![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
No exchange of gases occurs here. |
Segmental bronchi |
|
|
Secrete a fluid containing surfactant. |
Type Il cells |
|
|
Where the respiratory zone of the lungs begins. |
Respiratory bronchioles |
|
|
Composed of simple squamous epithelium. |
type l cells |
|
|
Terminates in alveoli. |
Alveolar duct |
|
|
Composed of cuboidal cells. |
Type Il cells |
|
|
The respiratory membrane is composed of fused basement membrane of the capillary walls and ________. |
type l cells |
|
|
TV + IRV + ERV + RV |
total lung capacity |
|
|
ERV + RV |
Functional residual capacity |
|
|
TV + IRV + ERV |
vital capacity |
|
|
TV + IRV |
inspiratory capacity |
|
|
The main site of gas exchange is the ________. |
aveoli |
|
|
The loudness of a person's voice depends on the ________. |
Force with which air brushes across the vocal folds |
|
|
Complete the following statement using the choices below. Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is ________. |
greater than the preassure in the atmosphere |
|
|
Type II alveolar cells secrete ________. |
surfactant |
|
|
The law of partial pressure is called ________ law. |
Dalton's |
|
|
The law that applies to the amount of CO2 you could dissolve in a Pepsi is called ________ law. |
Henry's |
|
|
The Bohr effect refers to the unloading of ________ in a RBC due to declining pH. |
oxygen |
|
|
A disorder characterized by permanent enlargement of the alveoli accompanied by destruction of the alveolar walls is ________. |
emphysema |
|
|
The cartilaginous flap that closes the trachea during swallowing is called the ________. |
epiglottis |
|
|
The archway in the back of the throat is called the ________. |
isthmus of the fauces (oropharynx) |
|
|
Terminal bronchioles are lined with ________ epithelium. |
cuboidal |
|
|
Air and food are routed into the proper channels by the ________. |
C) larynx |
|
|
The loudness of a personʹs voice depends on ________. |
D) the force with which air rushes across the vocal folds |
|
|
The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, type I and type II. The function of type II is ________. |
A) to secrete surfactant |
|
|
After the segmental (tertiary) bronchus, the next smaller branch of the respiratory passageway is (are) the ________. |
A) terminal bronchioles |
|
|
The smallest macroscopic subdivision of the lung is the ________. |
A) lobule |
|
|
The pleurae are vital to the integrity of the lungs because ________. |
D) they produce a lubricating serous secretion, allowing the lungs to glide over the thorax wall during breathing |
|
|
Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________. |
B) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs |
|
|
The relationship between the pressure and volume of gases is given by ________. |
A) Boyleʹs law |
|
|
The statement, ʺin a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the individual partial pressures of gases in the mixtureʺ paraphrases ________. |
C) Daltonʹs law |
|
|
Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________. |
C) interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid |
|
|
For gas exchange to be efficient, the respiratory membrane must be ________. |
B) 0.5 to 1 micrometer thick |
|
|
With the Bohr effect, more oxygen is released because ________. |
B) a decrease in pH (acidosis) weakens the hemoglobin-oxygen bond |
|
|
The most powerful respiratory stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is ________. |
B) increase of carbon dioxide |
|
|
Nerve impulses from ________ will result in inspiration. |
A) the ventral respiratory group |
|
|
In the plasma, the quantity of oxygen in solution is ________. |
A) only about 1.5% of the oxygen carried in dissolved form |
|
|
Which of the following statements is incorrect? A) During fetal life, lungs are filled with fluid. B) Respiratory rate is lowest in newborn infants. C) Descent of the diaphragm results in abdominal breathing. D) The chest wall becomes more rigid with age. |
B) Respiratory rate is lowest in newborn infants. |
|
|
Another name for the inflation reflex is ________. |
C) Hering-Breuer |
|
|
Which of the following does not influence the increase in ventilation that occurs as exercise is initiated? A) psychic stimuli B) decrease in lactic acid levels C) proprioceptors D) simultaneous cortical motor activation of the skeletal muscles and respiratory center |
B) decrease in lactic acid levels |
|
|
Which of the following is not a form of lung cancer? A) adenocarcinoma B) Kaposiʹs sarcoma C) small cell carcinoma D) squamous cell carcinoma |
B) Kaposiʹs sarcoma |
|
|
Which of the following is not an event necessary to supply the body with O2 and dispose of CO2? A) pulmonary ventilation B) blood pH adjustment C) internal respiration D) external respiration |
B) blood pH adjustment |
|
|
Which of the following is not true of the respiratory tract from the medium bronchi to the alveoli? A) Cartilage gradually decreases and disappears at the bronchioles. B) Resistance to air flow increases due to the increase in cross-sectional diameter. C) Proportionally, smooth muscle decreases uniformly. D) Lining of the tubes changes from ciliated columnar to simple squamous epithelium in the alveoli. |
B) Resistance to air flow increases due to the increase in cross-sectional diameter. |
|
|
Which of the following determines lung compliance? A) airway opening B) flexibility of the thoracic cage C) muscles of inspiration D) alveolar surface tension |
D) alveolar surface tension |
|
|
Tidal volume is air ________. |
B) exchanged during normal breathing |
|
|
The ideal vital capacity of an individual is around ________. |
C) 4800 ml |
|
|
Possible causes of hypoxia include ________. |
A) too little oxygen in the atmosphere |
|
|
The lung volume that represents the total volume of exchangeable air is the ________. |
B) vital capacity |
|
|
Since the lungs are filled with fluid during fetal life, which of the following statements is true regarding respiratory exchange? A) Respiratory exchanges are made through the ductus arterioles. B) Respiratory exchanges are not necessary. C) Respiratory exchanges are made through the placenta. D) Since the lungs develop later in gestation, fetuses do not need a mechanism for respiratory exchange. |
C) Respiratory exchanges are made through the placenta |
|
|
Which of the following is not a stimulus for breathing? A) rising carbon dioxide levels B) rising blood pressure C) arterial Po2 below 60 mm Hg D) arterial pH resulting from CO2 retention |
B) rising blood pressure |
|
|
Respiratory control centers are located in the ________. |
B) medulla and pons |
|
|
The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is called ________. |
C) inspiratory capacity |
|
|
Which statement about CO2 is incorrect? A) Its concentration in the blood is decreased by hyperventilation. B) Its accumulation in the blood is associated with a decrease in pH. C) More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs. D) CO2 concentrations are greater in venous blood than arterial blood. |
C) More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs. |
|
|
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs and through all cell membranes by ________. |
B) diffusion |
|
|
Select the correct statement about the pharynx. A) The pharyngeal tonsil is located in the laryngopharynx. B) The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx. C) The laryngopharynx blends posteriorly into the nasopharynx. D) The palatine tonsils are embedded in the lateral walls of the nasopharynx |
B) The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx. |
|
|
The larynx contains ________. |
A) the thyroid cartilage |
|
|
Which respiratory-associated muscles would contract if you were to blow up a balloon? A) diaphragm would contract, external intercostals would relax B) internal intercostals and abdominal muscles would contract C) external intercostals would contract and diaphragm would relax D) diaphragm contracts, internal intercostals would relax |
B) internal intercostals and abdominal muscles would contract |
|
|
The oropharynx does not include ________. |
D) pharyngeal tonsils |
|
|
Which of the following is not found on the right lobe of the lung? A) middle lobe B) cardiac notch C) horizontal fissure D) oblique fissure |
B) cardiac notch |
|
|
Impairments of oxygen transport include ________. |
B) carbon monoxide poisoning, a form of hypoxemic hypoxia |
|
|
Which of the following correctly describes mechanisms of CO2 transport? A) 20% of CO2 is dissolved directly into the plasma. B) 7-8% of CO2 is carried in the form of carbaminohemoglobin. C) The chloride shift mechanism enhances CO2 transport. D) Carbonic anhydrase is responsible for bonding CO2 to hemoglobin. |
C) The chloride shift mechanism enhances CO2 transport. |
|
|
Factors that influence the rate and depth of breathing include ________. |
B) voluntary cortical control |
|
|
Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for gas exchange? A) alveolar sacs B) alveoli C) respiratory bronchioles D) alveolar ducts |
B) alveoli |
|
|
The respiratory membrane is a combination of ________. |
B) alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes |
|
|
Gas emboli may occur because ________. |
B) a diver holds his breath upon ascent |
|
|
Inspiratory capacity is ________. |
A) the total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration |
|
|
Which center is located in the pons? A) pontine respirator group (PRG) B) expiratory C) inspiratory D) pacemaker neuron center |
A) pontine respirator group (PRG |
|
|
The nose serves all the following functions except ________. |
B) as the initiator of the cough reflex |
|
|
A premature baby usually has difficulty breathing. However, the respiratory system is developed enough for survival by ________. |
C) 28 weeks |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true regarding the respiratory rate of a newborn? A) The respiratory rate of a newborn is slow. B) The respiratory rate of a newborn varies between male and female infants. C) The respiratory rate of a newborn is approximately 30 respirations per minute. D) The respiratory rate of a newborn is, at its highest rate, approximately 40-80 respirations per minute. |
D) The respiratory rate of a newborn is, at its highest rate, approximately 40-80 respirations per minute |
|
|
Select the correct statement about the neural mechanisms of respiratory control. A) The pons is thought to be instrumental in the smooth transition from inspiration to expiration. B) The dorsal respiratory group neurons depolarize in a rhythmic way to establish the pattern of breathing. C) The pontine respirator group (PRG) continuously stimulates the medulla to provide inspiratory drive. D) The ventral respiratory group is contained within the pons. |
A) The pons is thought to be instrumental in the smooth transition from inspiration to expiration. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is correct? A) H+ acts directly on central chemoreceptors to decrease the rate and depth of breathing. B) Low arterial pH is the most powerful stimulator of respiration. C) Arterial pH does not affect central chemoreceptors directly. D) H+ has little effect on the blood pH. |
C) Arterial pH does not affect central chemoreceptors directly. |
|
|
The factors responsible for holding the lungs to the thorax wall are ________. |
D) surface tension from pleural fluid and negative pressure in the pleural cavity. |
|
|
The erythrocyte count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because ________. |
D) the concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes |
|
|
Most inspired particles such as dust fail to reach the lungs because of the ________. |
A) ciliated mucous lining in the nose |
|
|
Which of the following is not possible? A) Gas flow equals pressure gradient over resistance. B) Pressure gradient equals gas flow over resistance. C) Resistance equals pressure gradient over gas flow. D) The amount of gas flowing in and out of the alveoli is directly proportional to the difference in pressure or pressure gradient between the external atmosphere and the alveoli. |
B) Pressure gradient equals gas flow over resistance |
|
|
Select the correct statement about the physical factors influencing pulmonary ventilation. A) A decrease in compliance causes an increase in ventilation. B) A lung that is less elastic will require less muscle action to perform adequate ventilation. C) As alveolar surface tension increases, additional muscle action will be required. D) Surfactant helps increase alveolar surface tension. |
C) As alveolar surface tension increases, additional muscle action will be required. |
|
|
Select the correct statement about oxygen transport in blood: A) During normal activity, a molecule of hemoglobin returning to the lungs carries one molecule of O2 B) During conditions of acidosis, hemoglobin is able to carry oxygen more efficiently C) Increased BPG levels in the red blood cells enhance oxygen-carrying capacity D) A 50% oxygen saturation level of blood returning to the lungs might indicate an activity level higher than normal |
D) A 50% oxygen saturation level of blood returning to the lungs might indicate an activity level higher than normal |
|
|
Which of these is not a characteristic of emphysema? A) bronchial edema B) destruction of alveolar walls C) loss of lung elasticity D) air trapping |
A) bronchial edema |
|
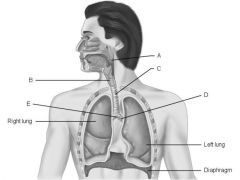
match the following: 1) Main (primary) bronchus. 2) Pharynx. 3) Larynx. 4) Carina of trachea. 5) Trachea. |
Answers: 1) Main (primary) bronchus. D 2) Pharynx. A 3) Larynx. B 4) Carina of trachea.E 5) Trachea.C |
|
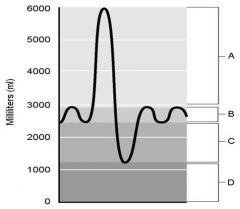
6) Tidal volume. 7) Inspiratory reserve volume. 8) Residual volume. 9) Expiratory reserve volume. 10) Air that does not participate in the exchange of gases. |
6) b 7) a 8) d 9) c 10) d |

