![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
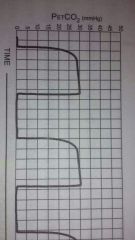
Capnography |
Normal |
|

Capnography |
Hyperventilation |
|
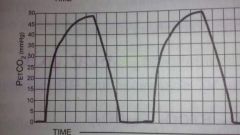
Capnography |
Obstruction |
|
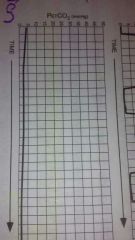
|
Disconnection, leak, apnea |
|
|
What color should a colormetric etCO2 detector change with proper ETT placement? |
Yellow |
|
|
How do you estimate anatomic deadspace? |
1ml per lb of IBW |
|
|
How do yo estimate mechanical deadspace? |
10ml per inch of flex tube |
|
|
What is the formula for P/F ratio? |
PaO2/FiO2 |
|
|
What is a normal P/F ratio? |
>380 torr |
|
|
What is considered mild ARDS? |
P/F ratio <200-300 |
|
|
What is considered moderate ARDS? |
P/F ratio <100-200 |
|
|
What is considered severe ARDS? |
P/F ratio <100 |
|
|
Swan-Ganz: Where shod the catheter sit when inserted through the jugulat or subclavian vein? |
Pulmonary Artery about the 50cm |
|
|
Swan-Ganz: Catheter is inserted >50cm and no waveform is obtained, why? |
Catheter is curling in the right atrium or right venteicle. |
|
|
Normal PAP |
25/8 |
|
|
Normal pulse pressure: |
40MmHg |
|
|
Normal Cardiac Output (Qt) |
4-8L/min |
|
|
Normal Cardiac Index: |
2.5-4.0 L/min/m2 |
|
|
Normal Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR): |
<20 mmHg |
|
|
Normal Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR): |
<2.5 mmHg/L/min |
|
|
CBC: Normal RBC |
4-6 |
|
|
Polycythemia indicates what? |
Chronic tissue hypoxemia (COPD) |
|
|
Anemia occurs with what condition? |
Blood loss or hemorrhagr |
|
|
CBC: Normal Hemoglobin (Hb) |
12-16 |
|
|
Low Hb indicates what? |
Anemia <RBC |
|
|
High Hb indicates what? |
Polycythemia >RBC |
|
|
CBC: Normal Hematocrit (Hct) |
40-50% |
|
|
What does Hct measure? |
The %of RBC in total blood volume |
|
|
Low Hct indicates? |
Anemia (<RBC) |
|
|
High Hct indicates what? |
Polycythemia (>RBC) |
|
|
CBC: Normal WBC |
5,000-10,000 |
|
|
Increased WBC |
Leukocytosis: bacterial infection |
|
|
Decreased WBC |
Leukopenia- viral infection |
|
|
WBC - Neutrophils increase with what chronic condition? |
COPD |
|
|
WBC - Eosinophols increase with what Chronic condition? |
Asthma |
|
|
WBC - Monocytes increase with what chronic condition? |
TB |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Potassium (K+) |
3.5-4.5 |
|
|
Hypokalemia (<K+) is associated with what clinical findings: |
Metabokic alkalosis, renal loss, vomiting/diarrhea, NG suction, cardiac issues. |
|
|
Hyperkalemia (>K+) is associated with what clinical findings? |
Acidemia, kidney failure |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Sodium (Na+) |
135-145 |
|
|
Hyponatremia (<Na) is significant with what clinical findings? |
Fluid loss, diuretics, vomiting/diarrhea, fluid gain from CHF, IV therapy |
|
|
Hypernatremia (>Na) is associated with what clinical findings? |
Dehydration |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Chloride (Cl-) |
80-100 |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Bicarbonate (HCO3) |
22-26 |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Magnesium (Mg) |
1.7-2.4 |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Calcium (Ca) |
4.5-5.25 |
|
|
Electrolytes: Normal Phosphorus/phosphate |
1.2-2.3 |
|
|
Cardiac Markers: Troponin |
<0.1 and increade with MI |
|
|
Cardiac Markers: Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) |
<100 elevated indicates CHF |
|
|
Normal Lactate |
0.5-2.2, greater than 4=sepsis, increase = >O2 demand |
|
|
Normal Serym Glucose |
70-100 |

