![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 5 basic radiographic densities?
|
Air- black
Fat-light gray soft tissue/fluid-Medium Gray Mineral (bone)- white metal-bright white |
|
|
what is MD PLOTS?
|
M = Mediastinum
D = Diaphragms P = Pleura L = Lungs O = Osseous structures T = Trachea S = Stomach/soft tissues |
|
|
what is VITAMINS?
|
V = vascular
I = infection T = trauma A = autoimmune / allergic M = metabolic I = inflammatory/inhalational N = neoplastic S = structural any problem can fall into one of these categories |
|
|
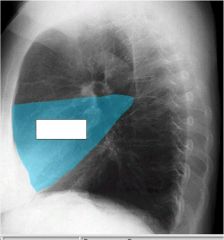
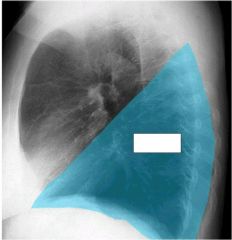
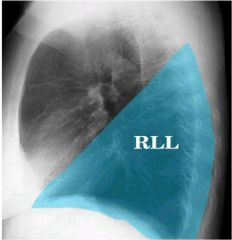
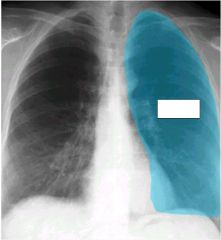
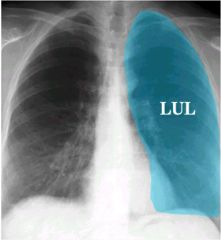
what lobes of the lung make contact with the heart and are where you look for the silhouette sign
*** |
middle lobe (right lung)
lingula (left lung) |
|
|
what can lead to a silhouette sign?
*** |
too much air, too little air, fluid, or no fluid
no air space between the lung and heart (the silhouette sign refers to loss of normal border between structures) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
what is the air bronchogram sign?
|
On a normal CXR, we can visualize the air-filled trachea, mainstem bronchi and initial portions of the lobar bronchi. Further branchings should only be seen with the injection of contrast during a bronchogram. When air can be visualized in the more peripheral intrapulmonary bronchi, this is known as the ‘air-bronchogram sign’. This abnormality is usually caused by an infiltrate/consolidation that surrounds the bronchi.
|
|
|
3 things cause alveolar lung disease...what are they?
|
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Pneumonia Pulmonary edema |
|
|
air bronchograms are seen in what general type of disease?
|
alveolar lung disease
|
|
|
linear or thin types of appearance in the lungs are seen in what general type of disease?
|
Interstitial Lung Disease
|
|
|
what is the most common type of interstitial lung disease?
|
fibrosis
|
|
|
if a chest xray appears nodular, or reticular what kind of lung disease do you have?
|
Interstitial Lung Disease
|
|
|
the border of a normally visible structure is obscured by adjacent pathology
**** |
Silhouette Sign
|
|
|
RML pneumonia obscures the right heart border..this is an example of what?
**** |
Silhouette sign
|
|
|
Occurs when blood, pus or fluid fills the alveoli providing a background such that air within bronchi becomes visible
**** |
Air bronchogram sign
|
|
|
what is the hallmark of alveolar lung disease?
|
air bronchogram
|
|
|
What are the 3 things that cause airspace disease?
**** |
Blood (i.e. pulmonary contusion)
Pus (i.e. pneumonia) Fluid (i.e. pulmonary edema) |
|
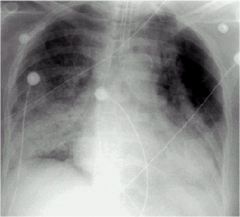
what does this show
|
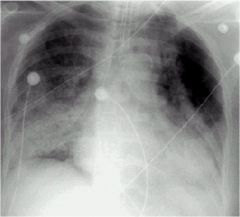
Cloud Like alveolar lung disease
|
|
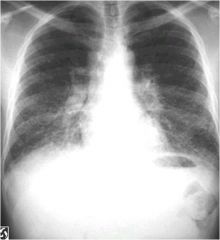
what disease does this show
|
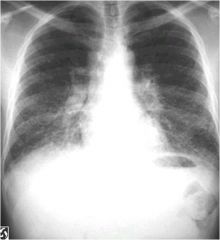
interstitial lung disease
|
|
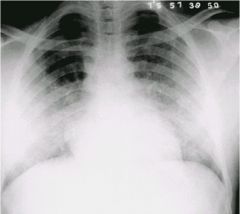
alveolar (airspace) or interstitial disease?
|
alveolar
|
|
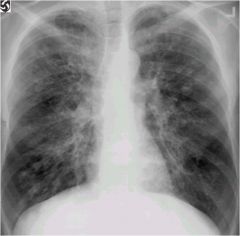
alveolar or interstitial lung disease?
|
interstitial
hyper inflated lungs, heart looks small |
|
|
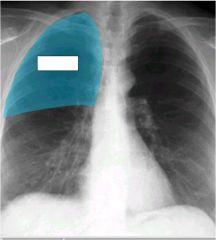
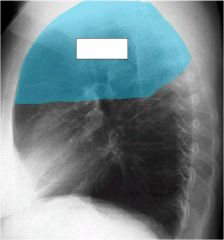
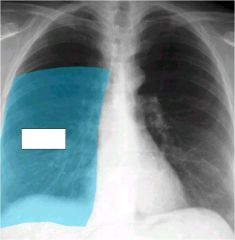
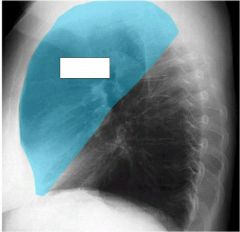
what lobe is affected? alveolar or interstitial
|
right upper
alveolar...minor fissure with sharp demarcation. |
|
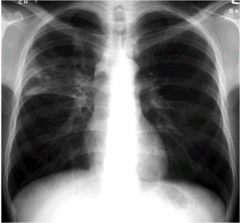
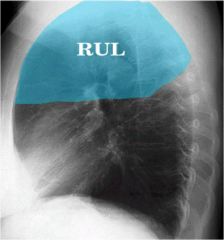
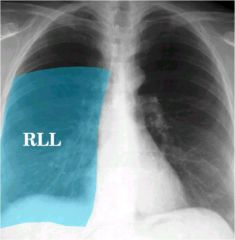
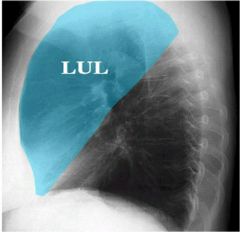
what lobe is affected? alveolar or interstitial
|
right upper
alveolar...minor fissure with sharp demarcation. |
|
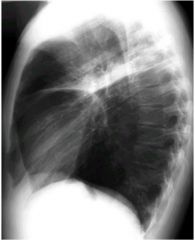
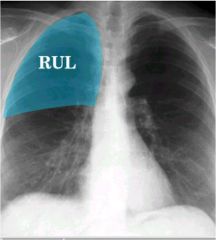
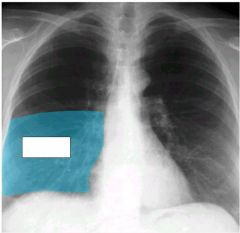
what lobe is affected
|
right upper lobe.
|
|
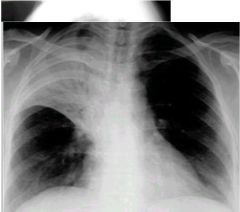
what is being shown here?
|
air bronchogram...alveolar disease
|
|
|
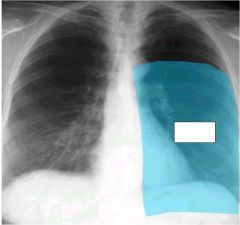
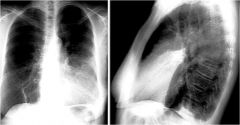
what is going on here
|
lingular pnuemonia
|
|
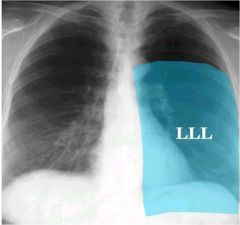
what is going on here
|
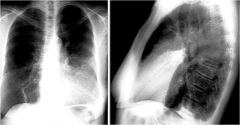
lingular pnuemonia
|
|
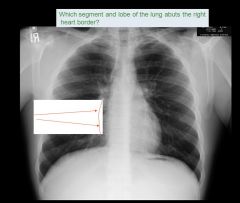
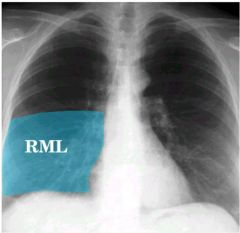
|
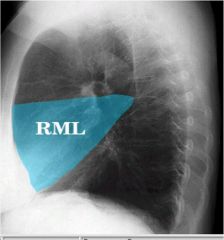
Right middle lobe
|
|
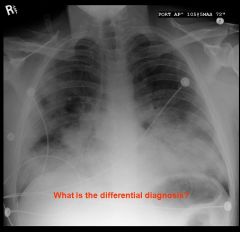
|
pneumonia (pus likely)
|
|
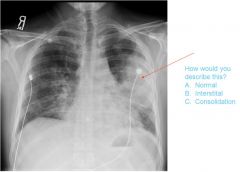
|
Consollidation
|
|
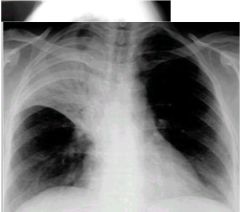
|
air bronchogram
|
|
|
hyperlucency in lung fields looks like what on a film? what is it seen in?
|
BLACK
COPD |
|
|
Flattening of the hemidiaphragms and increased AP diameter of the chest are seen in what?
|
COPD
|
|
|
What are Bulla?
What are Blebs? What are they both seen in? |
Bulla – coalescence of alveoli
Bleb – focal air collection in pleural space COPD |
|
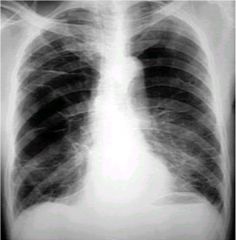
what specific disease is this
|
COPD
|
|
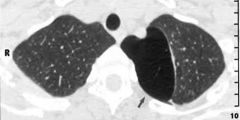
what does the black arrow show?
|
BLEB
|
|
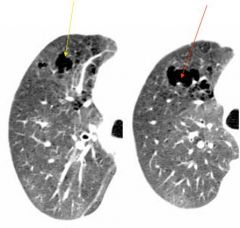
what do the arrows show
|
bullae
|
|
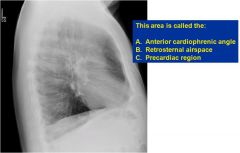
|
Retrosternal airspace
|
|
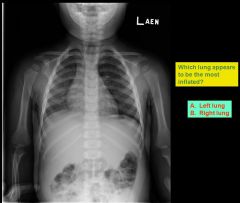
|
left lung
|
|
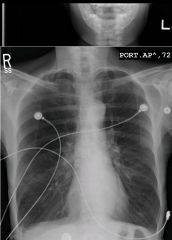
what are 3 important findings in this xray..and what do they have?
|
Hyperinflation, flattening, small heart
COPD |

