![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. What are the 2 types of respiration? b. Describe each kind |
a. - Cellular - External b. Cellular: Intracellular metabolic process Derive energy from nutrient molecules Uses O2 + produces CO2 External: Sequence of events Exchange of O2 + CO2 between environment and cellular tissues |
|
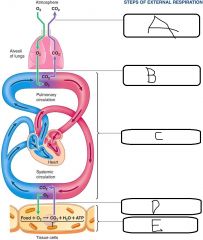
|
a. Gas exchange between atmosphere and alveoli in lungs b. Gas exchange between air in alveoli and blood in pulmonary capillaries c. Transport of O2 + CO2 by the blood between the lungs and the tissues d. Gas exchange between blood in systemic capillaries and tissue cells e. Cellular respiration |
|
|
Name 3 non-respiratory functions of the respiratory system |
- Acid-base balance (rate of ventilation>regulate CO2 - Defense against infection (cilia, mucus etc) - Respiratory pump - Nose (organ of smell) - Thermoregulation (route for water loss + heat elimination) |
|
|
Name the 3 components of the respiratory system |
- Airways - Lungs - Respiratory muscles |
|
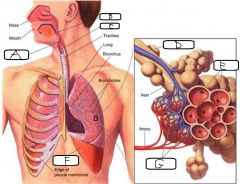
|
a. Epiglottis b. Pharynx c. Larynx d. Bronchiole e. Alveoli f. Diaphragm g. Capillaries |
|
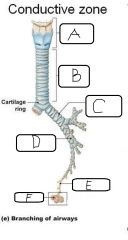
|
a. Larynx b. Trachea c. Left primary bronchus d. Secondary bronchus e. Bronchiole f. Alveoli |
|
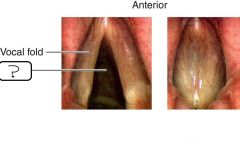
|
Glottis |
|
|
- The larynx is also known as the __(a)__ - The laryngeal opening is the __(b)__ - Sounds are made via vocal folds __(c)__ as a result of __(d)__ moving past them |
a. Voice box b. Glottis c. Vibrating d. Air |
|
|
a. Name 2 differences between Trachea/larger bronchi and smaller bronchioles b. What are smaller bronchioles innervated by? c. What are smaller bronchioles sensitive to? d. What is the functional significance of the properties of both Trachea/larger bronchi and smaller bronchioles? |
a. - Trachea/larger bronchi are non-muscular and are in cartilaginous rings - Smaller bronchioles have Smooth Muscle and have no cartilage b. Autonomic NS c. Hormones and Local Chemicals d. - Trachea/larger bronchi: Always stay open - Smaller bronchioles: Regulate airflow to each cluster of alveoli |
|
|
- Alveoli are thin-wall, inflatable __(a)__ encircled by __(b)__ - Alveolar walls are made up of a single layer of __(c)__ - __(d)__ forms a thin barrier between alveoli and pulmonary capillaries |
a. air sacs b. Pulmonary capillaries c. Type I alveolar cells d. Interstitial space |
|
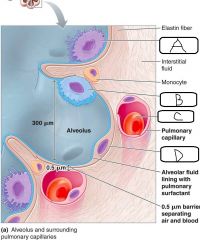
|
a. Alveolar Macrophage b. Type II alveolar cell c. Erythrocyte d. Type I alveolar cell |
|
|
- Alveolar type II cells account for __(a)__% of alveolar epithelium - These cells secrete a pulmonary surfactant called __(b)__ which facilitates __(c)__ |
a. 5% b. Phospholipoprotein complex c. Lung expansion |
|
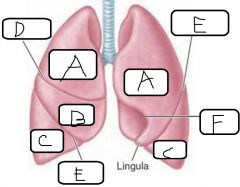
|
a. Superior lobe b. Middle lobe c. Inferior lobe d. Horizontal fissure e. Oblique fissure f. Cardiac notch |
|
|
a. Name 5 structures which occupy the thoracic cavity - The outer chest wall is also called the __(b)__ - Inside the (b) there are __(c)__ ribs which join anteriorly to the __(d)__ and posteriorly to the __(e)__ - The __(f)__ forms the floor of the thorax |
a. - Lungs - Heart - Oesophagus - Blood vessels -Nerves - Thymus b. Thorax c. 12 d. Sternum e. Thoracic vertebra f. Diaghragm |
|
|
- A __(a)__ separates lungs from thoracic wall and other structures - It is double-walled, the interior is called the __(b)__ - __(c)__ is the name of the condition where the (a) is inflammed |
a. Pleural sac b. Pleural cavity c. Pleurisy |
|
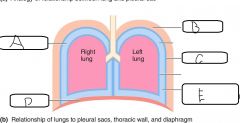
|
a. Pleural cavity b. Thoracic wall c. Parietal pleura d. Diaphragm e. Pleural cavity with intrapleural fluid |
|
|
__(a)__ pleura closely adheres to surface of lung __(b)__ pleura lines interior surface of thoracic wall |
a. Visceral b. Parietal |
|
|
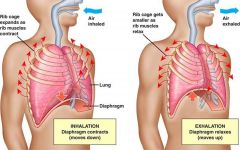
a. When activated, what do inspiratory muscles do? b. Name 2 inspiratory muscles |
a. Inspiratory muscles enlarge the thoracic cavity (when activated) b. - Diaphragm - External Intercostal muscles |
|
|
a. Which nerve supplies the diaphragm? b. What happens to the shape of the diaphragm when it contracts? c. When the diaphragm contracts, what happens to the vertical dimension of the thoracic cavity? |
a. Phrenic nerve b. Diaphragm flattens c. Increase in vertical dimension |
|
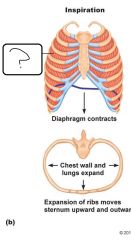
|
External Intercostal Muscles |
|
|
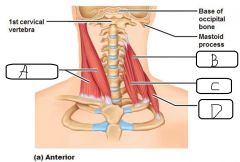
a. Sternocleidomastoid b. Middle Scalene c. Anterior Scalene d. Posterior Scalene |
|
|
- Expiration at rest is a __(a)__ process - Inspiration muscles are __(b)__ - Elastic properties of lung allow it to __(c)__ |
a. Passive b. Inactive c. Recoil |
|
|
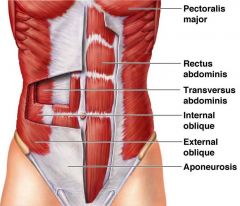
- In active expiration, lungs are emptied __(a)__ - The __(b)__ muscles are the most important expiration muscles - These include __(c)__ and __(d)__ - The other type of expiratory muscles the __(e)__ |
a. More quickly and forcefully b. Abdominal muscles c. Rectus abdominis d. Internal/External obliques e. Internal Intercostal (IC) muscles |
|
|
|

