![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
70 yr old living at home in ER with acute episode of shaking chills, increased fatigue, productive cough with *RUST COLORED SPUTUM* and shortness of breath x 2 days
What is this? |
Strep. pneumoniae
|
|
|
You have a patient with pneumonia caused by Strep. pneumoniae. What will a gram stain of sputum show?
|
gram +
lancet shaped diplococci **streptococcus pneumoniae** |
|
|
What drugs would you use to treat Strep. pneumoniae infection?
|
Beta lactam (penicillin, 3rd gen cephalosporins)
erythromycin, quinolones--> if allergic to pen. |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Community Acquired Pneumonia?
|
Strep. pneumoniae
|
|
|
You see a patient that is homeless, drinks a fifth a day and produces “red currant jelly” sputum. What are you thinking?
|
Klebciella pneumoniae
|
|
|
Klebciella pneumoniae gram stain?
|
Gram -
Rods |
|
|
Klebciella pneumoniae virulence factor?
|
Large polysaccharide capsule
|
|
|
A patient is in acute respiratory failure and you intubate her.
What tidal volume do you order? |
6-8 ml/kg
|
|
|
What formula is used to measure the efficiency of O2 diffusion between lungs and pulmonary circulation
|
A-a gradient
|
|
|
You have a patient with Cystic Fibrosis that has been on a ventilator for 3 months. Chest x-ray indicates infiltrates in the lungs. What are you thinking?
|
Pseudomons aeruginosa
|
|
|
Pseudomons aeruginosa
Gram stain? Oxidase? |
Gram negative rods
Oxidase + |
|
|
Underlying cause of cystic fibrosis
|
Sodium/chloride channel dysfunction
|
|
|
You are treating a heroin addict (IV drug use) recovering from the flu. What bacteria are you thinking?
|
Staph Aureus
|
|
|
You have a patient that is difficult to wean and develops left calf pain, swelling and edema
What do you suspect and what do you order? |
Pulmonary Embolism
Order a Pulmonary Angiogram (GOLD STANDARD) Order D-dimer |
|
|
Three risk factors for Venous Thrombolotic Events
|
VIRCHOW'S TRIAD
endothelial injury, venous stasis, hypercoagulability |
|
|
What are some causes of Acquired Hypercoagulability?
|
lupus, nephritic syndrome, HIT, cancer , birth control pills
|
|
|
What are some causes of Inherited Hypercoagulability?
|
Factor V leiden , protein C/s deficiency, antithrombim III deficiency
**blood test to check for these before using anticoagulants** |
|
|
Your patient has had a VTE due to Immobilization: surgery, trauma. How long do you treat with anticoagulants?
|
3 months
|
|
|
Your patient has had a VTE for the first time with no obvious cause. How long to you treat with anticoagulants?
|
3-6 months
|
|
|
Your patient has had reccurent VTEs Cancer, Hypercoagulable state. How long do you treat with anticoagulants?
|
12 months to LIFE
|
|
|
Despite several boluses of IV normal saline, your pt. is not maintaining adequate perfusion. Which pressures do you base the need for vasopressors?
|
Mean Arterial Pressure < 60 mmHg
|
|
|
First line vasopressor for sepsis?
First line vasopressor for everything else? |
NE= sepsis
Dopamine= everything else |
|
|
10 year old male with a 2 week history of a gradual onset of a non productive cough, fever, headache, and fatigue. Fluffy infiltrate in CXR. What are you thinking?
|
Could be viral, but...
Bacterial = mycoplasma pneumonia |
|
|
Best lab test for mycoplasma pneumonia?
|
Cold Agglutins
|
|
|
Does mycoplasma pneumonia have a cell wall?
|
NO CELL WALL
|
|
|
10 year old male with a 2 week history of a gradual onset of a non productive cough, fever, headache, and fatigue. Fluffy infiltrate in CXR.
You see obligate intracellular parasites on biopsy. What are you thinking? |
Chlamydia pneumoniae
|
|
|
What serotype of Chlamydia pneumoniae causes respiratory infections and pneumonia?
|
TWAR strain
|
|
|
**Bacterial vs. Viral**
-Onset – ? -Rigors- ? -Cough- ? -Temp- ? -mucous- ? -CXR-? |
-Onset – gradual if viral, acute if bacterial
-Rigors- present in bacterial -Cough- productive if bacterial -Temp- high grade for bacterial -mucous- purulent (bloody) in bacterial , non-purulent in viral -CXR- consolidation |
|
|
•6 yr old native American from SW Colorado home from school with flu-like symptoms, becomes acutely SOB, x ray shows pulmonary hemorrhage and edema.
|
HANTA Virus
**Spread by mouse droppings** |
|
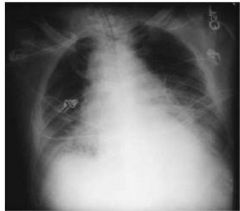
23 year old postal worker who works night shift at a hide processing plant with mild cough, fever, malaise develops acute dyspnea, stridor, fever, cyanosis. CXR shows a widened Mediastinum
|
Anthrax
|
|
|
You have a patient that presents with flu-like symptoms and a widened mediastinum on CXR. What's up?
|
Anthrax
|
|
|
Gram stain of Anthrax?
|
Large, Gram + rods
|
|
|
Why does an antibiotic fail?
|
Noncompliance
Resistance to drugs Drug-drug interactions |
|
|
What is the post antibiotic effect?
|
Still have suppression despite drug levels below Minimum IC
**Concentration-dependent drugs** |
|
|
This Virus causes:
-LRT diseases in CHILDREN -Acute respiratory dz of military recruits -Pharngoconjunctival fever- swimming pools -Epidemic keratoconjuctivitis -Infantile gastroenteritis -Common cold |
Adenovirus
|
|
|
**Flu Virus**
Antigenic drift- ? Antigenic Shift- ? |
*Antigenic drift* - small changes in hemagglutinin and/or neuraminidase single antigenic determinants. Due to mutation.
*Antigenic shift* - major change in most all antigenic determinants of hemagglutinin and/or neuraminidase. Intragenomic or intergenomic recombination (segment exchange, reassortment) between human and animal viruses. |
|
|
Some muscles will grow abnormally large when a patient has forced respiration due to conditions like COPD or Emphysema. Other muscles that would not normally be involved in breathing are recruited to assist. What are these muscles?
|
-Scalenes --> elevate 1st & 2nd ribs
-Pectoralis minor and major --> Can elevate anterior ribcage if arms are abducted and scapula is fixed. -Serratus anterior --> Can elevate lateral ribcage if scapula is fixed. -Trapezius, Levator scapulae, Rhomboids --> Stabilize (fix) the scapula so that other muscles can then work on the ribcage |
|
|
Why does an antibiotic fail?
|
Noncompliance
Drug interactions Resistance |
|
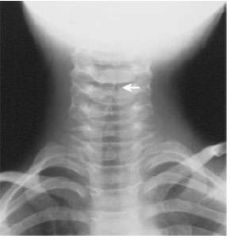
What's this?
|
Steeple Sign
|
|
|
What is sensitivity regarding lab results?
|
Sensitivity is the % of true positives that are really positive by the gold standard
|
|
|
What is specificity regarding lab results?
|
Specificity is the % of true negatives that are really negative by the gold standard
|
|
|
What causes symptoms of runny nose and congestion?
|
Our own immune system
|
|
|
what are PAMPS?
What receptors do they bind? |
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns
Bind to TLRs --> immune response |
|
|
Activation of what causes the release of pro-inflammatory mediators from cells?
|
NFKB
|
|
|
How does secretory IgA stop infection?
|
Neutralizes pathogens and toxins
|
|
|
Naso-oropharynxnasal hairs and mucus. Conducting
airways- about half of the cells are ciliated. Clears pathogens, dust, ect. from respiratory tract. |
Mucocilliary Clearance
|
|
|
What is the most common viral LRT?
|
influenza
|
|
|
What produces the most serious sequelae of flu?
|
Bacterial Pneumoniae
|
|
|
What is the most common LRT infection in kids/newborns?
|
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
|
|
|
3 yo boy with inspiratory stridor and barking cough comes in to the clinic. Tests reveal that the child has a viral infection. What's the virus?
|
Parainfluenza Virus
**Viral Croup** |
|
|
3 yo boy with inspiratory stridor and barking cough comes in to the clinic. Tests reveal that the child has a bacterial infection. What is it?
|
haemophilus influenza type B (G-)
Staph. aureus (G+) |
|
|
3 yo boy with inspiratory stridor and barking cough comes in to the clinic. The cause is not viral or bacterial infection. What is going on?
|
Foreign body airway obstruction
|
|
|
Cause of strep pharyngitis?
|
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (s. pyogenes)
|
|
|
Sequelae of strep infection?
|
Rheumatic fever
Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
Bacterial URT Treatment failure? (2)
|
noncompliance
beta lactamase producing bacterial flora (co-pathogens in the throat) |
|
|
Toxin mediated, pseudomembrane bacteria?
|
Corynebacterium diphtheria
-damages tissue through "A- toxin", and it develops a pseudomembrane |
|
|
Bacterial URT that causes paroxysmal cough?
|
Bordella pertussis
|
|
|
45 yr old Laotian male released from 3 mos immigration detention with night sweats, wt, loss, hemoptysis and dyspnea (cavitation on x ray). What are you thinking?
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
Gram stain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ?
|
Won't gram stain!
Acid-Fast membrane full of lipids |
|
|
Lesion seen in TB?
|
Gohn Complex
|
|
|
What does a positive PPD test look like?
|
10 mm induration after 48 hrs
|
|
|
Immunocompromised patient infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. What does this cause? Why is it bad?
|
Miliary TB
**SYSTEMIC INFECTION** |
|
|
Why use 4 drugs to treat TB?
|
we use four drugs to try to keep a pharmalogical therapy that works.
If we use just one drug, more likely to develop resistance to that drug. |
|
|
Rifampin Side effects
|
Potent CYP450 inducer
hepatic toxicity |
|
|
Isoniazid side effects:
|
CYP 34a inducer
Hepatitis CNS toxicity peripheral neuropathy ----> give Vitamin B6 |
|
|
Pyrazinamide side effects:
|
hepatotoxitcity
hyperuricemia |
|
|
Ethambutol side effects:
|
optic neuritis-->impaired red green vision
hyperuricemia |
|
|
Tx for Latent TB infections?
|
Isoniazide/rifampin
|
|
|
Tx for Isoniazide TB infections?
|
Ethambutol + Rifampin + Pyrazinamide
for 6 months |
|
|
A 12 year old with cough associated with wheezing and fatigue several times a week. No fever/chills. CXR swhows hyperinflation and flattened diaphragms
|
ASTHMA
|
|
|
FEV1/FVC ratio in asthma?
|
FEV1/FVC ratio will be <70%
|
|
|
Is there a bronchodilator response in asthma?
|
yes
|
|
|
**Asthma**
Rule of 2's to asses asthma control |
>2 uses of inhaler per week
>2 uses at night/month >2 canisters/year=poor control **Yes to any of these and you have poor control** |
|
|
What are the three components of asthma?
|
Chronic inflammation of the airways
Hypersecretion of mucus glands Airway smooth muscle hyperresponsiveness |
|
|
What is Status Asthmaticus?
|
Persistent attack despite nebulizer, O2, and steroid therapy
|
|
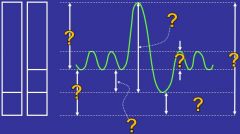
|
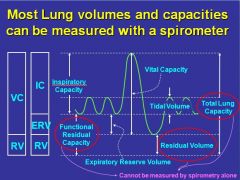
|
|
|
What are the 4 causes of hypoxemia?
|
Hypoventilation
Diffusion impairment Shunt V/Q Inequality |

