![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
564 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Surface furthest away from the ground |
Dorsal |
A Dolphins fin |
|
|
The surface nearest the ground |
Ventral |
Ventilation in the chest |
|
|
Towards the head |
Cranial |
With your brain in it |
|
|
Towards the tail |
Caudal |
Pull the chord not the tail |
|
|
Towards the nose |
Rostral |
Like your nostrils |
|
|
Closest to the body |
Proximal |
In close proximity |
|
|
Nearer the toes |
Distal |
Footsteps in the distance |
|
|
The midline or middle |
Medial |
A mediator in the middle |
|
|
To the outside of the body |
Lateral |
Flat sides |
|
|
Underneath back foot |
Plantar |
Plant your legs |
|
|
Underneath front foot |
Palmar |
The palm of your hand |
|
|
Three body cavities |
Thoracic, abdominal and pelvic |
Top middle and bottom but no head |
|
|
Boundaries of thoracic cavity |
Caudal - diaphragm Lateral- ribs and intercostal muscles Dorsal- thoracic spine and hypaxial muscles Ventral- sternum |
|
|
|
Serous membrane of the thoracic cavity |
Pleura; named further relating to what it covers e.g. Diaphragmatic pleura, costal pleura |
|
|
|
Division of the thoracic cavity into 2 pleural cavities by: |
Mediastinum |
Double layer in the middle |
|
|
Lungs are covered with |
Visceral (organ) pleura called pulmonary pleura |
|
|
|
Mediastinum forms pericardial cavity and contains (4/5) |
Heart, aorta, trachea, oesophagus (& thymus in young animals) |
|
|
|
Heart is contained within double layer of membrane called |
Pericardium |
|
|
|
11 body systems |
Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Nervous Endocrine Cardiovascular Lymphatic Respiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive |
|
|
|
Prefix of 1. above/more than 2. below/less than |
1. Hyper 2. Hypo |
|
|
|
Prefix of 1. Around 2. Many |
1. Peri 2. Poly |
|
|
|
Prefix of 1. Between 2. Within |
1. Inter 2. Intra |
|
|
|
Prefix of 1. Low/slow 2. Rapid/fast |
1. Brady 2. Tachy |
|
|
|
Body cavities are lined with an endothelium called: |
Serous membrane |
You cannot be serious |
|
|
Serous membrane that lines the cavities is called |
Mesentary |
A messy business |
|
|
Serous membrane that covers the organs is called |
Serosa |
Very serious |
|
|
Endothelium also produces ... |
Serous fluid, lubricant |
Protective goo |
|
|
Boundaries of the abdominal cavity |
Cranial- diaphragm Caudal- pelvic inlet Lateral- abdominal muscles Dorsal-lumbar vertebrae and hypaxial muscles Ventral- abdominal muscles |
|
|
|
Abdomen lined with serous membrane called |
Peritoneum |
Parrot |
|
|
Peritoneal cavity is |
The space between the parietal peritoneum of the walls and the visceral peritoneum that covers the organs |
|
|
|
Friction in the peritoneal cavity is prevented by |
Peritoneal fluid |
|
|
|
Folds of visceral peritoneum suspending the organs and keeping them separate |
Mesentary |
Miso soup |
|
|
Examples of renamed Mesentary |
Based on location : mesoduodenum, mesoovarium |
|
|
|
Folds of lace-like peritoneum containing vessels and fat |
Omentum |
The omen |
|
|
Boundaries of pelvic cavity |
Cranial- pelvic inlet Caudal- pelvic outlet and pelvic diaphragm Lateral- muscles and ligaments Dorsal- coccygeal vertebrae and sacrum Ventral- pubis and ischium |
|
|
|
Cavity lining is called_________ and organ lining is called_________ |
Parietal and visceral |
P and V |
|
|
Interstitial fluid ________________ and transcellular fluid _______________________________ |
Surrounds the cells
Travels around the body |
In the house or out and about |
|
|
Water in the body (2 things) |
Chemical reactions take place in water
Regulate optimal conditions and temperature |
|
|
|
Hypotonic solution is |
Lower concentration then body fluids; has higher OP in the body, water can only go IN, cells will expand |
|
|
|
Hypertonic solution is |
Higher concentration than body fluids; lower OP in body, water can only go OUT, cells lose water, shrink |
|
|
|
Intracellular fluid is ______ cells and Extracellular fluid is _______ cells |
Inside Outside |
|
|
|
Body's internal balance is called |
Homeostasis |
|
|
|
Negative feedback is: |
Where the body identifies a problem with the levels within the body, makes changes to rectify them, then gives a further message (negative feedback) to cease the changes when the levels are back to normal E.g thirst receptors tell you to drink, cease drinking when fluid levels restored (no longer thirsty) |
|
|
|
6 homeostatic mechanisms |
Osmoregulation- water levels Thermoregulation- temperature Excretion of waste- kidneys (urine) Buffer systems- maintains pH Blood pressure maintenance Metabolic rate- thyroid activity |
|
|
|
Definition of osmosis |
Movement of water through a semi permeable membrane from a Low to High concentration; gives water to create an even balance; can occur in Intra or Extracellular fluid |
|
|
|
Definition of diffusion |
Movement of particles from a High to Low concentration; occurs through cell membranes if particles are small enough; if too big then osmosis occurs |
|
|
|
Osmotic pressure is: |
The pressure balance needed to stop osmosis occurring; If lose water will increase concentration inside blood vessels, and increase osmotic pressure; OP will stop water from leaving the blood vessel, by ensuring that water can only move INTO the blood vessel |
|
|
|
The osmotic concentration of solution in reaction to body fluids is |
Tonicity |
|
|
|
3 solutions in relation to body fluids are |
Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic |
|
|
|
Isotonic solution is |
Same concentration as body fluids; water can move in or out of cel freely, same osmotic pressure |
|
|
|
A cell in a hypertonic solution will shrink - this is called |
Crenation |
|
|
|
Anabolic respiration is |
Simple substances creating complex substances, using energy |
Lego |
|
|
Catabolic respiration is |
Complex/compound substances breaking down into simple substances, creating energy |
Breaks down |
|
|
Internal respiration is |
Function of cells using food or energy |
|
|
|
ATP has to _________ a phosphate to create energy |
Lose |
Unstable |
|
|
ATP energy production occurs within the_____________ of the cell |
Mitochondria |
|
|
|
Which requires ATP conversion for energy, Active or Passive transport? |
Active: converts ATP to ADP creating energy allowing transport across the cell membrane |
|
|
|
3 examples of Passive transport are: |
Osmosis Diffusion Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
|
Endocytosis is where the __________________ wraps around a particle of fluid, and deposits it ________________ |
Cell wall Inside the cell |
|
|
|
A cell in a hypotonic solution will swell with water. This is known as |
Lyse |
|
|
|
pH stands for |
The power of hydrogen concentration |
|
|
|
The power of hydrogen concentration is a factor of |
10; one pH unit represents a tenfold change in hydrogen concentration |
|
|
|
The normal pH of blood is |
7.4 |
|
|
|
If blood pH drops below 7.4 this is known as |
Acidosis - nervous system becomes depressed and animal will be disorientated or even comatose |
|
|
|
If blood pH rises above 7.45 this is called |
Alkalosis - nervous system becomes over excitable and animal becomes nervous or may have convulsions |
|
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis is |
A loss of hydrogen due to hyperventilation (pain, stress, hyperthermia) E.g. Dogs in hot cars |
|
|
|
Respiratory acidosis is |
Retaining hydrogen due to hypoventilation (ruptured diaphragm,pneumothorax). Nervous system then shuts down |
|
|
|
Metabolic acidosis is |
Retaining hydrogen - acute renal failure, shock; kidneys stop filtering blood, causing lethargy All blood goes to the main organs, increasing the hydrogen which is not being excreted Needs to go on fluids!! |
|
|
|
Loose connective tissue is found |
All over! Beneath the skin, in vessels, nerves |
|
|
|
Types of muscle are: (4) |
Skeletal Smooth Cardiac Nervous |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
For movement, is attached to the skeleton |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle is |
Unconscious processes; involuntary controls such as the bladder |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle is |
In the heart; contracts the heart to pump blood |
|
|
|
Nervous muscle tissue |
Transmits nerve impulses; cell body are neurons and nerve fibers are dendrons and axons |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue types: (5) |
Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Stratified Transitional |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium is |
Easily permeable to oxygen; found in blood vessels and alveoli of the lungs |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium is |
Absorptive or excretory depending on location; lining if renal tubules or in the thyroid |
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium is |
Protects against abrasions; replaces in layers , i.e. Skin |
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium is |
Can change shape relating to internal pressure and capacity ; found in bladder, uterus |
|
|
|
Adipose is |
Fat - found in dermis of skin; kidney |
|
|
|
Ciliated epithelium is |
Coated in tiny hairs, waft particles along; found in trachea, nose, Fallopian tubes |
|
|
|
Dense connective tissue is |
Tendons and ligaments |
|
|
|
Spongey bone is found |
Mesh filled with marrow - ends of long bones , core of short and irregular bones, flat bones - create red blood cells |
|
|
|
Compact bone is |
Outer layer of bones |
|
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
Protects against friction , articulate surfaces of joints |
|
|
|
White fibro cartilage is |
Strong- attaches tendons and ligaments to bones In discs in vertebrae |
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage is |
For flexibility - epiglottis and external ear (pinna) |
|
|
|
Haemopoietic tissue is for |
Formation of blood cells, found in marrow of long bones |
|
|
|
Lymphoid tissue is |
In the lymphatic system, sends messages - lymph glands |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium is |
Single layer of rectangular cells on a basement membrane; found in stomach and intestines |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium is |
Single layer of rectangular cells on a basement membrane; found in stomach and intestines |
|
|
|
2 types of glands |
Endocrine and Exocrine |
|
|
|
Exocrine glands have: |
Ducts; excrete hormones directly where needed |
|
|
|
Endocrine glands : |
The hormones are released and travel around in the bloodstream to target tissues- do not have ducts |
|
|
|
Exception to endocrine glands is |
The pancreas : classified as a mixed gland as it releases insulin to regulate glucose (endocrine method), but also release digestive enzymes that directly break down food (using duct, exocrine method) |
|
|
|
Neuron is |
A nerve cell |
|
|
|
Definition of myelinated |
When the neuron is enclosed in a fatty sheath which allows the electrical impulse to move faster |
|
|
|
Definition of non-myelinated |
No fatty sheath, impulse moves slower |
|
|
|
Afferent fibers conduct information ___ the CNS, and Efferent fibers conduct information _________ the CNS |
Afferent - towards Efferent - away from |
|
|
|
Mucus is |
Thick protein filled fluid secreted by specialized epithelial cells to protect the tissue beneath |
|
|
|
Cilia is |
Small hair like projections of the surface of some epithelium light cells to move mucus along |
|
|
|
Keratin is |
Tough protein found in the top layer of stratified squamous epithelium where great protection is required |
|
|
|
Goblet cells are |
Specialists epithelial cells that secrete mucus and are an example of a simple or unicellular gland |
|
|
|
Aponeurosis is |
A sheet of muscle and dense connective tissue, e.g. Diaphragm |
|
|
|
Ligament is |
Connective tissue that connects bone to bone |
|
|
|
Tendon is |
Connective tissue that connects muscle to bone |
|
|
|
Haversian systems are |
Canal like structures that run the length of bone and make up the structure Carry blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics that serve the bone |
|
|
|
Osteocytes are |
Bone cells |
|
|
|
Periosteum is |
Tough fibrous membrane that covers all bone |
|
|
|
Perichondrium is |
Membrane that covers cartilage and supplies it with blood |
|
|
|
A Chondryte is |
A cartilage producing cell |
|
|
|
Sudiferous gland is |
Sweat gland |
|
|
|
Sebaceous gland is |
Secreting |
|
|
|
Ceruminous gland produces |
Ear wax |
|
|
|
Meibomian gland is |
Found on the margins of the eyelid and secretes fluid to lubricate and protect the eye ( NOT tears) |
|
|
|
Mammary glands produce |
Milk |
|
|
|
Anal glands |
Scent glands, the glands line the anal sacs |
|
|
|
Dendrons/dendrites carry information _________ the cell body |
Towards |
|
|
|
Axons carry information _____________ the cell body |
Away from |
|
|
|
Schwann cell is the _________ of the visible nerves |
White color |
|
|
|
Myelin sheath |
Increases speed of transmission |
|
|
|
Node of Ranvier |
Delivers oxygen and nutrition to the Axon |
|
|
|
Neuromuscular junction |
Connects to the muscle fiber |
|
|
|
3 layers of skin |
Epidermis, dermis and hypodermis (subcutaneous layer) |
|
|
|
4 layers of epidermis |
Bottom/1: stratum germinativum 2: stratum granulosum 3: stratum luciderm 4: stratum corneum |
|
|
|
Functions of the skin (6) |
Protection Production Sensory Storage Thermoregulation Communication |
|
|
|
Vibrissae is also known as |
Cilia |
|
|
|
Arrector pili muscles play a part in |
Thermoregulation |
|
|
|
Epidermis is composed of |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
Sudoriferous glands are |
Coiled |
|
|
|
Part of the distal phalanx covered by the claw is |
Ungual process |
|
|
|
Arrector pili are attached to |
Guard hairs |
|
|
|
The most vibrissae are located on |
The face |
|
|
|
Mitosis is the division of |
Somatic cells (non reproductive ) |
|
|
|
Meiosis is the division of |
Germ cells (sperm and egg combining) |
|
|
|
Rest phase in mitosis |
Interphase |
|
|
|
Phase of Lining up in mitosis |
Metaphase |
|
|
|
Rest phase of mitosis |
Interphase |
|
|
|
Term describing cell division in mitosis |
Binary fission |
|
|
|
Chromosomes lining up in mitosis |
Metaphase |
|
|
|
Meiosis requires initial _________ within the germ cells, which results in a ________ number of chromosomes within the ova or sperm. |
Division Haploid |
|
|
|
Meiosis second phase results in ___ daughter cells |
4 |
|
|
|
Chromosomes become shorter and fatter; they are then referred to as__________ |
Chromatids |
|
|
|
(mitosis) Nuclear membrane breaks down in |
Prophase |
|
|
|
(Mitosis) chromosomes attach to the spindle fibres and moves chromatids to opposite poles of the cells in |
Anaphase |
|
|
|
Maintenance fluids per day |
50-60ml/kg per day |
|
|
|
Fluid loss from urine |
20ml/ kg per day |
|
|
|
Fluid loss through faeces |
10-20ml /kg per day |
|
|
|
Fluid loss through respiration and sweating |
20ml /kg per day |
|
|
|
Intercellular cations |
Potassium Magnesium Sodium |
|
|
|
Intracellular anions |
Phosphate Bicarbonate Chloride |
|
|
|
Extra cellular cations |
Sodium Potassium Magnesium Calcium |
|
|
|
Extracellular anions |
Chloride Bicarbonate Phosphate |
|
|
|
Total body water % |
60% |
|
|
|
Total body water divided into: |
Extracellular- 20% Intracellular- 40% |
|
|
|
Extracellular fluid divided into: |
Interstitial fluid- 14-15% Plasma- 5% Transcellular fluid- <1% |
|
|
|
Examples of transcellular fluid |
Lymphatic fluid Synovial fluid Cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
|
Names of cell organelles |
Centrosomes Mitochondria Ribosomes Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body/apparatus Lysosomes |
|
|
|
Osteoblasts are |
Immature cells which can synthesise osteoid (the bone matrix) |
|
|
|
Osteocytes are |
Mature cells which maintain bone structure |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts are |
Cells which can break down and remodel bone |
|
|
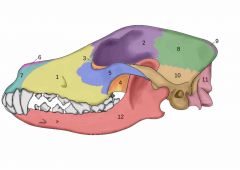
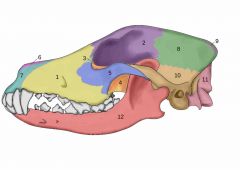
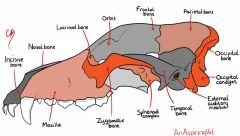
Bones of the skull |
Maxilla Frontal Lacrimal Sphenoid complex Zygomatic arch Nasal Incisor Parietal Occipital bone Temporal Occipital condyles Mandible |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Number of cervical vertebrae |
7:
Atlas Axis C3-C7 |
|
|
|
Number of cervical vertebrae |
7:
Atlas Axis C3-C7 |
|
|
|
Number of thoracic vertebrae |
13 |
|
|
|
Number of cervical vertebrae |
7:
Atlas Axis C3-C7 |
|
|
|
Number of thoracic vertebrae |
13 |
|
|
|
Number of lumbar vertebrae |
7 |
|
|
|
Number of sacral vertebrae |
3 (fused) |
|
|
|
Number of coccygeal vertebrae |
5-13 depending on breed, length of tail etc |
|
|
|
The process of new bone growing from cartilage and hardening |
Ossification |
|
|
|
Bones grow longer from the- |
Epiphyseal plate (growth plate ) |
|
|
|
Bones grow longer from the- |
Epiphyseal plate (growth plate ) |
|
|
|
Yellow marrow consists of |
Lipid and cartilage |
|
|
|
Bones grow longer from the- |
Epiphyseal plate (growth plate ) |
|
|
|
Yellow marrow consists of |
Lipid and cartilage |
|
|
|
Red marrow is |
Haemopoetic tissue; grow new red blood cells |
|
|
|
Supraspinatus muscle |
Origin: Fills supraspinatus fossa (scapula) Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus (cranial aspect) Action: extends and stabilises shoulder joint |
|
|
|
Supraspinatus muscle |
Origin: Fills supraspinatus fossa (scapula) Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus (cranial aspect) Action: extends and stabilises shoulder joint |
|
|
|
Muscles on the scapula |

|
|
|
|
3 muscles of elbow region |
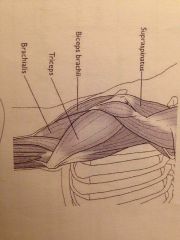
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Origin Insertion and action of triceps brachii |
Has 4 heads!!!
Origin : 3 from proximal humerus 2 from scapula Insertion: olecranon (with bursa between bone and tendon) Action: extend the elbow |
|
|
|
Extrinsic muscles |
Large movements involving a whole limb |
|
|
|
Vertebral formula for cat and dog |
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cc 20-23 |
|
|
|
Vertebral formula for horses |
C7 T18 L6 S5 Cc 15-20 |
|
|
|
Horse cervical vertebra have ___ __________ __ ____________ ___________ |
No spinous or transverse processes |
|
|
|
Radius and ulna are ________ in the horse |
Fused |
|
|
|
Name for horse metatarsal IV is |
Lateral splint bone |
|
|
|
Name for horse metatarsal _III is |
Cannon bone |
|
|
|
Horse tarsus is made of ________ small bones arranged in ___ rows |
6-7 3 |
|
|
|
Equine carpus |
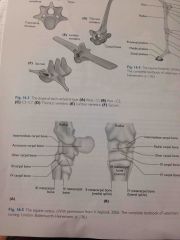
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Equine skull |
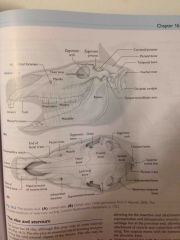
equine skull |
|
|
|
Equine skull |
Equine skull |
|
|
|
3 functions of vertebral column |
Protect the spinal chord Aid support of the head Provide attachment point for muscles |
|
|
|
Bulk of vertebrae (structure) made of the cylindrical ______ |
Body |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Foramina form the ____ _____ |
Spinal canal |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Foramina form the ____ _____ |
Spinal canal |
|
|
|
Intervertebral discs ; outer and inner names |
Outer: annulus fibrosis Inner: nucleus pulposus |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Foramina form the ____ _____ |
Spinal canal |
|
|
|
Intervertebral discs ; outer and inner names |
Outer: annulus fibrosis Inner: nucleus pulposus |
|
|
|
A slipped disc is |
Where the outer ring ruptures and gel protrudes out putting pressure on the spinal chord or associated nerves |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Foramina form the ____ _____ |
Spinal canal |
|
|
|
Intervertebral discs ; outer and inner names |
Outer: annulus fibrosis Inner: nucleus pulposus |
|
|
|
A slipped disc is |
Where the outer ring ruptures and gel protrudes out putting pressure on the spinal chord or associated nerves |
|
|
|
Dorsal from the neural arch is the ______ _______ |
Spinous process |
|
|
|
Vertebral foramen also known as |
Neural arch |
|
|
|
Foramina form the ____ _____ |
Spinal canal |
|
|
|
Intervertebral discs ; outer and inner names |
Outer: annulus fibrosis Inner: nucleus pulposus |
|
|
|
A slipped disc is |
Where the outer ring ruptures and gel protrudes out putting pressure on the spinal chord or associated nerves |
|
|
|
Dorsal from the neural arch is the ______ _______ |
Spinous process |
|
|
|
Lateral on the vertebrae there are 2... |
Transverse processes |
|
|
|
Transverse processes used for.. |
Muscle attachment : divide the muscles of the vertebral column into Expaxial and Hypaxial |
|
|
|
Transverse processes used for.. |
Muscle attachment : divide the muscles of the vertebral column into Expaxial and Hypaxial |
|
|
|
Describe cervical vertebrae |
7 vertebrae
1- Atlas (consists of only 2 large lateral processes, no body or spinous process), the YES joint)
2- Axis (large blade spinal process, attaches neck muscles, cranial projection - Dens/Odontoid process, NO joint) C1 C2 fit together C3-7 increasing length of spinal process, but look the same |
|
|
|
Thoracic vertebrae |
T1-T13
Short body, distinctive spinous processes: initially point Dorsally then gradually point Caudally further down
Short lateral process with Fovea on Lat process and Body that articulate with the tubercle and head of the Rib respectively
Mamillary process start at 2nd/3rd vertebrae : small rounded projection a of bone |
|
|
|
Lumbar vertebrae |
L1-L7 Longer bodies that increase in width Large transverse processes, angle cranioventrally Longest in mid lumbar region Suspend abdominal muscles Spinous processes angled cranially and larger in mid lumbar region |
|
|
|
Sacral vertebrae |
S1-3 Fused together, form the sacrum Fibrosynovial joint articulates with ilium of the pelvis: forms Sacroiliac joint |
|
|
|
Coccygeal (caudal) vertebrae |
Number varies breed to breed Decrease in size down the tail First few have neural arches and costo-transverse processes but the last are small rods of bone |
|
|
|
Number of pairs of ribs in cat and dog |
13 |
|
|
|
Ribs are classed as |
Flat bones |
|
|
|
Ribs are classed as |
Flat bones |
|
|
|
Dorsal part of rib is ______ and ventral part is _____________ also known as the _______________ ___________ |
Dorsal: bone Ventral: cartilaginous Costochondral junction |
|
|
|
Dorsal bone part of vertebrae articulates with vertebrae via the _______ |
Fovea |
|
|
|
Ribs 1-8 articulate with the ___________ and are known as ____ ribs |
Sternum True ribs |
|
|
|
Ribs 9-12 just touch the ______ _________ of the rib in front, area known as ______ ____ Do not touch the sternum Known as ________ or _____ ribs |
Costal cartilage Costal arch Asternal/false |
|
|
|
13th rib |
Does not articulate with the cartilage of the other ribs Floating rib |
|
|
|
Spaces between ribs are known as |
Intercostal space Are about twice the width of the adjacent rib Contain intercostal muscles |
|
|
|
Most ventral and midline point in the rib cage is the |
Sternum |
|
|
|
Bones of the sternum |
Sternebrae |
|
|
|
Number of sternebrae bones |
8 |
|
|
|
Most cranial part of the sternum is the |
Manubrium Slightly longer and projects in front of the first pair of ribs to form the thoracic inlet |
|
|
|
Most caudal sternebrae is the |
Xiphoid process Longer and slightly flattened Projecting caudally is xiphoid cartilage, point where linea alba attaches |
|
|
|
Bone matrix contains |
Collagen Calcium Phosphate |
|
|
|
Bone matrix contains |
Collagen Calcium Phosphate |
|
|
|
Bone diaphysis contains |
Medullary cavity |
|
|
|
Compact bone is mostly |
Solid matrix, forms diaphysis and outer coatings |
|
|
|
Compact bone is mostly |
Solid matrix, forms diaphysis and outer coatings |
|
|
|
In ossification , ________replace membranes or cartilage models with bone |
Osteoblasts |
|
|
|
Zygomatic arch consists of |
Joined processes from temporal and zygomatic bones |
|
|
|
Zygomatic arch consists of |
Joined processes from temporal and zygomatic bones |
|
|
|
Major blood vessels supplying the brain pass through the ________ _______ and the _________ _____________ |
Foramen magnum and carotid channels |
|
|
|
Hard palette is formed by (2) |
Maxilla and palatine bones |
|
|
|
Hard palette is formed by (2) |
Maxilla and palatine bones |
|
|
|
Teeth are housed in _________ in the maxilla and mandible bones |
Alveoli |
|
|
|
Hard palette is formed by (2) |
Maxilla and palatine bones |
|
|
|
Teeth are housed in _________ in the maxilla and mandible bones |
Alveoli |
|
|
|
Permanent teeth consist of (4) |
Incisors, canines, premolars and molars |
|
|
|
Adult dogs have __ premolars |
16 |
|
|
|
The carnassial is |
The fourth premolar in the upper jaw of the dog |
|
|
|
Individual muscle cells are known as muscle ----- |
Fibres |
|
|
|
Individual muscle cells are known as muscle ----- |
Fibres |
|
|
|
Muscle fibres are grouped together in ------- |
Fascicles |
|
|
|
The main part of a muscle is called the |
Belly |
|
|
|
Brachioceohalicus muscle |
Origin - cervical vertebrae Insertion - humerus (head) Action abductor of forelimb |
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi |
Origin- caudal thoracic and lumbar vertebrae Insertion- medial humerus Action- flexes the shoulder and retracts forelimb |
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi |
Origin- caudal thoracic and lumbar vertebrae Insertion- medial humerus Action- flexes the shoulder and retracts forelimb |
|
|
|
Triceps brachii |
Origin- caudal scapula and tricipital head of humerus Insertion- olecranon Action - flexes shoulder and extends elbow |
|
|
|
Biceps brachii |
Origin- Supraglenoid tubercle Insertion- radial tuberosity Action- extends the shoulder and flexes the elbow |
|
|
|
Epaxial muscles lie ______ the transverse processes of the vertebrae and hypaxial muscles lie ______ |
Epaxial- above Hypaxial - below |
|
|
|
Hindlimb biceps femoris |
Origin- ischial tuberosity Insertion - patella, tibial crest, calcaneus Action- retracts hip, flexes/extends stifle, extends hock |
|
|
|
Achilles' tendon connects with (3) |
Semitendonosus Biceps femoris Gastrocnemius |
|
|
|
Pectineus muscle |
Origin- prepubic tendon and pelvis Insertion- distal femur Action- adducts the hip |
|
|
|
Knee joint - discuss and label |
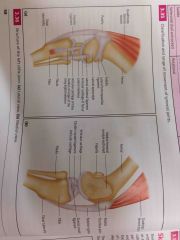
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
3 types of muscle |
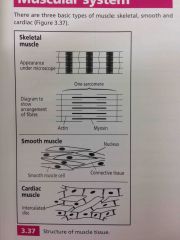
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Femur |
Most proximal bone of hindlimb Rounded head articulates with acetabulum of pelvis Has trochlear groove which forms part of the stifle (distal) Greater trochanter can be felt on proximal femur alongside hip joint |
|
|
|
Structure points of pelvis (5) |
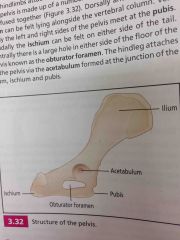
|
|
|
|
Structures of tarsus |
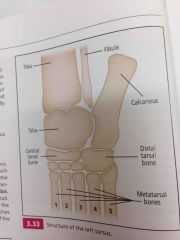
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Fabellae is found in |
The tendons of the gastrocnemius muscle |
|
|
|
Largest sesamoid bone is |
The patella |
|
|
|
Structure of carpus |
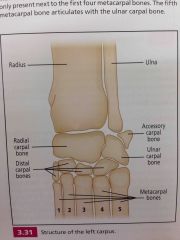
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Vertebral formula for rabbits |
C7 T12-13 L-7 S-4 Cc-15-16 |
|
|
|
Tortoise upper shell is called the _________ and the bottom is called the _________ |
Upper- carapace Lower- plastron |
|
|
|
Tortoise shell covered with bony plates covered with ________________ _________________ shields called ______ |
Keratinised epidermal shields Scutes |
|
|
|
Cockatiels craniofacial hinge is a |
Synovial joint |
|
|
|
Tortoise upper shell is called the _________ and the bottom is called the _________ |
Upper- carapace Lower- plastron |
|
|
|
Tortoise shell covered with bony plates covered with ________________ _________________ shields called ______ |
Keratinised epidermal shields Scutes |
|
|
|
Cockatiels craniofacial hinge is a |
Synovial joint |
|
|
|
Corn snake teeth are arranged |
In 6 rows with double rows in the upper jaw |
|
|
|
Snake teeth are shed ________________ _____ and are attached to _____ _____________ instead of the ______ |
Teeth are shed throughout life and are attached to the bone rather than the root |
|
|
|
Premolars and molars in Lagomorphs and rodents are also known as |
Cheek teeth |
|
|
|
Premolars and molars in Lagomorphs and rodents are also known as |
Cheek teeth |
|
|
|
Cheek teeth consist of |
3 upper and 2 lower premolar teeth on each side 3 molars in each quadrant Form nearly straight dental arcades contacting with opposite side to create continuous chewing surface |
|
|
|
Adult rabbit dental formula |
2 X 2/1 0/0 3/2 3/3 = 28 |
|
|
|
Teeth are made of (3 things) |
Enamel Dentine Cement |
|
|
|
2 muscle filaments are |
Actin and myosin |
|
|
|
2 muscle filaments are |
Actin and myosin |
|
|
|
Muscle tone means |
The amount of tension in a muscle |
|
|
|
A single nerve together with the muscle fibres that it supplies are called a |
Motor unit |
|
|
|
A single nerve together with the muscle fibres that it supplies are called a |
Motor unit |
|
|
|
Muscles that perform accurate and delicate movements, a nerve fibre will supply ___ muscle fibres Muscles that perform less accurate movements, the never fibre will supply ____ muscle fibres |
Accurate - few muscle fibres Less accurate- many muscle fibres |
|
|
|
Extrinsic muscles bring about ______ movements and Intrinsic muscles bring about ______ movements |
Extrinsic big Intrinsic small |
|
|
|
Actin filaments are Myosin filaments are |
Actin thin Myosin thick |
|
|
|
Muscle fibres overlap creating bands or striations called |
Sarcomeres |
|
|
|
Isometric contraction happens when |
Tension is generated in the muscle , tone is increased but the muscle does not shorten |
|
|
|
Isometric contraction happens when |
Tension is generated in the muscle , tone is increased but the muscle does not shorten |
|
|
|
Isotonic contraction happens when |
Muscle actually moves or shortens |
|
|
|
Exercised muscle gets larger = Unused muscle shrinks = |
Larger = hypertrophy Shrinks= atrophy |
|
|
|
A bursa is |
A connective tissue sac lined with synovial membrane and filled with synovial fluid |
|
|
|
A bursa is |
A connective tissue sac lined with synovial membrane and filled with synovial fluid |
|
|
|
Synovial or tendon sheath is |
When a bursa wraps completely around a tendon |
|
|
|
The facial nerve is also known as |
Cranial nerve VII |
|
|
|
Muscles of the face |
Digastricus (opens jaw) Masseter (closes jaw) Temporalis (closes jaw) |
|
|
|
Other facial muscles |
Medial and lateral pterygoids- deep muscles medial to the mandible Aid in closing jaw Side to side motion of jaw |
|
|
|
Muscles of the eye |
Rectus (dorsal medial ventral) lateral Dorsal oblique Ventral oblique Retractor bulbi |
|
|
|
Eye nerves (2) |
Trochlear nerve Optic nerve |
|
|
|
Thorax muscles |
External intercostals - most superficial Origin: caudal border of rib Insertion: cranial border of rib in front Action- Inspiration
Internal intercostals- below ex/int Origin: cranial border of rib Insertion: causal border of rib in front Action: passive expiration (not much activity !!) |
|
|
|
3 openings in the diaphragm |
Aortic hiatus : sorta, a thou she vein and thoracic duct
Oesophageal hiatus : oesophagus and vagal nerve trunks
Caval foramen : lies within central tendon, transmits caudal vena cava |
|
|
|
4 abdominal muscles |
Inserting into linear alba (3) : External abdominal oblique Internal abdominal oblique Transverse abdominus
NOT inserting into linear alba: Rectus abdominus |
|
|
|
Inguinal ring is |
Slit-like opening in aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique, in the groin Allows passage of blood vessels from the abdomen to external genitalia and mammary glands, transmits the structures of the spermatic chord to the scrotum |
|
|
|
A synsarcosis is |
The attachment of a structure to the skeleton by muscles instead of the more conventional joint |
|
|
|
Triangular sheet of muscle in the forelimb |
Trapezius |
|
|
|
_________ muscles run from the ribs and sternum and insert on the humerus |
Pectoral |
|
|
|
_________ muscles run from the ribs and sternum and insert on the humerus |
Pectoral |
|
|
|
Large fan shaped muscle with broad origin on the thoracic spine and inserts onto the humerus |
Latissimus dorsi |
|
|
|
_________ muscles run from the ribs and sternum and insert on the humerus |
Pectoral |
|
|
|
Large fan shaped muscle with broad origin on the thoracic spine and inserts onto the humerus |
Latissimus dorsi |
|
|
|
Muscle that runs from the base of the skull to an insertion on the cranial aspect of the humerus |
Brachiocephalicus |
|
|
|
The ____________________ extends the shoulder joint and the ________________ flexes the shoulder joint |
Supraspinatus extends shoulder Infraspinatus flexes the shoulder |
|
|
|
4 headed muscle with separate origins, that flexes the elbow joint |
Triceps brachii |
|
|
|
4 headed muscle with separate origins, that flexes the elbow joint |
Triceps brachii |
|
|
|
Origins and insertion of the triceps brachii are |
3 on the proximal humerus 1 on the scapula All insert into the olecranon of the ulna |
|
|
|
Carpus and digits |
Carpal extensors originate on humerus, insert in the carpals Digital extensors originate on humerus and insert on 3rd phalanx
2 carpal extensors- in front of lower limb and foot 2 carpal flexors - behind the carpus and foot
2 digital extensors - in front of the lower limb and foot 2 digital flexors- superficial (2nd phalanx) and deep (3rd phalanx) |
|
|
|
Muscles/ groups of hindlimb muscles |
Gluteals- superficial, middle and deep
Hamstring - biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
Quadriceps femoris
Adductor muscles - pectineus, sartorius, gracilis |
|
|
|
Muscles / tendon of lower limb |
Gastrocnemius- extends hock and flexes the stifle Achilles' tendon- includes tendons of insertion of gastrocnemius, biceps femoris and semitendinosus; has a bursa at the point of insertion on the calcaneus |
|
|
|
Muscles of hock and digits |
Anterior tibialis 3 digital extensors 2 digital flexors
Superficial digital flexor runs from femur to phalanges and is a component of Achilles' tendon |
|
|
|
Fused bones in the rabbit |
Fibula to tibia Radius and ulna |
|
|
|
Gap in rabbits mouth between incisors and premolars |
Diastema |
|
|
|
Gap in rabbits mouth between incisors and premolars |
Diastema |
|
|
|
Name of second incisors in rabbit on upper jaw |
Peg teeth |
|
|
|
Gap in rabbits mouth between incisors and premolars |
Diastema |
|
|
|
Name of second incisors in rabbit on upper jaw |
Peg teeth |
|
|
|
Skeleton of rabbit only makes up ______ of body weight |
7-8% |
|
|
|
Rabbit scapula |
More sharply triangular Has hook shaped suprahumate process on acromion |
|
|
|
Rabbit hip joint |
Comprises of ilium,ischium, and the is acetabuli (accessory bone) Pubis is not involved |
|
|
|
Rabbit incisors only have enamel on |
The outer surface- wear down much slower than on the inner surface |
|
|
|
Malocclusion is |
Where the teeth are misaligned or there is an inappropriate diet, resulting in the teeth not wearing properly |
|
|
|
A snake Skull is described as |
Kinetic- the bones of the Jaw are loosely connected and the two halves of the Mandible are joined by an elastic ligament to allow wide separation |
|
|
|
A snake Skull is described as |
Kinetic- the bones of the Jaw are loosely connected and the two halves of the Mandible are joined by an elastic ligament to allow wide separation |
|
|
|
Number of snake vertebrae |
150-400 all with similar shape Each gives off a pair of ribs which are fused to the vertebrae but not to the midline There is no sternum |
|
|
|
Bones of the snake skull (4) |
Orbit Cranium Squamosal Quadrate Lower jaw |
|
|
|
The os penis is a ________ bone |
Splanchic |
|
|
|
THe primary centre of ossification happens in the |
Diaphysis |
|
|
|
Tears drain into the nose through the |
Lacrimal bone |
|
|
|
An example of a joint that is an amphiathrosis is |
Between the bodies of the vertebrae |
|
|
|
The mandible articulate with the temporal region of the skull by the |
Condylar process |
|
|
|
The mandible articulate with the temporal region of the skull by the |
Condylar process |
|
|
|
The thoracic vertebra articulates with the tubercle of the rib by the _____________ _____ |
Transverse fossa |
|
|
|
Which part of the ulna is received by olecranon fossa during extension of the elbow ? |
Anconeal process |
|
|
|
Where do you find the medial malleolus ? |
The tibia |
|
|
|
How many short bones are there in the tarsus? |
7 |
|
|
|
The __________ muscle inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible |
Temporalis |
|
|
|
Extraocular muscles insert into the |
Sclera |
|
|
|
The thoracic duct passes through the _________ (opening in the diaphragm) |
Aortic hiatus |
|
|
|
The trapezius inserts into the _________ of the ________ |
Spine of the scapula |
|
|
|
The patella sits in the tendon of insertion of which muscle ? |
Quadriceps femoris |
|
|
|
The anterior tibialis ________ the hock |
Flexes |
|
|
|
3 components of Achilles' tendon |
Gastrocnemius Biceps femoris Semitendinosus |
|
|
|
Simple diffusion allows molecules that are soluble in - - - - - - to passively dissolve in the - - - - - part of the cell membrane and diffuse across it. ----- and - - - - - enter this way |
Lipids (fats) Lipid Oxygen and water |
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion is another type of - - ---- diffusion where the substance is moving - - - - - a concentration gradient, but the substance enlists the help of a carrier - - - - —- to help it cross the membrane. -------- uses this method to enter the cell |
Passive diffusion Down a gradient Carrier protein Glucose |
|
|
|
Active transport mechanisms usually mean substances move from - - - to - - - - concentration and require - - - - - - These use carrier - - - - - - to transfer them across, at a cost of - - - molecules ------- enters this way |
Low to high concentration Require energy Carrier proteins ATP molecules Sodium |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm fills the interior of the cell, providing - - - - - - - - Found inside are (5): |
Support 5: Nucleus Organelles Glucose Proteins Ions |
|
|
|
Nucleus contains - - - - - - - - - - which carry - - - which carry the information for - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Chromosomes DNA Protein synthesis |
|
|
|
ATP energy conversion |
ATP has to lose a phosphate to become adenosine diphosphate and energy is released as this snaps off Metabolism re attaches a phosphate molecule and the energy is stored again as ATP. |
|
|
|
Ribosomes float in cell cytoplasm and are the site for - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has numerous - - - - - - - - - attached to the surface. Transports - - - - - - - that have been synthesised, some of which are not required in that cell, so are - - - - - - - outside the cell |
Ribosomes Proteins exported |
|
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have - - - - - - - and its functions include synthesis and transport of - - - - - - - and - - - - - - - - |
Ribosomes Lipids and Steroids |
|
|
|
Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened - - - - within the cytoplasm Function includes modification of - - - - - (adding a - - - - - - - - - - - - - -) and helps to form - - - - - - |
Sac Proteins Carbohydrate Lysosomes |
|
|
|
Lysosomes are membrane bound sacs that contain - - - - - - - - - - - - - Digest materials taken in by the cell by - - - - - --------- Also destroy worn out - - - - - - - - - - or even the cell itself |
Digestive enzymes Phagocytosis Organelles |
|
|
|
Nasal chamber is formed by the -------- and ---- bone It is divided lengthways by the nasal -------- and the chambers are filled with nasal -------------- which are also known as --------- |
Maxilla and nasal bone Septum Nasal turbinates / conchae |
|
|
|
Spinal chord passes through the ------- -------- into the base of the skull at the -------- region. On either side are the ---------- --------which articulate with the ---- (first cervical vertebrae) At the side are the ---------- --------- which are sites for muscle attachments |
Foramen magnum Occipital region Occipital condyles Atlas Jugular processes |
|
|
|
A tuberosity/trochanter/tubercle is a ------------- on bones which are usually for the attachment of ------- |
Protuberance Muscles |
|
|
|
A tuberosity/trochanter/tubercle is a ------------- on bones which are usually for the attachment of ------- |
Protuberance Muscles |
|
|
|
Trochlea are bony structures through/over which a -------- passes, usually in the ------- in the bone and allow them to act as -------- |
Tendon Groove Pulley |
|
|
|
Condyle is a ----------- ---------- on a bone usually for ----------- with another bone |
Rounded projection Articulation |
|
|
|
Epicondyle is a ------------ of bone on the -------- edge above its condyle |
Projection of bone Lateral edge |
|
|
|
Foramen is an ---------- into or through a ---- , e.g. To allow the passage of -------- -------- and -------- |
Opening Bone Blood vessels and nerves |
|
|
|
Fossa is a --------- or ----------- ---- on a bone |
Hollow or depressed area |
|
|
|
Tendon connects --------- to ---- |
Muscle to bone |
|
|
|
Tendon connects --------- to ---- |
Muscle to bone |
|
|
|
Ligament connects ---- to ---- |
Bone to bone |
|
|
|
Temporal bone lies below the --------- bone on the ---------------- surface of the skull . Most ventral part forms the ----------- ----- which houses the structures of the -------- --- with an opening into the ------- ----. This is called the -------- ---------- -------. |
Below the Parietal bone Caudolateral Tympanic bulla Middle ear Tympanic bulla External auditory meatus |
|
|
|
Mandible / lower jaw comprises 2 halves or ----------- joined together at the ---- by a cartilaginous joint called the ----------- -------- The horizontal part is called the ---- which carries the ------- for the teeth of the lower jaw. The vertical part is called the ----- which articulates with with the rest of the skull at the ---------------- joint via the --------- process. The rounded coronoid process projects into the ----------- fossa is the point where the --------- muscle attaches.
|
2 halves are Dentaries Joined at chin Mandibular symphysis Body Carries the alveoli for the teeth Ramus Temporomandibular joint Condylar process Temporal fossa Temporalis muscle |
|
|
|
The nuchal ligament attaches to the ------ processes and extends from the ---- to the first --------- vertebrae |
Spinous processes Axis to first thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
|
The ---- or ------- process fits into the vertebral foramen of the ---- which serves as a pivot around which it can be rotated . The remaining cervical vertebrae get progressively ---------- as they approach the junction with the ---------- vertebrae |
Dens / odontoid process Atlas Smaller Thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
|
Distinguishing feature of thoracic vertebrae is tall --------- --------- and ----- ------ They are articulate with ribs at 2points: the ----- fovea which forms a ---------- joint with the ---- of the rib, and the ------------ fovea which forms the same with the --------- of the rib |
Tall spinous processes Short bodies Costal fovea forms a synovial joint with the head of the rib Transverse fovea forms a synovial joint with the tubercle of the rib Height of spinous processes decreases as it progresses towards lumbar region |
|
|
|
Lumbar vertebrae have ------ bodies and long -------- processes angled ---------------- to which the lumbar muscles attach |
Large bodies Long Transverse processes Cranioventrally |
|
|
|
Sacral vertebrae are - vertebrae fused together to form the ------ in the dog and cat This forms a --------------- joint with the wing of the ------ of the pelvic girdle, called the -------------- joint |
3 vertebrae fused together Form the sacrum Fibrosynovial joint Wing of the ileum Sacroiliac joint |
|
|
|
3 types of joints |
Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
|
Synovial joints are also known as |
Diarthroses |
|
|
|
Some synovial joints possess one or more intra-articular fibro-cartilaginous discs or --------- within the joint cavity Two are Found in the ------ joint (crescent shaped) 1 in ------------------ joint between mandible and skull Act as ------ --------- reducing wear and tear |
Menisci Stifle joint Temporomandibular Shock absorbers |
|
|
|
5 types of synovial joint |
Plane/gliding Hinge Pivot Condylar Ball and socket |
|
|
|
Example of plane gliding joint |
Joints between rows or carpal and tarsal bones |
|
|
|
Example of plane gliding joint |
Joints between rows or carpal and tarsal bones |
|
|
|
Example of hinge joint |
Elbow ,stifle |
|
|
|
Example of pivot joint |
Atlantoaxial joint (c1 and c2) |
|
|
|
Example of condylar joint |
Hock (or tarsus) |
|
|
|
Example of condylar joint |
Hock (or tarsus) |
|
|
|
Example of ball and socket joint |
Hip, shoulder |
|
|
|
Striated muscle fibre is filled with myofibrils made of 2 contractile proteins ----- and ------- Muscle contraction results from the formation of ----- --------- between those molecules |
Actin and myosin Cross bridges |
|
|
|
Number of muscle fibres supplied by a single nerve fibre is called a ------ ---- |
Motor unit |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue is always under a degree of tension known as |
Muscle tone |
|
|
|
Extrinsic muscles are attached from one major structure to another such as a limb and bring about movement of the ------ ---- in relation to other body parts |
Whole limb |
|
|
|
Intrinsic muscles are attached at ---- ---- within the one structure . Bring about movement ------- the individual limb |
Both ends Within |
|
|
|
Overlapping muscle fibres appear as dark bands or ----------- which are known as -------- |
Striations Sarcomeres |
|
|
|
Sarcomeres are units of ----------- |
Contraction |
|
|
|
Cross bridges between actin and myosin act as a --------- --------- and ------ the muscle |
Ratchet mechanism Shorten the muscle (contraction) |
|
|
|
Cross bridges between actin and myosin act as a --------- --------- and ------ the muscle |
Ratchet mechanism Shorten the muscle (contraction) |
|
|
|
Muscle contractions require energy , provided by --- molecules and ------- ions |
ATP calcium |
|
|
|
Muscle tone is achieved by a proportion of the motor units within that muscle being --------- so that some of the muscle fibres are ---------- while others are ---------- |
Activated Contracting Relaxed |
|
|
|
Muscle starting point is it's -------- and its end point is it's -------- |
Origin Insertion |
|
|
|
A bursa is a ----------- ----- --- lined with ---------- ------- and filled with -------- ----- |
Connective tissue sac Synovial membrane Synovial fluid |
|
|
|
A bursa wrapped completely around a tendon is called a -------- or --------- sheath |
Synovial / tendon sheath |
|
|
|
Muscles of mastication are (4) |
Digastricus Masseter Temporalis Medial and lateral pterygoids |
|
|
|
Most superficial abdominal muscles are --------- -------- -------- |
External abdominal obliques |
|
|
|
Intermediate muscles of lateral abdominal wall are ------- ------- ------- |
Internal abdominal oblique |
|
|
|
Deepest lateral abdominal muscles are --------- -------- --------- |
Transverse abdominal obliques |
|
|
|
The broad band of muscle on each side of the linea alba that forms the floor of the abdomen is the ------- -------- |
Rectus abdominus |
|
|
|
The inguinal ring is a slit in the ------------ of the -------- --------- ------- muscle in the region of the groin, which allows passage of------ -------- from the abdomen to the -------- -------- and ---------- ------- and transmits the --------- ----- to the scrotum |
Aponeurosis External abdominal oblique muscle Blood vessels External genitalia Mammary glands Spermatic chord |
|
|
|
Example of ungulates |
Cows, sheep, horses |
|
|
|
Latin for cat and dog |
Cat: felis catus Dog: Canis familiaris |
|
|
|
Lysosomes are sacs that contain ---------- -------- Function is to ------ particles taken in by -------------- and destroy worn out ------------- |
Digestive enzymes Digest particles Phagocytosis Organelles |
|
|
|
Centrosome contains rod like structures called ----------- which lie at right angles to each other and are involved in ---- ----------- |
Centrioles Cell division |
|
|
|
Mitosis is the division of -------- cells by a process called ------- ----- |
Somatic cells Binary fission |
|
|
|
Before a cell can divide it must make a copy of its --- The normal number of chromosomes is called the ------- number and before the division takes place the cells are ------------ |
DNA Diploid number Duplicated |
|
|
|
Rest phase and duplication of mitosis is |
Interphase |
|
|
|
Nuclear membrane breaks down in mitosis in --------- when the chromosomes contract and become shorter and fatter |
Prophase |
|
|
|
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell in -------- when the chromatids draw apart at the -------- |
Metaphase Centromere |
|
|
|
Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibres and move to opposite piles of the cell in |
Anaphase |
|
|
|
Spindle fibres break down and the nuclear membrane reforms in ---------. This creates - daughter cells (mitosis) The cell then returns to --------- |
Telophase 2 daughter cells Returns to Interphase |
|
|
|
Meiosis is the process where ---- cells divide within the ------- and the ----- This results in the production of these containing ---- the number of chromosomes which is the ------- number This must occur before ---------------- |
Germ cells Half Haploid number Before fertilisation |
|
|
|
Meiosis results in - identical daughter cells each of which is --- ----------- to the parent cell |
4 Non identical |
|
|
|
Organic compounds contain ------ but inorganic compounds do not. |
Carbon |
|
|
|
Plasma takes up about -% of body weight |
5% |
|
|
|
Transcellular fluid is formed by active ------- --------- and its volume varies, but it is considered to take up about -% of body weight and includes ---, digestive juices and -------active |
secretory mechanisms 1% body weight CSF digestive juices and lymph |
|
|
|
Interstitial fluid is formed by a process of ----------------- where smaller molecules and ions are separated from bigger ones The walls of the capillaries act like a ----- holding back the ------ plasma proteins and cellular components |
Ultrafiltration Sieve Large plasma proteins |
|
|
|
A reduction in circulating blood volume is also known as -------------- shock |
Hypovolaemic |
|
|
|
Typical daily water loss in urine is --ml/kg |
20ml/kg |
|
|
|
Daily water loss in faeces in -----ml/kg |
10-20ml/kg |
|
|
|
To balance daily fluid loss an adult healthy animal should take in ----- ml/kg per day |
50-60ml/kg |
|
|
|
A molecule is two or more atoms linked by a --------- ---- |
Chemical bond |
|
|
|
A substance whose molecules contain more than one type of atom is called a ------- |
Compound |
|
|
|
An electrolyte is a chemical substance that when dissolved in ----- splits into ---- and is capable of conducting an ------------- --------- |
Water Ions Electric current |
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration takes place in the |
Mitochondria |
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration takes place in the |
Mitochondria |
|
|
|
With a light microscope it is possible to observe |
Living organisms |
|
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum contains |
Ribosomes |
|
|
|
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for |
Protein modification |
|
|
|
A light microscope measures a specimen in |
Micrometers |
|
|
|
The part of the plasma membrane involved in cell recognition is |
Glycoproteins |
|
|
|
An example of a typical prokaryote is |
A bacteria cell |
|
|
|
Protein microtubules are found in |
Centrioles |
|
|
|
Proteins are synthesised in the |
Ribosomes |
|
|
|
Water moving from low concentration to high concentration is |
Osmosis |
|
|
|
During active transport particles move -------- a concentration gradient and -------- is used |
Against a gradient Energy is used |
|
|
|
Glucose crosses cell membranes through protein channels in a process called |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
|
The rate of diffusion increases as the ----------- increases |
Temperature |
|
|
|
When a red blood cell is placed in pure water it |
Bursts |
|
|
|
The water potential of pure water is |
0 |
|
|
|
Diffusion is when particles move to an area of ----------- concentration |
Lower |
|
|
|
An intracellular sodium potassium pimp is an example of |
Active transport |
|
|
|
An example of regular sense fibrous connective tissue is |
Tendon |
|
|
|
An example of regular sense fibrous connective tissue is |
Tendon |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue consists of two types of cell- Neurones and the surrounding ------cells |
Glial |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Ciliated columnar epithelium can be found in the |
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Ciliated columnar epithelium can be found in the |
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Haversian canal system is found in |
Bone |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Ciliated columnar epithelium can be found in the |
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Haversian canal system is found in |
Bone |
|
|
|
Protein found in muscle fibres essential for contraction is |
Myosin |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Ciliated columnar epithelium can be found in the |
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Haversian canal system is found in |
Bone |
|
|
|
Protein found in muscle fibres essential for contraction is |
Myosin |
|
|
|
Cells of a similar type and function combined in sheet or layers are known as |
A tissue |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle consists of fibres with many nuclei. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as |
A syncitium |
|
|
|
Areolar,adipose and reticular tissue are all types of |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
|
Ciliated columnar epithelium can be found in the |
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Haversian canal system is found in |
Bone |
|
|
|
Protein found in muscle fibres essential for contraction is |
Myosin |
|
|
|
Cells of a similar type and function combined in sheet or layers are known as |
A tissue |
|
|
|
Specialised cells lining the small intestine are adapted by having |
Villi to create a larger surface area |
|
|
|
Skin is made of |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
Skin is made of |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
The anal glands of a dog are modified ----------- glands |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
The number of pairs of mammary glands on dog and cat are |
Dog 8 Cat 10 |
|
|
|
Phase of hair cycle when follicle begins to atrophy |
Catagen |
|
|
|
Gland that produces sebum |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Gland that produces sebum |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Structure responsible for supplying the growing hair with nutrients is the -------- --------- |
Dermal papilla |
|
|
|
Gland that produces sebum |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Structure responsible for supplying the growing hair with nutrients is the -------- --------- |
Dermal papilla |
|
|
|
Long thick hairs with sensory nerve endings are known as -------- hairs |
Tactile |
|
|
|
Gland that produces sebum |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Structure responsible for supplying the growing hair with nutrients is the -------- --------- |
Dermal papilla |
|
|
|
Long thick hairs with sensory nerve endings are known as -------- hairs |
Tactile |
|
|
|
Claws of a cat are composed of ------------ epidermis |
Keratinised |
|
|
|
The --------- connects the dermis to the underlying structures |
Subcutis |
|
|
|
Tendon connects |
Muscle to bone |
|
|
|
Muscle that helps to open the jaw is |
Digastricus |
|
|
|
Muscle that helps to open the jaw is |
Digastricus |
|
|
|
A muscle that helps to close the jaw is |
Masseter |
|
|
|
Muscle that decreases the angle between two bones is |
A flexor |
|
|
|
Muscle that decreases the angle between two bones is |
A flexor |
|
|
|
Ventral rectus muscles move the |
Eye |
|
|
|
Muscle that decreases the angle between two bones is |
A flexor |
|
|
|
Ventral rectus muscles move the |
Eye |
|
|
|
If the Achilles' tendon is torn the animal loses its ability to ------- the hock |
Extend |
|
|
|
The clavicle lies with the the ------------------- muscle |
Brachiocephalicus muscle |
|
|
|
The clavicle lies with the the ------------------- muscle |
Brachiocephalicus muscle |
|
|
|
The ---------------- muscle is responsible for extending the shoulder |
Supraspinatus |
|
|
|
Contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle produces ---------- of the stifle |
Extension |
|
|
|
Contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle produces ---------- of the stifle |
Extension |
|
|
|
The muscle that most completely covers the dorsolateral surface of the femur is the |
Biceps femoris |
|
|
|
The muscle which extends the shoulder joint is the |
Semitendinosus |
|
|
|
The muscle which extends the shoulder joint is the |
Semitendinosus |
|
|
|
The primary action of the triceps brachii is to ------- the elbow |
Extend |
|
|
|
The muscle which extends the shoulder joint is the |
Semitendinosus |
|
|
|
The primary action of the triceps brachii is to ------- the elbow |
Extend |
|
|
|
Groups of muscles known as hamstrings are (3) |
Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus |
|
|
|
Aortic hiatus is found in the |
Diaphragm |
|
|
|
The vagal nerve passes through the diaphragm at the |
Oesophageal hiatus |
|
|
|
The vagal nerve passes through the diaphragm at the |
Oesophageal hiatus |
|
|
|
The Achilles' tendon inserts into the |
Calcaneus |
|
|
|
The vagal nerve passes through the diaphragm at the |
Oesophageal hiatus |
|
|
|
The Achilles' tendon inserts into the |
Calcaneus |
|
|
|
Layer of cartilage between the epiphysis and diaphysis is known as the |
Growth plate |
|
|
|
Insertion of the temporal muscle is on the ---------- side of the ---------- process |
Medial side Coronoid process |
|
|
|
Insertion of the temporal muscle is on the ---------- side of the ---------- process |
Medial side Coronoid process |
|
|
|
Masseter muscle originates at the ---------- ---- |
Zygomatic arch |
|
|
|
The tuberculum of the rib articulates with the ----------- process of the vertebrae |
Transverse |
|
|
|
The tuberculum of the rib articulates with the ----------- process of the vertebrae |
Transverse |
|
|
|
The joint st the mandibular symphysis is ------------ |
Cartilagenous |
|
|
|
The greater trochanter is at the ----------- --- of the femur |
Proximal end |
|
|
|
The head of the femur sits in the |
Acetabulum |
|
|
|
The head of the femur sits in the |
Acetabulum |
|
|
|
Hyaluronic acid is found in ---------joints |
Synovial |
|
|
|
The head of the femur sits in the |
Acetabulum |
|
|
|
Hyaluronic acid is found in ---------joints |
Synovial |
|
|
|
Example of a condylar joint is the ------ |
Carpus |
|
|
|
The head of the femur sits in the |
Acetabulum |
|
|
|
Hyaluronic acid is found in ---------joints |
Synovial |
|
|
|
Example of a condylar joint is the ------ |
Carpus |
|
|
|
The temporal bone forms a joint with the -------- process |
Condylar process |
|
|
|
The joints between the sternebrae are --------------------- |
Cartliagenous |
|
|
|
The joints between the sternebrae are --------------------- |
Cartliagenous |
|
|
|
The elbow joint is classed as a ------ joint |
Hinge |
|
|
|
In the dog there are -sternebrae |
8 |
|
|
|
Forelimb muscles / flexor / extensor ECR CDE LDE FUL FCL |
Extensor carpi radialis Common digital extensor Lateral digital extensor Flexor ulnaris lateralis Flexor carpi ulnaris |
|

