![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is breathing? |
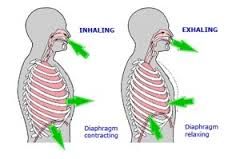
The process of the exchange of air between the lungs and the environment, including inspiration and expiration. |
|
|
What is the membrane where the diffusion of oxygen and other gases occurs between the living cells of the body and the external environment called? |
The respiratory membrane. |
|
|
What is respiration? |
All processes involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between cells and the environment, including breathing, gas exchange, and cellular respiration. |
|
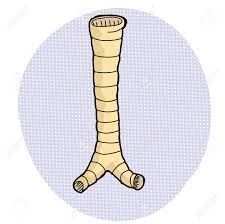
What is the windpipe known as? |
The trachea |
|

What are the tiny hairlike structures found on some cells that sweep away foreign debris called? |
Cillia |
|
|
What is the epiglottis? |
The structure that covers the opening of the trachea during swallowing. |
|
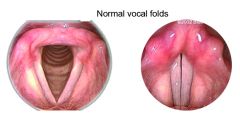
What is the voice box known as? |
The larynx. |
|
|
What are the bronchi? |
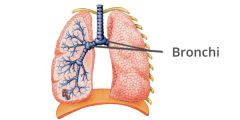
The passages from the trachea to the left and right lung. |
|
|
What are the smallest passageways of the respiratory tract? |
The bronchioles. |
|
|
What are the alveoli? |
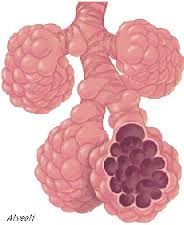
Sacs of the lung in which gas exchange occurs. |
|
|
What is the thin membrane that surrounds the outer surface of the lungs and lines the inner wall of the chest cavity? |
The pleural membrane. |
|
|
What is the diaphragm? |
A sheet of muscle that separates the organs of the thoracic cavity from those of the abdominal cavity. |
|
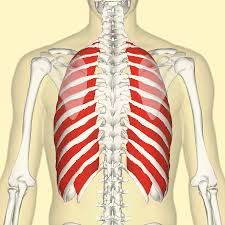
What are the muscles that raise and lower the rib cage called? |
Intercostal muscles. |
|
|
What is hemoglobin? |
The oxygen-carrying molecule in red blood cells. |
|
|
What is hemoglobin bound to oxygen called? |
Oxyhemoglobin |
|
|
What is carbonic anhydrase? |
An enzyme found in red blood cells that speeds the conversion of carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid. |
|
|
What is a substance capable of neutralizing acids and bases, thus maintaining the original pH of the solution called? |
A buffer. |
|
|
What is a chemoreceptor? |
A specialized nerve receptor that is sensitive to specific chemicals. |
|
What is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes called? |
Bronchitis |
|
|
What is emphysema? |
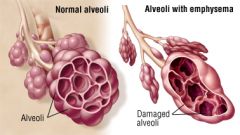
A respiratory disorder characterized by an overinflation of the alveoli. |
|
|
What is a respiratory disorder characterized by reversible narrowing of the bronchial passages known as? |
Bronchial asthma |
|
|
What is cardiac muscle? |
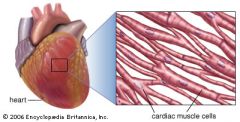
The involuntary muscle of the heart. |
|
|
What is the involuntary muscle found in the lining of many organs? |
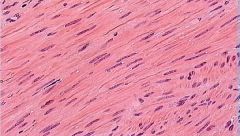
Smooth muscle |
|
|
What is skeletal muscle? |
The voluntary muscle that makes the bones of the skeleton move. |
|
|
What is a band of connective tissue that joins muscle to bone called? |
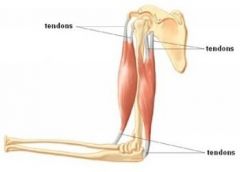
A tendon. |
|
|
What are antagonistic muscles? |
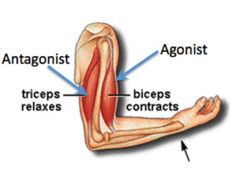
A pair of skeletal muscles that are arranged in pairs and that work against each other to make a joint move. |
|
|
What is the muscle that must contract to bend a joint called? |
A flexor |
|
|
What is an extensor? |
The muscle that must contract to straighten a joint. |
|
|
What is the delicate sheath that surrounds the muscle fibres called? |
Sarcolemma |
|
|
What is a myofilament? |
A thread of contractile proteins found within muscle fibres. |
|
|
What is the compound in muscle cells that releases a phosphate to ADP and helps regenerate ATP supplies in muscle cells? |
Creatine phosphate |
|
|
What is summation? |
Increased muscle contraction produced by the combination of stimuli. |
|
|
What is the state of constant muscle contraction cased by sustained nerve impulses called? |
Tetanus |

