |
|
|
There are - ventricles of the brain responsible for the production of CSF : |
Lateral ventricle Third ventricle Fourth ventricle ? Wtf |
|
|
Oestrogen from the Graafian follicle of the ovaries prepares the ------- ------------ ---- for ------ |
Female reproductive tract Mating |
|
|
Oestrogen from the Graafian follicle of the ovaries prepares the ------- ------------ ---- for ------ |
Female reproductive tract Mating |
|
|
------------- acts on sperm to give it --------- ---- |
Oestrogen Longer life |
|
|
Hyperparathyroidism is |
A result of increase in size/ growth of the PThyroid Causes can be tumour, paraphasia resulting in an increase in PTH Increase PTH = keep releasing Calcium from bones |
|
|
The aqueduct of Silvius lies within the -------- of the CNS |
Midbrain |
|
|
The cranial nerve responsible for gustation is |
Glossopharyngeal (IX) |
|
|
The cells of the ----------- ------- reflect light back to the photoreceptors cells of the ----- |
Tapetum lucidum Retina |
|
|
The cells of the ----------- ------- reflect light back to the photoreceptors cells of the ----- |
Tapetum lucidum Retina |
|
|
The reflex used to test for level of anaesthetic is |
Palpebral |
|
|
The --------- and ---------- is used to monitor balance |
Utricle and saccule |
|
|
Pancreas location |
In the loop of the duodenum in the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Pancreas location |
In the loop of the duodenum in the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Endocrine secretions from pancreas (3) from the ------- -- --------- |
Islets of langerhans |
|
|
Islets of langerhans release |
Alpha : Glucagon Beta : Insulin Delta : Somatostatin |
|
|
Insulin is released if |
The blood glucose levels are too high
Insulin targets blood, puts glucose into the cells If any excess, stored in the liver |
|
|
Percentages of T4 vs T3 |
T4 93% T3 7%
T3 far more potent so don't need to release as much |
|
|
Location of thyroid glands |
Pair, lies either side of the trachea just below the larynx |
|
|
T4 and T3 are made from |
Iodine, taken in through the diet |
|
|
Process of metabolism |
Anterior pituitary gland releases TSH Targets thyroid gland Thyroid releases T4 and T3 Regulates metabolism (creates homeostasis ) |
|
|
Hypothyroidism can result in |
Stunted growth ( from poor nutrition absorption) Dwarfism in young animals |
|
|
Hypothyroidism can result in |
Stunted growth ( from poor nutrition absorption) Dwarfism in young animals |
|
|
Symptoms of under active thyroid |
Slow metabolism - overweight, tired, sluggish, lethargic, depressed |
|
|
Causes of hypothyroidism |
Primary cause : Atrophy of the thyroid gland (= reduction in T4)
Secondary : Issue with Anterior Pituitary gland causing reduction in TSH secretion
(Check levels of BOTH T4 and T3) |
|
|
The White of the eye is called |
Sclera |
|
|
The sclera is covered by a thin membrane called |
Conjunctiva |
|
|
The ------- is a clear dome on the front of the eye that lets light in |
Cornea |
|
|
Functions of the cornea (2) |
Protect the front of the eye Helps focus light on the retina at the back of the eye |
|
|
The ---- controls the amount of light that enters the eye by making the pupil smaller or large |
Iris |
|
|
The ---- changes shape to focus light onto the retina, by the contractions/relaxing of ------------ ------------ |
Lens Ciliary muscles |
|
|
When ciliary muscles contract the lens gets ------------ and when they relax is gets ----------- |
Contracts : thicker Relaxes : thinner |
|
|
The ------ contains the cells that sense light (photoreceptors) |
Retina |
|
|
In dogs, the most sensitive area of the retina is called |
Area centralis |
|
|
Each photoreceptor is connected to |
Nerve fibre |
|
|
All nerve fibres in the eye are bundled together to form the |
Optic nerve |
|
|
Photoreceptors in the retina convert the image into ---------- ------- which are carried to the ------ by the optic nerve |
Electrical impulses Brain |
|
|
Blinking purposes (3) |
Helps spread tears over the surface of the eye Keeps eye moist Clears away small particles |
|
|
The third eyelid is also called |
Nictating membrane |
|
|
Tears are produced by (2) |
Lacrimal glands (top outer edge of eye) Mucus glands in the conjunctiva , produce mucus part that mixes with eatery part from lacrimal gland |
|
|
Structures that protect the eye (6) |
Orbit Eyelash Eyelid Lacrimal gland Lacrimal excretory ducts Nictating membrane |
|
|
Outer ear consists of |
Pinna and ear canal |
|
|
Outer ear consists of |
Pinna and ear canal |
|
|
Middle ear consists of |
Ear drum (tympanic membrane) Auditory ossicles (3) - malleus, incus and stapes Oval window 2 muscles Eustachian tube |
|
|
Outer ear consists of |
Pinna and ear canal |
|
|
Middle ear consists of |
Ear drum (tympanic membrane) Auditory ossicles (3) - malleus, incus and stapes Oval window 2 muscles Eustachian tube |
|
|
Inner ear consists of |
Cochlea containing endolymph Semicircular canals Utricle Saccule Perilymph Vestibular system |
|
|
Ear wax is produced by |
Ceruminous glands |
|
|
The boundary between the middle and inner ear is |
Oval window |
|
|
The movement of ------------ stimulates sensory cells within the membranous walls of the ear |
Endolymph |
|
|
The movement of ------------ stimulates sensory cells within the membranous walls of the ear |
Endolymph |
|
|
The ------- -- ------- contains the receptor cells for hearing |
Organ of corti |
|
|
The semi circular ducts arise from the ---------- and the cochlear ducts arise from the ------ |
Semicircular: utricle Cochlear: saccule |
|
|
Process of sound from outer to middle ear |
Tympanic membrane- ossicles- middle ear wall- middle ear cavity- oval window |
|
|
The foramen ovale |
Allows blood to enter left atrium from right atrium in foetal heart |
|
|
The foramen ovale |
Allows blood to enter left atrium from right atrium in foetal heart |
|
|
Ductus arteriosa |
Is a blood vessel connecting the pulmonary artery to the descending aorta |
|
|
The foramen ovale |
Allows blood to enter left atrium from right atrium in foetal heart |
|
|
Ductus arteriosa |
Is a blood vessel connecting the pulmonary artery to the descending aorta |
|
|
Ductus venosus |
Takes blood flow from left umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava |
|
|
4 functions of blood |
Regulation Transportation Defence against infection Maintain pH |
|
|
At the start of the clotting process, ---------- is the enzyme release by the thrombocytes |
Thromboplastin |
|
|
4 constituents of plasma |
90% water Mineral salts Proteins Foodstuff |
|
|
Difference between plasma and serum |
Plasma = fluid from NON CLOTTED blood Serum = fluid from CLOTTED blood |
|
|
Vitamin K is needed by the liver to form |
Prothrombin |
|
|
The granules in the cytoplasm of ----------- contain histamine |
Basophils |
|
|
Myeloid tissue is found |
In bone marrow |
|
|
Correct name for immature erythrocytes |
Reticulocyte |
|
|
Monocytes and neutrophils can both be described as |
Phagocytic (cell eating) |
|
|
Pulmonary circulation is |
Takes de-oxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and takes oxygenated blood back to the heart to be pumped around the body |
|
|
The function of the capillary bed is |
Gaseous exchange : this occurs between the capillaries |
|
|
Clotting process |
Is where blood changes from a liquid to a gel (coagulation)
|
|
|
Primary hemostasis includes the activation adhesion and aggregation of ------- |
Platelets Form a plug at the injury |
|
|
Primary hemostasis includes the activation adhesion and aggregation of ------- |
Platelets Form a plug at the injury |
|
|
Secondary hemostasis is the deposition and maturation of ------ |
Fibrin Additional clotting "factors" happen in "Cascade" to form Fibrin strands to strengthen the clot |
|
|
Neutrophil is the ---- -------- --- in samples. Associated with (3 things) Has a ------ nucleus |
Most common WBC Inflammation, stress , corticosteroid use Lobed nucleus |
|
|
Lymphocytes are present in ----- ----- ------------, stress, corticosteroid use Have a ------ ------------ nucleus that dominates the cell |
Early viral infections Large rounded nucleus |
|
|
Monocytes are associated with --------- -------------- and have a large---- -------- nucleus |
Chronic inflammation Bean shaped |
|
|
Eosinophils are present with ------------- or ------------- ----------. Covered in ---------- and appears ----------- with stain |
Hypersensitivity or parasitic infection Granules Raspberry like |
|
|
Basophils are also covered in --------, store ---------- and are associated with --------- ---------- Stains ---- |
Granules Histamine Allergic reactions Blue |
|
|
Basophils are also covered in --------, store ---------- and are associated with --------- ---------- Stains ---- |
Granules Histamine Allergic reactions Blue |
|
|
Blood vascular system is made up of 4 parts |
Blood Heart Circulatory system Lymphatic system |
|
|
Blood consisted of several different types of cells suspended in ------- |
Plasma |
|
|
Blood consisted of several different types of cells suspended in ------- |
Plasma |
|
|
Blood makes up about -% of total body weight |
7% |
|
|
Blood consisted of several different types of cells suspended in ------- |
Plasma |
|
|
Blood makes up about -% of total body weight |
7% |
|
|
Functions of blood (2) |
Transport and regulation |
|
|
Transported in blood (4) |
Nutrients Gases in solution Waste products Hormones and enzymes |
|
|
Transported in blood (4) |
Nutrients Gases in solution Waste products Hormones and enzymes |
|
|
Regulation by blood (5) |
Volume and constituents of blood Body temperature and redistribution of heat Stopping haemorrhage though clotting Protect body against infection Assist in maintenance of correct pH of tissues |
|
|
6 parts of plasma |
Amino acids Nutrients Proteins Nitrogenous waste Electrolytes Gases |
|
|
3 types of proteins in plasma |
Albumins Globulins Fibrinogen |
|
|
3 parts of Formed elements in blood (solids) |
Leukocytes (WBC) Platelets Erythrocytes (RBC) |
|
|
2 types of leukocytes |
Granulocytes Agranulocytes
|
|
|
2 types of leukocytes |
Granulocytes Agranulocytes
|
|
|
3 types of Granulocytes |
Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils |
|
|
2 types of Agranulocytes |
Lymphocytes Monocytes |
|
|
Red blood cells are --------- ----- without ------ |
Biconcave discs Without nuclei |
|
|
Haemoglobin is a ------- that contains ---- |
Protein Iron |
|
|
Haemoglobin gives the --- ------- and carries ------ |
Red colour Oxygen |
|
|
Erythrocytes are surrounded by a ---- --------- ---- ------- which enables them to squeeze through capillaries |
Thin flexible cell membrane |
|
|
Erythrocytes have a lifespan of ---- days after which it is broken down in the ------ or ----- ----- |
120 days Spleen or lymph nodes |
|
|
Development process of erythrocytes |
Stem cell Erythroblasts Normoblasts Reticulocytes Mature erythrocytes |
|
|
Stem cells are located |
Located in the bone marrow |
|
|
Stem cells are located |
Located in the bone marrow |
|
|
Erythroblasts are |
Located in the bone marrow and contain nucleus |
|
|
Normoblasts are |
Located in bone marrow, have smaller nucleus, now contains haemoglobin |
|
|
Normoblasts are |
Located in bone marrow, have smaller nucleus, now contains haemoglobin |
|
|
Reticulocytes are |
Located in bone marrow, very tiny nucleus, consist of fine threads known as Howell-Joly bodies |
|
|
Disappearance of nucleus in nature red blood cells finally happens at ----- days and is then released into --------- |
4-7 days Circulation |
|
|
Erythrocyte production is under control of ------------- which is a hormone secreted by the ------ |
Erythropoietin Produced by the kidney |
|
|
Leukocytes are (4 things) |
Larger than RBC Less of them than RBC Cells contain nuclei Defend the body against infection |
|
|
Leukocytes are (4 things) |
Larger than RBC Less of them than RBC Cells contain nuclei Defend the body against infection |
|
|
% of Granulocytes % of Agranulocytes |
Gran.: 70% Agran.: 30% |
|
|
B lymphocytes produce -------- and are involved in ------ --------- |
Antibodies Humoral activity |
|
|
B lymphocytes produce -------- and are involved in ------ --------- |
Antibodies Humoral activity |
|
|
T Lymphocytes are involved in ------ -------- ------- |
Cellular immune response |
|
|
Sensory nerves carry impulses -------- the CNS Motor nerves carry ---- ---- the CNS Mixed nerves carry ---- |
Sensory towards CNS Motor away from CNS Mixed nerves carry both |
|
|
Intercalated neuron lies --------- -------- and ----- neurons |
Between sensory and motor |
|
|
Somatic sensory and motor nerves are associated with receptors in (6) |
Skin Muscles Joints Tendons Ear Eye |
|
|
Parasympathetic nervous system supplies (8) |
Eye Tear glands Salivary glands Heart Lungs and bronchioles Abdominal viscera Urogenital organs Large intestine (part) |
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system serves (14) |
Eye Tear glands Salivary glands Heart Lungs and bronchioles Liver Stomach Kidney Small intestine Large intestine Bladder Coeliac ganglion Cranial mesenteric ganglion Causal mesenteric ganglion |
|
|
Examples of insectivores |
Shrews, moles |

