![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give e.g of obstructive lung dx |
COPD (chronic bronchitis + emphysema)
Asthma
Bronchiectasis |
|
|
What is chronic bronchitis ?
-pathology -Criteria |
-Mucous gland hypertrophy - due to chronic irritation from smoking
I.e "blue bloaters"
Criteria: productive cough > 3months over 2 years |
|
|
What is Emphysema ?
Is it reversible or irreversible ? |
-Imbalance of proteases/antiproteases -> destruction of alveoli
i.e "pink puffers"
irreversible
|
|
|
for COPD describe the
S/S Ix Rx
|
S/S: Constant productive cough, SOB, wheeze, recurrent pneumonia , Blue bloaters ( cyanosis), Pink puffers ( barrel chest+ hyperresonant)
Ix: Spirometry, CXR, FBC
Rx: 1st: Salbutamol or ipratropium. 2nd: Salmeterol or tiotropium. 3rd: ADD beclomethasone to the salmeterol . 4th: Salmeterol + tiotropium + beclomethasone
|
|
|
What are the complications of COPD ? |
Type II resp. failure
Recurrent infections
Cor pulmonale
Bullae
Polycythemia
CANCER |
|
|
How else should you manage COPD ? (other than Rx) |
Home O2 therapy
Chest physiotherapy
Smoking cessation advice
pneumovax + Influenza vaccinations
N-acetylcysteine (mucolytic) |
|
|
In an acute exacerbation of COPD
-What is the commonest organism? -Ix -Rx |
HiB - following a URTI
Ix: Sputum culture, CXR , FBC/ABG ect..
Rx: (SOPIA) -Salbutamol -O2 -Prednisolone PO or IV hydrocortisone -ABx prophylaxis -amoxicillin |
|
|
What is the definition of asthma |
recurrent reversible airway obstruction |
|
|
For asthma
-what is the type of HSR ? (describe what is involved) -Subtypes -Associations
-What does it consist of (triad of..)? |
-TYpe I HSR -IgE, eosinophils, mast cells, basophils
Subtypes: Atopic & non-atopic (exercise/infection/ASA induced)
Associations: Atopy (eczema + hayfever/rhinitis) & Samter's triad ( ASA insensivitiy+ nasal polyps)
triad of : hyperresponsiveness, reversible obstruction, Airway inflammation |
|
|
For asthma, describe the
S/S Ix
|
S/S: Episodic wheeze, dry cough, diurnal variation , triggering factors , Better w/ salbutamol
Ix: peak flow/ spirometry Skin prick test/Rast testing Provocation test (give methalcoline - then improvement w/ salbutamol) Bronchoscopy + lavage (looking for eosinophils
|
|
|
What is the Rx for Asthma |
1st. Salbutamol 2nd. INH beclomethasone 3rd -Salmeterol (Nocturnal) -Increase beclomethasone
-Antihistamines -Antimuscarinics (NEB ipratropium/tiotropium) -Anti leukotrienes (PO Monteleukast) ( for allergy/exercise)
Prophylactic -Sodium chromoglycate - for children -Xanthines (PO Aminophylline) - SIDE EFFECTS -Omalizumab
4th- PO prednisolone |
|
|
What is the Rx of acute exacerbation of asthma (describe administration method) |
(OSHIAM)
O2 Salbutamol NEB Hydrocortisone IV Ipratropium NEB Aminophylline PO Mg sulphate |
|
|
What are the side effects of β agonist ? |
Tachycardia
tremor |
|
|
What are the side effects of Xanthines (aminophylline/theophylline) |
Cardiotoxicity , Arrhythmias
Seizures
GI S/S
requires regular monitoring |
|
|
Which prophylactic asthma Rx is used for children ( as a steroid sparring agent) |
Sodium Chromoglycate |
|
|
What are the symptomatic relievers of Asthma? |
Beta-agonist
Antileukotrienes
Antimuscarinics
Antihistamines
Xanthines |
|
|
What are the prophylactic agents for asthma ? |
Beclomethasone
Sodium chromoglycate
Xanthines |
|
|
What is Bronchiectasis ?
Caused by? S/S? Ix? Rx?
management? |
Chronic dilatation of bronchioles --> recurrent infection
Caused by: CF, Kartagener's syndrome , TB
S/S: Copious sputum ,hemoptysis , Clubbing , recurrent pneumonia
Ix: CXR , CT - shows dilated bronchioles
Rx: Prophylactic ABx, SABA, beclomethasone , ? mucolytics
management: chest physio, Smoking cessation, vaccinations (pneumovax + influenza)
|
|
|
What vaccinations should ppl with bronchiectasis/COPD receive ? |
Pneumovax influenza |
|
|
Give e.g of restrictive lung diseases |
Chest wall abnormalities: obesity, neurogenic
ARDS/NRDS
Interstitial lung dx: Idiopathic fibrosis, Pneumoconiosis, Vasculitis', Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, Sarcoidosis |
|
|
What is Neonatal RDS ?
-Risk factor -Ix -Rx
-Complications |
Decreased surfactant production -> alveolar collapse
Risk factor: C-section, maternal DM (insulin decreases surfactant) , prematurity
Ix: lecithin sphingomyelin ratio (normal > 2)
Rx: Artificial surfactant + O2
Complications: PDA (giving supplemental O2 --> retinopathy of prematurity, Bronchopulmonary dysplasia) |
|
|
How do you prevent neonatal RDS ? |
If risk of preterm delivery then give 2xINJ betamethasone within 12 hrs
B/w 24-34 weeks gestation |
|
|
What is ARDS ?
-Criteria ? -Complications |
Injury to lung parenchyma
Criteria: Acute + bilateral infiltrates + resistant Hypoxemia + no signs of CHF
Complications: Fibrosis , resp. failure |
|
|
What type of HSR is interstitial lung dx mostly ?
-What is the characteristic pathological finding ? |
Type IV HSR - w/ granuloma formation |
|
|
What are the subtypes of interstitial lung dx ? |
-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis -Pneumoconiosis -Hypersensitivity pneumonitis -Sarcoidosis (fibrosis) -TB (caseating granulomas) |
|
|
What are the S/S of interstitial lung dx? |
Gradual dry cough & SOB
Crackles (w/ fluid/fibrosis)
Clubbing -w/ fibrosis |
|
|
What are the Ix of interstitial lung dx ? |
-CXR: bilateral infiltrates
-CT: shows Ground glass appearance , Honeycombing , nodules (w/ pneumoconiosis/TB)
-Pulmonary function test: ↓TLCO |
|
|
What is the general Rx for interstitial lung dx |
PO Steroids
O2
immunosuppressants |
|
|
what is acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis ?
Risk factors ? S/S? ix? |
Allergen triggering interstitial inflammation
Risk factors: Bird owners, farmers
S/S : Dry cough , SOB, Crackles ( within a few hrs of exposure!)
Ix: CXT ; shows alveolar infiltrates , CT , precipitins/IgG serology
|
|
|
What is Chronic HSR pneumonitis? |
Chronic exposure of allergen --> fibrosis
S/S: dry cough, SOB,Crackles, Clubbing . Hypoxia
Ix: CT shows honeycombing |
|
|
Picture of HSR pneumonitis showing bialteral infiltrates . |
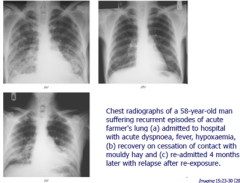
|
|
|
What is the Rx for idiopathi pulmonary fibrosis ? |
Supportive !
O2 Chest physio |
|
|
for Sarcoidosis ,
-Who is it classically found in ? -Characteristics?
|
Afrocaribbean women
(GRUELIN-CNS) Granuloma - non caseating RA- arthritis/arthralgia Uveitis Erythema nodosum Lung infiltrates - bilateral hilar Interstitial Fibrosis Neg. TB test
C-hypercalcemia NSAIDS Steroids |
|
|
What is Lofgren's syndrome - in sarcoidosis ? |
Arthralgia + Bilateral hilar LN + Erythema nodosum |
|
|
What Ix are appropriate for sarcoidosis ? |
-U&E for calcium levels -serum ACE ↑↑↑ -CXR -Biopsy - shows noncaseating graunloma
Ziehl-niehsen stain - to exclude TB |
|
|
What is pneumoconiosis ? |
Occupational exposure -> interstitial fibrosis |
|
|
What is Caplan's syndrome ? |
Pneumoconiosis + RA + rheumatoid nodules in lung |
|
|
What are the classifications of pneumoconiosis ? |
Simple - no S/S but abnormal CXR
Complication - S/S (SOB, dry cough, crackles) + abnormal CXR + restrictive Pulmonary function test |
|
|
What are the types of pneumoconiosis ? (give characteristic features) |
Coal workers lung - in miners
Silicosis - in metalwork/sandblasters. Risk of TB reactivation & Bronchogenic CA
Berylliosis - in NASA/aerospace industry
Asbestosis - shipyard/construction/plubing/roofing workers (has lower lung fibrosis -cf. others which have apical lung fibrosis first) |
|
|
What does asbestos bodies look like ?
what is asbestosis associated w/?
Ix? |
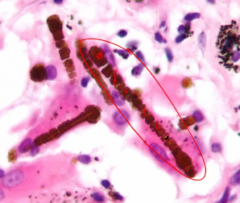
Dumbell shaped
Associated w/ Pleural plaques, Bronchial CA , mesothelioma , Interstitial fibrosis
Ix: Sputum microscopy , Biopsy , CXR/CT - shows pleural plaques |
|
|
What are the S/S of malignant mesothelioma?
Ix? Rx? |
S/S; Chronic unilateral pleuritic pain , pleural effusion, B symptoms , SOB
Ix: CXR/CT , Aspiration - shows bloody fluid
Rx: pleurodesis ( no curative Rx available) |
|
|
What is pneumothorax ?
-Subtypes? |
Air in pleural space
types : Spontaneous (due to bullae), tension (due to trauma) |
|
|
For Pneumothorax, describe the
S/S Ix Rx
|
S/S: Acute chest pain, SOB , Unilateral chest expansion Hyperresonant chest +decreased breath sounds/fremitus , tracheal deviation (toward if spontaneous, away if tension).
Ix: CXR (diagnosis)
Rx: If small-> observe if SOB/symptomatic -> Aspiration in 2nd intercostal space midclavicular line If failure w/ aspiration -> Chest drain @ 5th intercostal space mid-axillary line
If tension -> emergency needle thoracocentesis (2nd intercostal space mid-clavidular line) + chest drain |
|
|
Which cancers commonly metastasize to the lungs ? |
Breast GI |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Lung CA? |
-Smoking -Asbestos -Radiation/pullutants |
|
|
For lung CA , describe the
-S/S -What other local conditions can it cause |
S/S: Hemoptysis , B symptoms, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy ( painful clubbing)
(SPHERE) -SVC syndrome -Pancoast tumor -Horner's syndrome -Esophageal compression -Recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy -Effusions
|
|
|
For Lung CA, describe the
Ix Metastasis Rx |
Ix - CXR, FNA/percutaneous biopsy , sputum/peural fluid for cytology
Metastasis: adrenal glands, brain, bone, liver
Rx: if small cell -> Chemo . If Non-small cell -> excision |
|
|
What are the different types of lung CA ? (give characteristics) |
Small cell - Smoking, Central, ACTH/ADH/lambert eaton (Rx- Chemo)
Squamous cell - Smoking, Central, PTHrP , Psamomma bodies
Adenocarcinoma - Non smoker, peripheral
Large cell carcinoma
Mesothelioma - Asbestos + pleural plaques (Uncurable)
Carcinoid tumor - associated w/ other GI carcinoid tumors. |
|
|
Which of the lung cancers have the poorest prognosis ?
(2) |
Small cell
Large cell (b/c it's poorly differentiated!) |
|
|
Which lung CA is classically cavitating ? |
Squamous cell CA |
|
|
What are the S/S of carcinoid syndrome ? |
-Diarrhoea -Flushing -Wheeze ( due to bronchospasm ) -R. heart pathology |
|
|
Which is the commonest primary lung tumor in children ? |
Carcinoid lung |

