![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
which muscles are not paralysed during REM |
Eye muscles Diaphragm |
|
|
which kind of respiratory control is used during sleep |
only reflex/ autonomic (no cortical control) |
|
|
what controls the voluntary breathing: |
Voluntary breathing (when awake) comes from the motor homunculus (located in the brain between motor areas for the shoulder and the trunk). |
|
|
what is the Pre-Botzinger Complex |
The cluster of respiratory nuclei. Neurones reciprocally inhibit each other (when one fires, the other stops) which allows breathing. |
|
|
breathing awake vs asleep |
10% reduction (6.28 to 5.44 l/min) lower tidal volume (500 ml vs 350) lower O2 sat lower frequency |
|
|
O2 changes during sleep |
O2 sat decrease but not too much because the oxygen dissociation curve is sigmoid |
|
|
CO2 changes during sleep |
CO2 levels rise (Hypercapnia) o CO2 level required to trigger breathing is lower when awake than when we are asleep (0.5 kPa) Reduced sensitivity of chemoreceptors to CO2 during sleep |
|
|
what is hypercapnia and hypocapnia |
increased/ reduced CO2 blood levels |
|
|
what is the apnoeic threshold |
the threshold overwhich CO2 level has to be in order to allow us to breathe |
|
|
what is central sleep apnea? |
the CO2 levels do not raise above the apnoeic threshold and so breathing stops faulty CO2 chemoreceptors |
|
|
what is obstructive sleep apnoea |
occlusion of the phalangeal airway during sleep the person try to breathe but cannot |
|
|
heart failure and sleep apnoea |
heart failure is associated with central sleep apnoea because patients hyperventilate so have a low PaCO2 |
|
|
effects of the motor cortex on cough |
inhibitory. |
|
|
efferent pathways for cough |
motor cortex: inhibitory cough centre in the medulla: stimulatory |
|
|
problems of heart failure and lungs |
can cause pulmonary eodema |
|
|
problems of pulmonary oedema |
activation of J receptors increase ventilation low CO2 when they go to sleep theu do not breathe (do to imbalance on the chemical components) stain stoke respiration |
|
|
what is chain and stokes respiration |
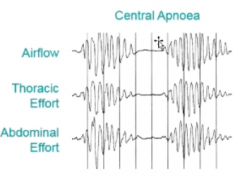
|
|
|
which drugs make asthma worse |
beta blockers non-steroid anti-inflammatory (eg ibuprofen) |
|
|
asthma symptoms |
wheezing cought .. .. |

