![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the fxn of the Respiratory System? |
allow O2 into blood CO2 out of the blood vocalization smell odors carried in air pH balance regulation |
|
|
What are the organs of the Respiratory System? |
Nasal Cavities Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory Bronchioles Alveolar Sacs |
|
|
What is the fxn of nasal cavities? |
warm air (if needed) humidify clean air |
|
|
What tissues are made from Nasal Cavities? |
Pseudostratified Columnar ET with Cilia Goblet Cells (make mucus)
Same as Trachea |
|
|
What tissues are made from Pharynx? |
Pseudostratified ET Stratified Squamous ET |
|
|
What is the fxn of Larynx? |
Vocal cords - produce sound, speech Conducting Air |
|
|
What is the Epithelial lining of Larynx? |
Nonkeratinizied stratified squamous ET Pseudostratified ciliated columnar ET |
|
|
What supports the wall of Larynx? |
9 pieces of cartilage |
|
|
What is the function of Trachea (windpipes)? |
Conduct Air |
|
|
What epithelial lining is in Trachea? |
Pseudostratified ciliated Columnar Epithelium Goblet Cells (mucus)
same as Nasal Cavity |
|
|
What supports the wall of Trachea? |
C-shaped cartilage rings (hyaline cartilage) open nends of C-shaped cartilage = trahcealis muscle |
|
|
What is the fxn of trachealis muscle? |
relax (expands esophagus during swallowing, accommodate large materials) contract (coughing) -reduce trachea diameter |
|
|
What is the fxn of tracheal gland? |
Mucus Production |
|
|
What is the fxn of the C-shaped cartilages in Trachea? |
Prevent trachea from collapsing Reinforce and provide some rigidity to trachea wall, to ensure it remain open all times |
|
|
Where does air travel after Trachea? |
Bronchi Primary Bronchus (right and left) Secondary Bronchi (Right = 3) (Left = 2) |
|
|
Which lung is smaller and why? |
The left lung is smaller because the heart is located on the Left. (2 lobe) |
|
|
What are bronchioles? |
division of smaller tubules from bronchi |
|
|
What are the epithelium lining of bronchioles? |
Simple Columnar Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Do bronchioles have cartilage? |
NO, smaller diameter prevents collapse Have thicker smooth muscle than bronchi = help regulate airway constriction / dialation |
|
|
What comes after bronchioles? |
Respiratory Bronchioles |
|
|
What is the wall support of Bronchioles? |
No cartilage, more smooth muscle |
|
|
What is the epithelial lining of Bronchioles? |
Simple Columnar (larger) or Simple Cuboidal (smaller) ET |
|
|
What is the fxn of bronchioles? |
Conduct Air: smooth muscle in walls allow bronchoconstriction and brochodialtion |
|
|
What is the wall support of respiratory bronchioles? |
No cartilage smooth muscle is scarce |
|
|
What is the epithelial lining of Respiratory bronchioles? |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
What is the fxn of respiratory bronchioles? |
Respiratory: Gas Exchange |
|
|
What makes up the alveolar sacs? |
Alveolar duct and alveoli |
|
|
What is the fxn of alveolar ducts? |
Respiratory: Gas Exchange
|
|
|
What is the wall support of alveolar ducts? |
No cartilage, no smooth muscle |
|
|
What is the epithelial lining of Aveolar Ducts? |
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
What is the fxn of Alveoli? |
Respiratory: Gas Exchange |
|
|
What is the wall support of Alveoli? |
No Cartilage No smooth muscle |
|
|
What is the epithelial lining of Alveoli? |
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
What are the two cell types formed in the alveolar wall? |
1. Alveolar Type 1 Cell 2. Alveolar Type 2 Cell |
|
|
Which alveolar cells secrete surfactant? |
Alveolar Type 2 Cells |
|
|
What is the fxn of surfactant? |
fluid (lipid and proteins)COATs inner alveolar surface to reduce surface tension, prevent collapse of alveoli = decrease work of breathing |
|
|
What is the fxn of Alveolar Type I Cells? |
promotes rapid gas diffusion across alveolar wall |
|
|
What is site of gas exchange with capillaries? |
Alveoli |
|
|
What contains vocal cords? |
Larynx |
|
|
What is a "lid" that covers glottis? |
Epiglottis |
|
|
Common passageway for food, air, water |
Pharynx |
|
|
Connects Larynx to Primary Bronchi |
Trachea |
|
|
Warms, moistens, filters incoming air |
Nasal Cavity |
|
|
Bronchus (Bronchi) |
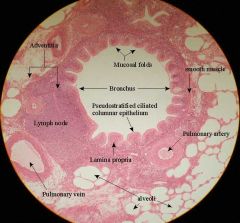
Pseudostratified columnar w/ cilia
Simple columnar w/cilia |
|
|
Bronchioles |
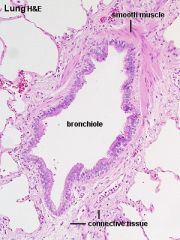
Simple Columnar Simple Cuboidal |
|
|
Respiratory Bronchiole |
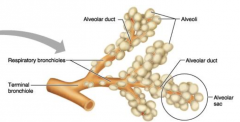
Simple Cuboidal |
|
|
alveolar sac alveolar duct alveoli |
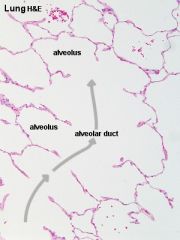
Simple Squamous ET |
|
|
Which vein is most commonly used for venipuncture (drawing blood or injection)? |
Median Cubital Vein |
|
|
Which organs receive blood from superior and inferior mesenteric arteries? |
Small and Large Intestine |
|
|
Which organ receive blood from celiac trunk? |
Liver Stomach Spleen |
|
|
What are the bulges that appear on the veins of the lower limb? |
Venous valves |

