![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nasal Cavity |
Hollow space in nose and skull lined with hairs and mucus membrane Filters air, warms it, moisturizes, before it gets to the lungs |
|
|
Pharynx |
Pathway for air (warms, moisturizes, filters) and food |
|
|
Larynx |
Houses vocal chords, manipulates pitch and volume, beneath pharynx |
|
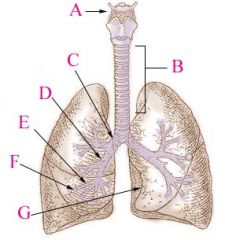
Trachea |
(windpipe) wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of lungs - provides airflow |
|
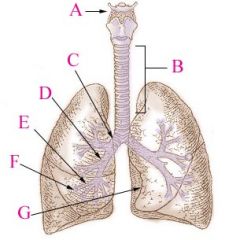
Primary Bronchi |
Conducts air to lungs (R & L), branch into smaller sections |
|
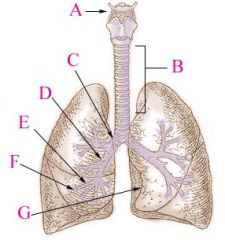
Secondary Bronchi |
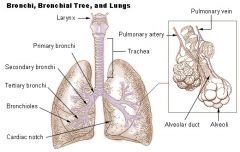
R main bronchus subdivides into 3 secondary bronchi, aka the lobar bronchi. L divides as well |
|
|
Alveoli Sac |
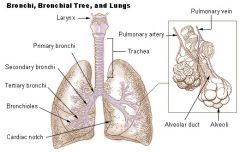
Contain pouches called alveoli |
|
|
Alveoli - what and where are they? What type of tissue is found in them? |
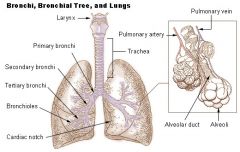
Hollow, cup shaped cavity surrounded by many tiny capillaries, lined with simple squamous epithelial cells - gas diffusion of o2 and co2 from blood stream |
|
|
Inspiration |
Inhalations |
|
|
Expiration |
Exhalation |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Dome shaped sheet of muscle and tendon that serves as main muscle of respiration |
|
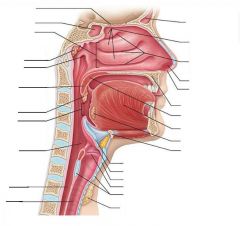
Nasopharynx |
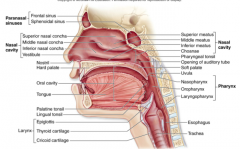
Psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelial tissue |
|
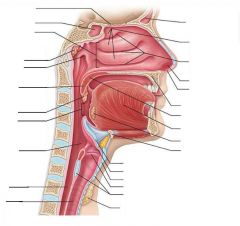
Oropharynx |
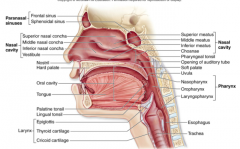
Passageway for food and air from level of soft palate to epiglottis -Lining of stratified squamous epithelium -isthmus of fauces - opening to oral cavity -palatine tonsils in lateral walls of fauces -lingual tonsil on posterior surface of tongue Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Describe the path of 02 in the respiratory system |
Air enters through the oral or nasal cavity, down the pharynx (includes naso, oro and laryngopharynx). These sections are posterior to the nasal cavity and back of the throat, and at the entrance to the larynx. From the Larynx, flows through the trachea, into R and L branches. Enters primary bronchii, then secondary, then tertiary, terminal bronchii, then bronchioles and and alveoli in alveolar sacs. |
|
|
Parietal Pleura |
The outer membrane which is attached to the inner surface of the thoracic cavity. Also separates the pleural cavity from the mediastinum. Innervated by the intercostal nerves and the phrenic nerve. Between the membranes is a fluid filled space called the pleuralcavity. |
|
|
Phrenic Nerve |
The phrenic nerve is a nerve that originates in the neck (C3-C5) and passes down between the lung and heart to reach the diaphragm. It is important for breathing, as it passes motor information to the diaphragm and receives sensory information from it. There are two phrenic nerves, a left and a right one. *If cut, cannot breath! |
|
|
Visceral Pleura |
The delicate serous membrane that covers the surface of each lung (the lung parenchyma) and dips into the fissures between the lobes. |
|
|
Oblique Fissure |
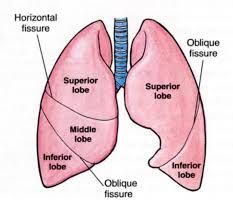
Divides the lung on both sides into upper and lower lobes. The upper lobe on the right is further subdivided by the horizontal fissure into definitive upper lobe - above the fissure - and middle lobe - below the fissure. The fissures extend from the surface of the lung to its hilum. Along this route, visceral pleura apposes visceral pleura. Both surfaces are smooth and separated by a layer of lubricant fluid. This allows individual lobes to move freely with respect to one another. |
|
|
Thyroid Cartilage |
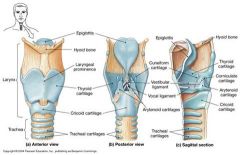
A large cartilage of the larynx, a projection of which forms the Adam's apple in humans. Made of Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Cricoid Cartilage |
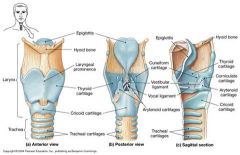
The ring-shaped cartilage of the larynx Made of Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Epiglottis |
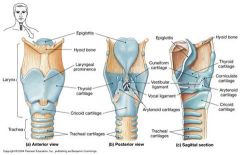
The epiglottis is a spoon shaped flap made of elastic cartilage tissue covered with a mucous membrane, attached to the entrance of the larynx choking prevention |
|
|
Cartilage Rings |
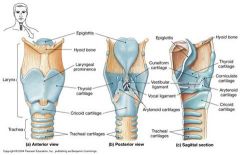
There are multiple c shaped cartilages, also known as tracheal cartilages. Made of Hyaline cartilage -Help support the trachea while still allowing it to move and flex during breathing |
|
|
Trachealis Muscle |
Smooth muscle that connects posterior parts of cartilage rings The primary function of the trachealis muscle is to constrict the trachea, allowing air to be expelled with more force, e.g., during coughing |
|
|
Mucosa |
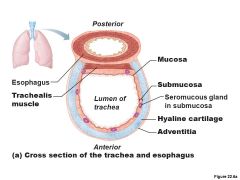
Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells |
|
|
Submucosa |
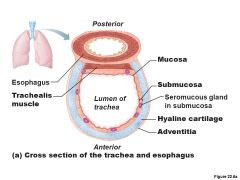
connective tissue with seromucous glands |
|
|
Adventitia |
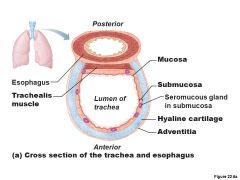
Outermost layer made of connective tissue; encase C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Carina |
Spar of cartilage on last, expanded tracheal cartilage point where trachea branches into two main bronchi |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage |
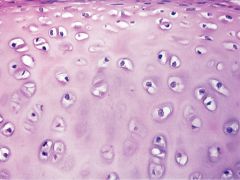
-Most abundant type of cartilage -supportive tissues in the nose, ears, trachea, larynx, and smaller respiratory tubes. Articularcartilage, meaning that it is found covering the articular surfaces of bones in synovial joints. |
|
|
What are the five basic functions of the respiratory system? |
1. Provide area for gas exchange between air and blood 2. Move air to and from the exchange surfaces of the lungs 3. Protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration or other environmental variations to prevent the invasion of pathogens 4. Produce sounds 5. Provide olfactory sensations to the CNS |
|
|
List the major organs of the Respiratory system |
-Nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses -Pharynx -Larynx -Trachea -Bronchi and their branches -Lungs and alveoli |
|
|
Laryngopharynx |
Found inferior to the oropharynx Passageway for food and air Posterior to upright epiglottis Extends to larynx, where continuous with esophagus Lined with stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Larynx - what does it attach to? |
Attaches to hyoid bone, opens into the laryngopharynx, continuous with trachea Functions -provides airway -Routes air and food into proper channels -Voice production - vocal chords found here |
|
|
How many cartilages in the Larynx? |
There are 9 total. All are hyaline other than the epiglottis, which is elastic cartilage. Need to know -Thyroid - adams apple -Cricoid - ring shaped -Epiglottis - govers laryngeal inlet when swallowing |
|
|
What are vestibular folds? |
False Vocal chords -superior to vocal chords -no part in sound production -helps to close glottis during swallowing |
|
|
What are vocal ligaments? |
Deep to laryngeal mucosa -Attach artenoid cartilages to thyroid cartilage -Contain elastic fibers -From core of vocal folds (true vocal cords) - Glottis-opening between vocal chords -Folds vibrate to produce sounds as air rushes up from lungs |
|
|
What is the Trachea? |
Windpipe - from larynx into mediastinum Wall composed of three layers -mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells -Submucosa - connective tissue with seromucuous glands -Adventitia - outermost layer made of connective tissue; encases C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage |
|
|
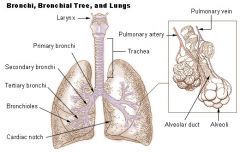
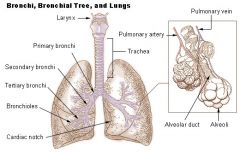
List the divisions of the bronchial tree: |
Trachea L and R branches of primary bronchus L and R branches of secondary bronchus L and R branches of Tertiary bronchus Bronchioles Terminal Bronchioles Respiratory Bronchiole Alveoli in a pulmonary lobule |
|
|
Respiratory Bronchiole |
Can be identified by the presence of some alveoli along their walls Splits into a number of alveolar ducts, which terminate in alveolar sacs and individual alveoli. |
|
|
What is the Apex of the lung? |
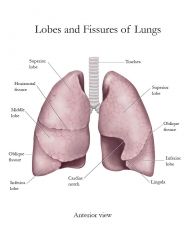
The superior tip, deep to clavicle |
|
|
What is the Base of the lung? |
Inferior surface; rests on diaphram |
|
|
What is the Hilum? |
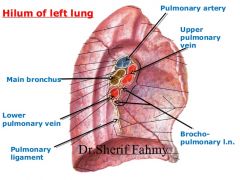
On mediastinal surface; site for entry/exit of blood vessels, bronchi, lymphatic vessels, and nerves |
|
|
Cardiac Notch |
Concavity for heart |
|
|
Secondary/Lobar bronchi |
Main branches of the brochus3 on right, 2 on left due to cardiac notch |
|
|
Tertiary/segmental bronchi |
Secondary/Lobar bronchi divide into these and then divide repeatedly, 8-10 |
|
|
How many alveoli in lungs? |
About 300 million |
|
|
What is Hemoglobin? How many O2 can a single Hemoglobin carry? |
Hemoglobin, or Hb, is a protein molecule found in red blood cells (erythrocytes) made of four subunits. Each hemoglobin molecule can bind to four oxygen molecules. |
|
|
How much Hemoglobin can each RBC carry? |
Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million of these hemoglobin molecules. |
|
|
What are defenses used in the respiratory |
Twisted, cilia, and mucous |
|
|
True vs False Vocal chords |
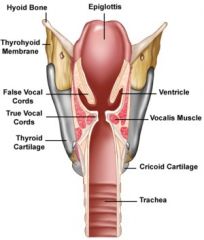
Above both sides of the glottis are the two vestibular folds or false vocal folds which have a small sac between them. |
|
|
What are the tissues composing the tracheal wall? |
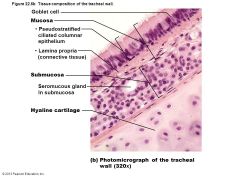
|
|
|
Terminal Bronchioles |
Lead to the respiratory bronchioles, which then leave to the alveolar duckts and then the outpocketings called alveoli |
|
|
Alveolus - how many in lungs total? What types of cells compose the sacs? |
~400 million total Wall is formed from two types of cells 1. alveolar type 1 cells, simple squamous - promotes diffusion of gases 2. Alveolar type 2 cells produce surfactant, decrease surface tension and prevent collapse cuboidal |
|
|
What cells are found inside the alveolus? |
Erythrocytes Macrophages (monocytes) Alveolar type II cells |
|
|
Pleural Fluid |
Fills slitlike pleural cavity Provides lubrications and surface tension, assists in expansion and recoil |

