![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what are the functions of the respiratory system? and how many?
|
5 functions
1. provide surface area for gas exchange between the air and blood 2. moving air to and from the exchange surface. 3. protection against dehydration, temperature change, and pathogens. 4. production of sound for speaking, singing, and other forms of communication. 5. facilitating the detection. |
5
|
|
|
what are the internal structures of the external nose have how many functions and what are they?
|
3
1. warming, moistening, and filtering air. 2. detecting olfactory stimuli. 3. modifying speech. |
|
|
|
the external portion of the nose visible on the face consists of what?
|
bone and hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
|
what skull bones contain the paranasal sinuses
|
frontal
sphenoid ethmoid maxillea |
|
|
|
then respiratory region of the nasal cavity is lined with?
|
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
|
|
what is the first part of the pharynx? it lies posteriorly to what? and extends to the what
|
the nasopharynx, lies posteriorly to the nasal cavity and extends to the soft palate
|
|
|
|
anteriorly, the nasal cavity merges with the external nose, and posteriorly it communicates with what? through two openings called?
|
the pharynx and the internal mares or choanae.
|
|
|
|
what is the nasal vestibule?
|
anterior portion of the nasal cavity just inside the nostrils
|
|
|
|
what is the nasal septum?
|
the vertical partition that divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides.
|
|
|
|
how many regions and what are they?
|
3 regions
nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
the conchae subdivide the nasal cavity into grove like passageways?
|
superior, middle and inferior meatus
|
|
|
|
what 3 anatomical regions can the pharynx be divided?
|
1. nasopharynx
2. oropharynx 3. laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
the first part of the nasopharynx is located where?
|
lies posterior to the nasal cavity and extends to the soft palate
|
|
|
|
the nasopharynx is line with?
|
pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
|
|
the intermediated portion of the pharynx is what and located where?
|
the oropharynx, lies posterior to the oral cavity and extends from the soft palate inferiorly to the level of thy hyoid bone
|
|
|
|
the oropharynx is lined with? what else is found in the oropharynx?
|
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
two pairs of tonsils the palatine and lingual tonsils |
|
|
|
what is the inferior portion of the pharynx and where is it located?
|
the laryngopharynx, begins at the level I of the hyoid bone.
inferior end it opens into the esophagus posteriorly and the larynx anteriorly |
|
|
|
what is the laryngopharynx line with?
|
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
|
|
|
|
THE BLANK is a short passageway that connects the laryngopharynx with the BLANK?
|
the larynx or voice box and trachea.
|
|
|
|
the wall of of he larynx is composed of nine pieces what are they?
|
three occur singly
• thyroid gland •epiglottis • cricoid cartilage three occur in pairs • arytenoid cartilages •cuneiform cartilages • corniculate cartilages |
|
|
|
the ligament that connects the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone?
|
thyrohyoid membrane
|
|
|
|
the thyroid cartilage consists of two fused plates of?
|
hyaline cartilage that form the anterior wall of the larynx and give it a triangular shape.
|
|
|
|
leaf-shaped piece of elastic cartilage that is covered with epithelium.
|
the epiglottis
the broad " leaf " is unattached and able to move up and down lime a trap door. |
|
|
|
the glottis consists of?
|
a pair of folds of mucous membranes including the vocal folds ( true vocal cords) and space between them called rima glottis
|
|
|
|
these do not function in voice production?
|
the superior folds are the ventricular folds ( false vocal cords)
|
|
|
|
these function in voice production?
|
the inferior folds are the vocal folds (true vocal cords)
|
|
|
|
the trachea is posterior or anterior to the esophagus?
|
anterior to the esophagus.
|
|
|
|
the layers of the trachea wall from deep to superficial are:?
|
1 mucosa
2 submucosa 3 hyaline cartilage 4 adventitia |
|
|
|
true or false:
there are 14-18 incomplete, horizontal rings of the Hyaline cartilage that resembles the letter C, each responsible for providing semi Ridge support to the trachea? |
false there are 16-20 incomplete horizontal rings
|
|
|
|
the open part of each C-shaped ring faces posteriorly toward the esophagus and is stand by a BLANK? with in the membrane are transverse smooth muscle fiber is called the BLANK?
|
fibromuscular membrane and trachealis muscle
|
|
|
|
at which thoracic vertebra does the trachea divided into right pulmonary bronchus and left pulmonary bronchus?
A. third thoracic vertebra B. fifth thoracic vertebra C. sixth thoracic vertebrae D. none of these |
at the level of the 5 thoracic vertebra |
|
|
|
what is the Carina?
A. the middle of the esophagus. B. part of the trachea rings C. where the trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi. D. part of the lung where the heart sits on the left side |
the Carina is the point where the trachea divides into left and right primary bronchi.
|
|
|
|
true of false
inflammation of the pleural membrane is called pleurisy/ pleuritis |
true
|
|
|
|
fluid accumulation in the pleura space is called?
A. pleuritis B. mediastinum C. alveolar pressure D. pleural effusion |
pleural effusion
|
|
|
|
in between the visceral and the parietal pleura is a space called What, which contains a small amount of lubricating fluid responsible for reducing friction during breathing?
|
pleura cavity
|
|
|
|
the broad inferior portion of the lung, the base, fits over the what? the narrow, superior, portion is the What!
|
diaphragm
apex |
|
|
|
the lung contains a What? through which, the bronchi, pulmonary vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter and excited?
A. hilum/hilus B. oblique / horizontal fissure C.pleuritis/pleurisy D. aveolus |
hilum or hilus
|
|
|
|
the left lung contains 2 parts for the heart what are they?
|
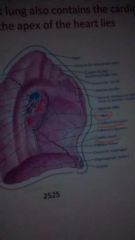
the cardiac notch and cardiac impression
|
|
|
|
fissures divide the lungs into lobes, how many and where are they what are there names?
|
the left Lung has 2 lobes and inferior and superior lobes.
the right lung has 3 lobes in inferior, meddle, and superior. |
|
|
|
the oblique and horizontal fissure?
|

|
|
|
|
the secondary bronchi give to tertiary bronchi, there are how many tertiary bronchi in each lung?
the segment of each lung tissue supplied by each tertiary bronchus is called? |
10 tertiary bronchi
bronchopulmonary segment |
|
|
|
each lobule is wrapped in elastic connective tissue and contains a lymphatic vessel and arterial, a venule and a branch from a blank?
|
terminal bronchiole
|
|
|
|
what are lobules and respiratory bronchioles
|
Each bronchopulmonary hookman has many small compartment called lobules.
Terminal bronchioles subdivide into a microscopic branches called respiratory bronchioles |
|
|
|
true or false?
around is shaped out housing lined by simple squamous epithelium and supported by sin elastic basement membrane? |
false
A cup shaped outpouching lined by simple squamous epithelium and supported by a thin elastic basement membrane. |
|
|
|
two or more alveoli that share a common opening?
A alveolus B. surfactant C. alveolar sac D. brochioles |
alveolar sac
|
|
|
|
Type 1 cells cuboidal cells with microvili secrete what? And the secretion does what?
|
Surfactant lower surface tension of alveolar are fluid produces alveolar collapse.
|
|
|
|
Phagocytes that removes fine dust particles and other debris from alveolar space?
A. respiratory membrane B. alveolar macrophages C. androgens D. proprioceptors |
alveolar macrophages dust particles
|
|
|
|
combined the alveolar and capillary walls where exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place by diffusion?
A. respiratory membrane B. alveolar sac C. Carina D. diaphragm |
Respiratory membrane
|
|
|
|
What for layers does the respiratory membrane consist of?
|
Player of type 1 and type 2 associated with alveolar macrophages known as the alveolar walls
An epithelial basement membrane A capillary basement membrane Capillary epithelium |
|
|
|
Perfusion coupling this is a process does what?
|
ventilation
|
|
|
|
the process of gas exchange in the body?
|
respiration
|
|
|
|
what are the three steps of respiration?
|
Pulmonary ventilation- inhalation and exhalation of air involves an exchange of air between the atmosphere in the alveoli of the lungs
External respiration - the exchange of gases between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries Internal respiration - the exchange of gas between the blood in the systemic capillaries and the tissue cells |
|
|
|
The pressure of a gas in a closed container is inversely proportional to the volume of the container
If the size of the container is increased the pressure of the gas inside of the container decreases If the size of the container is decreased the pressure of the gas inside the container increases? |
Boyle's law
|
|
|
|
what is a domed shaped skeletal muscle that forms the floor of the thoracic cavity; inverted by the phrenic nerves, supplies by the phrenic arteries?
A. elastic recoil B diaphragm C.lungs D. internal intercostal muscle |
diaphragm
|
|
|
|
The external intercostal muscles also help with the respiration and are responsible for the elevation of the ribs
accessory muscles of the forest inhalation include the SCM the scalene muscle and the pectoralis minor muscle what is this part of? |
inhalation-breathing in
|
|
|
|
The tendency for the chest wall and lung to spring back after they have been stretched?
A elastic recoil B exhalation C hypercapnia D atmospheric pressure |
Elastic recoil
|
|
|
|
atmospheric pressure?
|
pressure of the outside air; always 760 mmHg
|
|
|
|
Pressure between two pleural layers always sub atmospheric?
|
intrapleural pressure (inthrathoracic)
|
|
|
|
alveolar pressure?
|
pressure inside the lungs alveolar
pressure is less than atmospheric pressure during inhalation and more than atmospheric pressure during exhalation |
|
|
|
This causes the alveoli to assume the smallest possible diameter must be overcome to expand the long during inhalation responsible for two thirds of the elastic recoil of the lungs?
|
surface tension of alveolar fluids.
|
|
|
|
The amount of effort needed to stretch along and chest wall high compliance means the lungs and chest wall expand easily low compliance means for lungs and chest wall resist expansion?
True or false? |
true
|
|
|
|
Airway resistance - any condition that narrows or obstruct the airways decreases resistance so more pressure is required to achieve the same amount of air flow?
true or false? |
false
Airways resistance - any condition that narrows or obstruct the airway increases resistance so more pressure is required to achieve the same amount of air flow |
|
|
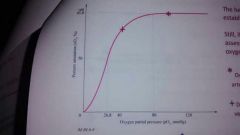
|

|
|
|
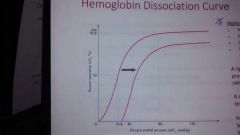
|

|
|
|
|
the greatest % of what gas is transported via bicarbonate ions?
|
CO2(70%)
|
|
|
|
how much of CO2 is dissolved in blood plasma?
how much is present in the blood as carbaminohemoglobin A 8%. A. 23% B 10%. B. 12% C 5%. C. 32% D 7%. D. 25% |
7% and 23%
|
|
|
|
as HCO3 is produced it can exchange with chloride ions into or out of RBC to maintain electrical balance between blood plasma and RBC cytosol? this is termed?
|
chloride shift
|
|
|
|
the lower the amount of oxyhemoglobin the higher the CO2 capacity in the blood, this is termed the?
|
haldane effect
|
|
|
|
Widely dispersed group of neurons responsible for respiratory regulation can be broken into three areas based on function?
|
respiratory center
|
|
|
|
controls the basic rhythm of respiration; broken down into the inspiratory area is what?
A. inspiratory area B. expiratory area C. medullary rhythmic area D. apneustic area |
medullary rhythmic area
|
|
|
|
Establishes the basic rhythm of breathing is what?
A. Inspiratory area B. Medullary rhythmic area C. Expiratory area D. Pneumotaxic area |
Inspiratory area
|
|
|
|
remains inactive during quiet breathing activated in forceful breathing out?
A. Medullary rhythmic area B. Inspiratory area C. Expiratory area D. apneustic area |
Expiratory area
|
|
|
|
helps turn off the inspiratory area before lungs become to full?
A. Pneumotaxic area B. apneustic area C. medullary rhythmic area D. Inspiratory area |
Pneumotaxic area
|
|
|
|
which of these send stimulator impulses to the inhalation area allowing deep inhalation?
A. Inspiratory area B. apneustic area C. Medullary rhythmic area D. Pneumotaxic area |
apneustic area
|
|
|
|
what is hypercapnia?
|
increase in arterial PCO2
|
|
|
|
chemoreceptors
central chemoreceptors - aortic bodies - carotid bodies - |
Central chemoreceptors - in or near the medulla - CNS
your body's - associated with arc of the aorta - PNS Carotid bodies - associated with the common carotid arteries - PNS |
|
|
|
what is the normal PCO2?
|
40 mmHg
|
|
|
|
what is hypocapnia?
|
decrease in arterial PCO2
|
|
|
|
Central and peripheral chemoreceptors are not typically stimulated with lower PCO2, meaning what?
|
The local area that it's all in moderation pace until normal levels are reached
|
|
|
|
baroreceptor reflex involved with the vagus nerve (cranial nerve 10) that prevents or installation of the lungs?
|
hering-breuer reflex
|
|
|
|
responsible for increases in breathing rate and breathing. During exercise?
|
proprioceptors
|
|

