![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
*POSTERIOR Chest wall landmarks:
|
-Left scapular line
-Vertebral Line -right scapular line |
|
|
*LATERAL chest landmarks:
|
-posterior axillary line
-midaxillary line -anterior axillary line |
|
|
*ANTERIOR Chest landmarks:
|
-Midsternal line
-Midclavicular Line -Anterior axillary Line |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms for hypoxia?
|
*Restless & fatigue
*restless is an early sign, that is often missed |
|
|
Reduced oxygenation causes changes in?
|
-mental alertness b/c of the brain's sensitivity to lowered oxygen levels
|
|
|
Key landmarks of the chestAngle
|
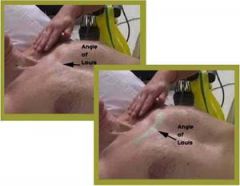
-Angle of Louis, suprasternal notch, costal angle, clavicles, nipples,vertebrae:
|
|
|
Name some signs assessed that would indicate oxygenation problems?
|
-reduced mental alertness
-nasal flaring -somnolence=Sleepiness, the state of feeling drowsy, ready to fall asleep -cyanosis |
|
|
Normal size of the CHEST CONTOUR?
|
-Symmetrical, with the anteroposterior diameter 1/3 to 1/2 of the transverse, or side to side diameter. (# of hands under the arm compared to anterior transverse chest 1:2 ratio)
|
|
|
Anteroposterior diameter equals transverse diameter?
|
-Barrel-Shaped chest (2:2 ratio)
-characterizes aging & chronic lung disease |
|
|
Chest contour is ROUND shape?
|
-Infants
|
|
|
What causes abnormal chest contours?
|
-congenital
-postural alterations |
|
|
Funnel Chest
|

Pectus Excavatum
|
|
|
Describes a protrusion of the chest over the sternum, often described as giving the person a bird-like appearance.
|
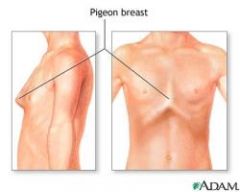
Pectus carinatum (pigeon breast)
|
|
|
When assessing a client, the normal appearance of the SCAPULA is ________.
|
-symmetrical and closely attached to the thoracic wall
|
|
|
Bulging?
|
-indicates the client is using great effort to breathe
*Normally NO bulging or active mvmt occurs w/in the intracostal spaces* |
|
|
What is assessed when performing palpation of th thorax and lungs?
|
-chest excursion
-surface characteristics -tactile fremitus |
|
|
What are some reasons for Reduced chest excursions?
|
-pain
-postural deformity -fatigue |
|
|
*TACTILE (VOCAL) FREMITUS?
|
-vibration of the chest wall during speaking that is palpable on physical examination.
Tactile fremitus may be decreased or absent when vibrations from the larynx to the chest surface are impeded by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obstruction, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax. It is increased in pneumonia. -Ask client to say "ninety-nine" *Normally a Faint vibration is equal posterior & anterior as the client speaks* |
|
|
Respiratory Disease affects?
|
-V/S (pulse, Respiration)
-oxygenation -mental status=(confusion/dizziness), not getting enough O2 to the brain |
|
|
*estimates the DEPTH of breathing*
With thumbs aligned parallel along the spine at the level of the tenth rib, and the hands flattened around the client's back, instruct the client to take a deep breath? |
Chest Excursion or expansion of posterior thorax (Palpation)
-thumbs should move outward approximately 5 cm when the client takes a deep inspiration |
|
|
Questions to ask during assessment of "Thorax and Lungs"?
|
-cough (when does it occur, productive or non-productive,sound, color or sputum)?
-Allergies to pollens, animal or dust? -Horaseness? (larynx part of resp. system) -SOB (at rest/ while in bed/ when do you experience SOB) -# of pilow you sleep w/? (does it help breathing) -Pain in chest when taking a deep breath? -Pain (cough/breath) |
|
|
Difficulty in breathing that occurs while the patient is lying down or standing or sitting erect?
|
ORTHOPENIA
-occurs in many disorders of the cardiac and respiratory systems, such as asthma, pulmonary edema, emphysema, pneumonia, congestive heart failure, and angina pectoris. Assessment includes noting the number of pillows used by the patient. Patients with orthopnea also report sleeping in recliners |
|
|
FROTHY
|
-Coughing usually brings up white or pink-tinged frothy sputum
-thin/think mucous -associated w/ pulmonary edema |
|
|
Only lung sound a client can hear themselves?
|
-Wheezing
|
|
|
Smoking is a risk factor for?
|
-lung cancer
-heart disease, -cerebrovascular disease -emphysema -chronic bronchitis (assess hx of tobacco or marijuana use, type of tobacco, duration & amt) |
|
|
Pack Year=
|
-number of years smoked X number of packs per day
|
|
|
What are some warning signs for Lung Cancer?
|
-persistent cough
-sputum streaked w/ blood -voice change -chest pain -recurrent attacks of pneumonia or bronchitis |
|
|
Environemental risk factors that increase chance for various lung diseases?
|
-asbesto
-arsenic -coal dust -exposure to Radiation -second hand smoke |
|
|
What are some risk factors for TB?
|
-HIV
-substance abuse -low income -resident or employee of nursing home -homeless -recent prison inmate -family member of TB -immigrant to US |
|
|
Risk Factors for BOTH TB and HIV
|
-persistent cough
-hemoptysis -unexplained wt loss -fatigue -night sweats -fever |
|
|
HEMOPTYSIS
|
-coughing up of blood or bloody sputum from the lungs or airway
|
|
|
A client with a history of chronic hoarseness is an indicator of?
|
-laryngeal d/o or
-abuse of cocaine or opioids (sniffing) |
|
|
Symptoms that often are caused by an ALLERGIC RESPONSE?
|
-choking feeling
-bronchospasm w/ respiratory stridor -wheezes on auscultation -dyspnea (assess hx of allergies to pollen, dust, foods, drugs or chemical substances) |
|
|
What are some conditions that could place client at risk for Lung Disease?
|
-history for cancer
-tuberculosis -allergies -COPD |
|
|
What clients are at an INCREASE risk for Rispiratory disease?
|
-very young
-very old -Chronic respiratory problems -immunosuppressive diseases **Educate these clients on the need to have a Flu, pneumonia vaccine and TB test* |
|
|
Who are thoracic breathers?
|
-women
|
|
|
Who are abdominal breahter?
|
-men and infants
|
|
|
Intercostal Bulging is seen in client with, (what disease)?
|
-COPD
|
|
|
Abnormal Findings with an ALTERED CHEST SYMMETRY:
|
-spinal deformities
-kyphosis -scoliosis |
|
|
Normal chest shape?
|
-No retraction
-No use of accessory muscles |
|
|
Abnormal findings that causes ALTER BREATHING SYMMETRY:
(chest shape is affected) |
-fractured ribs
-flail chest -pnuemothorax -atelectasis=Failure of full expansion of the lung at birth or a collapse of the lung |
|
|
CREPITUS
|
-characterized by a peculiar crackling, crinkly, or grating feeling or sound under the skin, around the lungs, or in the joints.
|
|
|
Normal finding when Palpating the chest?
|
-chest non-tender
-no masses -No crepitus -symmetrical excursion at bases anterior & posterior, No lags -Equal tactile fremitus anterior & posterior |
|
|
Crepitus is present in client with?
|
-Subcutaneous Emphysema
|
|
|
Abnormal findings that causes ALTER BREATHING SYMMETRY:
(chest shape is affected) |
-fractured ribs
-flail chest -pnuemothorax -atelectasis=Failure of full expansion of the lung at birth or a collapse of the lung |
|
|
CREPITUS
|
-characterized by a peculiar crackling, crinkly, or grating feeling or sound under the skin, around the lungs, or in the joints.
|
|
|
Normal finding when Palpating the chest?
|
-chest non-tender
-no masses -No crepitus -symmetrical excursion at bases anterior & posterior, No lags -Equal tactile fremitus anterior & posterior |
|
|
Crepitus is present in client with?
|
-Subcutaneous Emphysema
|
|
|
Abnormal findings with INCREASED FREMITUS:
|
-pneumonia
-bronchitis -thin chest wall -atelectasis -pulmonary edema |
|
|
Abnormal findings with DECREASED FREMITUS:
|
-emphysema
-asthma -obese chest wall (can't feel vibrations) effusion -pneumothorax=collasped lung -Airway obstruction |
|
|
What is the ratio for Anterior/posterior to Transverse (lateral) diameter?
|
-1:2
-costal angle 90 degrees (number of hands under arm compared to anterior & transverse chest) |
|
|
Altered chest shape (barrel chest) ratio is
|
1:1
-costal angle > 90 degrees -COPD |
|
|
Normal diaphragmatic excursion?
|
-3 to 6 cm
|
|
|
Accessory muscles of breathing:
|
-sternocleidomastoid
-trapezius -abdominal muscles *muscles move little with normal passive breathing *accessory and abdominal muscles contract w/ strenuous exercise & COPD (client may produce a grunting sound) |
|
|
Abnormal findings upon Percussion:
|
*DULLNESS
-tumors -fluid -pulmonary edema -pneumonia *HYPERRESONACE -air trapping of emphysema |
|
|
RESONANCE:
|
-the clear, long, low pitched sound elicited over the normal lung
|
|
|
HYPERRESONANCE:
|
-a more vibrant, lower pitched, louder and longer sound heard over the lungs during maximum inspiration
*Emphysema* |
|
|
DULLNESS
|
-short, high pitched, soft and thudding sound which lacks the vibratory quality of sound.
*pneumonia -fleural effusion -tumors -fluid |
|
|
FLATNESS
|
-occurs when there is no air present in the underlying tissue
-found over the muscles of the arm or thigh |
|
|
Normal Breath Sounds:
|
-vesicular
-bronchovesicular -bronchial |
|
|
BRONCHIAL/ (breath sound
TRACHEAL= |
-loud and high pitched w/ hollow quality
*EXPIRATION last longer than INSPIRATION (3:2 ratio) Tracheal: breath sounds are heard over the trachea. These sounds are harsh and sound like air is being blown through a pipe. |
|
|
Where are Bronchial breath sounds heard?
|
-ONLY over Trachea
-created by air moving through trachea close to chest wall |
|
|
BRONCHOVESICULAR:
|
-blowing sounds
-medium pitched *INSPIRATORY phase is EQUAL to EXPIRATORY phase* |
|
|
Where are Bronchovesicular breath sounds best heard?
|
-posteriorly b/w scapulae
-Anteriorly over bronchioles (laterally to sternum) |
|
|
Describe VESICULAR breath sound:
|
-soft, breezy & low pitched
*INSPIRATORY phase is 3 times LONGER than EXPIRATORY phase* |
|
|
Where are Vesicular breath sounds best heard?
|
-lung's periphery= most of lung fields (except over scapula)
*Created by air moving through smaller airway* -85% of lungs are vesicular breath sounds |
|
|
Which breath sound is created by air moving through trachea, close to chest wall?
|
-Bronchial
|
|
|
Which breath sound is created by air moving though LARGE airways?
|
-Bronchovesicular
|
|
|
Proper technique when auscultating Breath sound:
|
-Anteriorly
-Laterally -Posteriorly |
|
|
BRONCHOVESICULAR:
|
-blowing sounds
-medium pitched *INSPIRATORY phase is EQUAL to EXPIRATORY phase* |
|
|
Where are Bronchovesicular breath sounds best heard?
|
-posteriorly b/w scapulae
-Anteriorly over bronchioles (laterally to sternum) |
|
|
Auscultation (listening) to mvmt of air through Tracheobronchial tree detects?
|
-increased mucus
-obstructed airways -increased fluid associated w/ CHF -emphysema -pleural effusion |
|
|
-snoring sounds=
|
Sonorous
|
|
|
-loud, low pitched, rumbling coarse sounds
-heard during inspiration or expiration |
-RHONCHI (Sonorous wheeze)
|
|
|
Rhonchi is primarily heard over?
|
-trachea and bronchi (upper (larger airways)
|
|
|
What is the cause of Rhonchi?
|
-fluid or mucus in upper airways
|
|
|
Treatment for Rhonchi?
|
-suction or coughing
|
|
|
loud, bubbly sounds heard during inspiration?
|
-Coarse crackles (not cleared w/ coughing)
|
|
|
high-pitched fine, short interrupted crackling sound heard during end of inspiration
|
-Fine crackles
|
|
|
lower, more moist sounds heard during middle of inspiration
|
-Middle crackles (not cleared w/ coughing)
|
|
|
What causes CRACKLES/RALES?
|
-air is trying to get to the alveoli (alveoli is trying to open resulting in a crackling sound)
|
|
|
CRACKLES=
|
-fine to coarse popping heard as air passes through fluid or re-expands collapsed small airways
*characterized as -Fine -Medium and Coarse crackles |
|
|
Possible tx for crackles:
|
-Lasix
|
|
|
Known as "death rattles"
|
-Rhonchi
|
|
|
Most common site auscultated for crackles/rales?
|
-right & left lung bases
|
|
|
-heard over all lung fields
-high-pitched musical sounds (inspiration & expiration) |
-WHEEZES (sibilant wheeze)
|
|
|
Known as "death rattles"
|
-Rhonchi
|
|
|
Most common site auscultated for crackles/rales?
|
-right & left lung bases
|
|
|
-heard over all lung fields
-high-pitched musical sounds (inspiration & expiration) |
-WHEEZES (sibilant wheeze)
-Do Not clear w/ cough -louder on exipration |
|
|
What causes Wheezing?
|
-air mvmt through narrowed bronchials or obstructed airway
|
|
|
Wheezing is seen in clients w/?
|
-asthma
-COPD |
|
|
Treatment for Wheezing?
|
-bronchodilators
|
|
|
Rhonchi is seen in client w/?
|
-Pneumonia
-bronchitis |
|
|
Which Adventitious sound is heard when a client has pneumonia, pulmonary edema or atelectasis?
|
-Crackles/Rales
|
|
|
Adventitious breath sound heard w/ pleuritis
|
-PLEURAL FRICTION RUB
*Do Not clear w/ cough* *Very painful to breath |
|
|
Low pitch, Dry, rubbing or grating adventitious sound?
|
-PLEURAL FRICTION RUB=visceral & parietal pleura rub against each other)
(sounds like an old rocking chair) |
|
|
Where is pleural friction rub heard?
|
-anterior lateral lung field w/ the client in an up right position
*Best heard on INSPIRATION* |
|
|
Warning signs for Lung Cancer?
|
-cough
-blood in sputum -chest pain -repeat bouts of pneumonia & bronchitis |
|
|
Client teaching strategies:
|
*Explain risk factors for chronic lung disease & cancer
-smoking -environmental pollution -radiation -radon=in pipes of old houses -discuss cancer warning signs -benefits of receiving flu & pneumoina vaccinations (older adults) -Teach COPD client in coughing & Pursed-lip breathing exercises |

