![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
282 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What causes y chromosome to be fore males |
It codes for protein H-Y antigen needed for testicular development |
|
|
Amount of eggs made from immature ova |
One |
|
|
Gonodal sex |
Presence of testies or ovarys |
|
|
What dictates gonodal sex |
Presense of y chromosome |
|
|
When H-Y antigen appears for meales |
Week 7-8 |
|
|
What happens if no H-Y antigen is present by week 9 |
Become female and have oogenesis occur at day 77-84 |
|
|
What H-Y antigen causes |
Seminiferous toubules. Leydig cells. Testosterone peaks |
|
|
What is present in undifferentiated gonads |
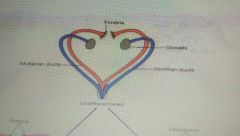
|
|
|
What is left for males in gonads |
Prostate. Seminal vesicles. Vas reverend. Tested. Epididymis |
|
|
Epididymis |
Attach testes to vas reverend |
|
|
What remains for females in gonads |
Cumbria. Overies. Fallopian tubes and uterus |
|
|
Phenotypic sex |
Outward apperance. |
|
|
What determines phenotypic sex |
Gonadal sex |
|
|
When external genitalia differentiates at |
Week 10 |
|
|
Parts of an undiferenciates genitalia |
Genital tubercle. Urethral fold. Genital swelling. Anal opening |
|
|
What the genital toubercle develops onto |
Gland penis or clitoris |
|
|
What the genital swelling turns into |
Scrotum or labia |
|
|
Hormonaly how females develop |
The lack of trigger hormones |
|
|
What testosterone causes for ginadal development in males |
Wolgfian ducts differentiate. Cause male external genitalia to develop |
|
|
What mis causes for in males |
Regression if mulmrtian duct |
|
|
What causes Internal genitalia |
Presense or lack I'd testorone |
|
|
What causes external genitalia diferientation |
DHT (males)or lack of |
|
|
Gender idenity and genetics |
Not coded in gens |
|
|
What androgens in early embryo causes |
More male behavior |
|
|
Where androgens effect males |
Aromatization (E2) |
|
|
Where females are protected from androgens |
Alphafetoprotein |
|
|
Turners syndrome |
XO. Gonodal dysgenesis |
|
|
Superfemale |
XXX |
|
|
YO genetics |
Is lethal |
|
|
Klinefelter syndrome |
XXY. Have seminiferous tubule dysgenesis |
|
|
Two types of hormonal sexual abnormalityes |
Female and male psudohermaphroditism |
|
|
Female psudohermaphroditism |
Make genitsila in genetic female due to androgens week 8-13. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
Male psudohermaphroditism |
Female genitalia in genetic male due to defect in androgen synthesis or action. Testicular demonizing syndrome |
|
|
How psudohermaphrodia is found |
Delayed orvabsense of puberitey by 17 in females and 20 on males |
|
|
Panhypopituitarism |
Endocrine dysfunction |
|
|
Primary amenorrhea |
Endocrine dysfunction |
|
|
Gonodal dysgenesis |
Endocrine / genetic dysfunction |
|
|
True precocious puberty |
Gamrtogenesis and secondary sexual chacteristics |
|
|
Psrudkprecocious puberty |
Early secondary sexual chacteristcs by exposure to androgens for males and estrogen by females but no gametogensis |
|
|
Negative long loop feedback of testosterone and ordtradiol |
Inhibit anterior pituitary and hypothalamus |
|
|
What hypothalamus releases to stimulate sex hormones |
Gn-RH |
|
|
What the pituitary relapses to release sex hormones |
LH FSH |
|
|
What starts sex hormone release |
Early gonadal autonomous. Unrestricted release of pituitary gonadotropins. Negative feedback steroid at term. Neonatal stimulation due to loss of maternal steroids |
|
|
What starts puberty theorys |
Critical size hypothesis. Missing link (positive drive) hypothesis. Gonadostat hypothesis |
|
|
Menopause |
Stop of menstration at 45-55 years. |
|
|
What causes menopause |
Depleated follicles and less resposive to gonadotropins. Estrogen and progesterone reduced |
|
|
Climqcteric |
Make reduction in androgens |
|
|
What causes climscteric |
Reduced sensaticity to LH. Reduced testies size. Reduced testorsterone production and action |
|
|
Amount of time sperm must mature for |
10 day |
|
|
What vasdefferns store |
Nutrients |
|
|
Role of epididymis |
Sperm transport. Maturation. Motility. Fertility |
|
|
Role of seminal vessicles |
Seminal fluid |
|
|
What's in seminal fluid |
Fructose and prostaglandin |
|
|
Prostate |
Alkaline prostatic fluid. Rich in prostaglandin |
|
|
Prostaglandin |
Is a base |
|
|
Bulbo-urethral gland |
Pre ejaculatory lubrication fluid |
|
|
Penis |
Erection. Ejqctualtion. Intromission |
|
|
Way blood flows to the testies |
Counter current |
|
|
Role of counter current blood flow |
Venous blood cools arterial blood as they flow past each other |
|
|
Temp of testicles |
2 degrees less then body temp |
|
|
Extra function of counter current blood flow of tested |
Testosterone can leave vein and enter arteries beciase it's needed for gsmetogrnesis |
|
|
Where sperm are made |
In seminiferous tubules |
|
|
Two cell types if testies |
Spermatogrnic cells and interstitial cells |
|
|
Role of interstitial cells |
Make testosterone |
|
|
Amount of mass that is semeriferous tubules of testies |
80-90% |
|
|
How semiferous tubules are decided |
Into lobules |
|
|
Volume of testies |
18-20ml |
|
|
Amount of lobules per testis |
250 |
|
|
Length of seminiferous tubules |
800 feet/ testis |
|
|
Cells that line the walls of the tubules |
Sertoli cells |
|
|
What fsh causes in sertoli cells |
Testosterone to estradiol |
|
|
What LH causes on leydig cells of men |
Cholesterol to pregnenalone to testosterone |
|
|
Where DHT is made |
Mostly in target tissuev |
|
|
Ways testosterone acts |
On receptor to form protein. Turns to estrodiol then protein. To DHT to protein |
|
|
How testerostorne causes gametogenisis |
Act on sertoli cells which signal germ cells which lack testorsterone receptors |
|
|
Testicular feminizing syndrome |
Androgen resistance or 5 alpha reductase deficiency |
|
|
Cryptorchidism |
Undecended testicles |
|
|
Juveinle hypogonadism |
Sexual immaturity due to low LH and FSH |
|
|
Post pubertal hypogonadism (simmonds disease) |
Loss of testosterone and secondary sexual chacteristics |
|
|
Stages of sperm production |
Mitotoc proliferation. Meiosis. Packaging |
|
|
Cells of mitotic proliferation |
Spermatogonium. Spermatogonia. Primary spetmocyte all with 46 chromosome |
|
|
How spermatogina work |
One stays on wall other becomes sperom |
|
|
Cell types of meiosis |
Secondary spermatocytes. Spermatids |
|
|
Packaging cell types |
Spermatozoa |
|
|
How spermatogenisis function |
Move closer to lumen with each divide |
|
|
Seperqtion from primary spermatocytes and secondary |
A tight junction |
|
|
What signals all dividison up to secondary |
Autonomous |
|
|
What starts final mitosis |
Testosterone |
|
|
What starts final stage |
FSH |
|
|
What maintains final stage of spermatogenisis |
Testosterone |
|
|
Area with higher concentration of testosterone |
Lumen over plasma |
|
|
What triggers waves of spermatovensis |
Phagocytosis of spermatozoan cytoplasm by sertoli cells |
|
|
Role of sertoli cells |
Maintain blood testis barrier. Nurismnrt of germ cells. Produce seminiferois fluid. Eat old cells and spermatozoan cytoplasm |
|
|
What sertoli cells produce |
Androgen binding protein. Inhibin and estrogen. Mullerian regressing factor (MRF) |
|
|
Parts of sperm |
. Cap acrosome and flagellum |
|
|
What happens to cytoplasm of sperm |
Buds off during development |
|
|
What is on end if the head of a sperm |
Acrosome |
|
|
What makes up tail of sperm |
Microtubules |
|
|
What's in the midpiece of a sperm |
Mitochondria |
|
|
Amount if semen ejaculated |
1-5ml |
|
|
Amount of sperm ejaculated |
100mil / ml |
|
|
Amount of sperm ejqculated to to be infertile |
Less then 20 mil |
|
|
What majority of seamen is |
Seamen plasma |
|
|
What the seminal vesicles produce |
45-80% of semen. Viscous secretion. Fructose rich. PG rich |
|
|
What viscous secretion does |
Adhesion within the vagina |
|
|
What PG causes |
Increased smooth muscle contraction in females tract |
|
|
Amount if semen made by prostate |
15-30% |
|
|
Things that the prostate secretion has |
Alkaline. Protease rich. PG rich |
|
|
What protease causes |
Liquification of ejaculate after ejaculation |
|
|
Cowpers gland (bulbourethral) |
Mucuus for vaginal penitration |
|
|
What causes sperm movement in males |
Fluid pressure from : production from sertoli. Contraction of myorpithelial cells around toubules. Addition of secretion of seminal vesicles. Prostate and bulbourethral gland. And cilia movement in tubules |
|
|
What causes contraction of myoepithelial cells |
Oxytocin in androgen dependent cells |
|
|
What causes sperm movement in females |
Muscular contractions by oxycoticin. Cilia movement in female tract. Swimming |
|
|
Two processes of sperm maturation in females |
Capacitation. Acrosome reaction |
|
|
Capacitation |
Secretion of female tract allowing for adhesion to ovum and removes proteins from head of Sperm |
|
|
Acrosome reaction |
Factors from ovum ruptures sperm acrosome causing the release of proteolitjc enzymes that break down ovum membrane |
|
|
Layers of uterus |
Endometrium. Myometrium |
|
|
Oviduct |
Tube that connet flopian tube to urterus |
|
|
Parts that are at the entrance to the uterus |
Cervical canal. And cervix |
|
|
Antrum |
Space that occurs for developing secondary follicle |
|
|
Outer layers of follicle |
Thecal cells. Grabulosa cells then zona pellucida |
|
|
Amount ovum per follicle |
One |
|
|
What happens at ovulation |
The ovum is ejected from folicule |
|
|
What happens to foliculr after ovulation |
Luteinzation |
|
|
Lutenization |
Formation of corpus lutenum |
|
|
Luteolysis |
Death of corpus luteum |
|
|
Corpus albicans |
Scar tissue |
|
|
Steroids of ovary and placenta and corpus luteum |
Estrogen. Progesterone. Androgen |
|
|
Endocrines Peptides of ovary and placenta and corpus luteum |
Relaxin. Inhibin |
|
|
What LH causes in females thecal cells |
Testosterone production |
|
|
What FSH causes in granulosa cells in females |
Transition of testosterone to estradiol which is released to blood |
|
|
Luteal phase in granulosa cell |
Lh causes testosterone and the. FSH turns testerstorne to estrogens and both progesterone are released to blood |
|
|
What estrogen causes in the ovary and follicles |
Growth and development |
|
|
Estrogens effect on uterus |
Prepares endometrium for implantation. Induces progesterone receptors. Induces thin watery mucus. And promotes contractions at term |
|
|
What estrogen causes in breasts |
Growth of ducts and fat deposits |
|
|
Estrogen effect on the female body |
Female configuration. Secondary sexual characteristics. Closure of epiphyseal plates. Protects against osteoporosis |
|
|
Hypothalamo pituitary axis causes from estrogen |
Positive and negative feedback |
|
|
Progesterone effect on uterus |
Decidualization and endometrial secretion. Induce thick sticky mucus. Decrease contractions |
|
|
Progesterone effect on breasts |
Growth of glandular tissue |
|
|
Progesterone effect on hypothalmo pituitary axis |
Negative feedback |
|
|
Inhibin is made in |
Granulosa cell through out menstrual cycle prior to ovulation and during lutral phase |
|
|
What inhibin inhibits |
FSH postly in the pituitary |
|
|
Relaxin is synthesized in |
Corpus luteum and placenta |
|
|
What us caused by relaxin |
Decreases uterine contractility in early pregnancy to prevent abortion. Lossen pelvic joints and soften and dilate cervix |
|
|
Gonadal dysfunction of females |
Pseodohermaphroitism. True precocious puberty |
|
|
When a fetus female goes from primordial follicles to primary follicles |
5 months |
|
|
When amount of folicules peaks |
6 months into fetal development |
|
|
Amount of mature oocytes in adults |
400-500 |
|
|
Amount if polar bodies made to make a egg |
Two |
|
|
Menstrual abnormalities |
Amenorrhea |
|
|
Polycystic ovary syndrome |
Have high lvls of androgens |
|
|
What congenital adrenal hyperplasia causes |
Make external genitalia to form |
|
|
Deficiency of congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
21 hydroxylase |
|
|
XX adrenogenital syndrome |
Psudohermamphroditism causing saddle bag scrotum no vagina |
|
|
Hirsutusm |
Androgen excess causing secondary sexual characterists |
|
|
Period of time that occurs from menstruation to ovulation |
Follicular phase |
|
|
Period of time after ovulation to menstruation |
Luteal phase |
|
|
Phase that effects length of menstrual cycle |
Flollicular phase |
|
|
Hormone peak that causes ovulation |
LH and FSH |
|
|
Hormone drop that occurs for ovulation |
Estrogen |
|
|
Hormone that has most for menstruation |
FSH and estrogen |
|
|
Hormone that peaks after ovulation |
Progesterone |
|
|
What estrogen causes |
Decrease in FSH and increase in LH |
|
|
What high FSH lvls causes at the begining if folliculogensis |
Follicle recruitment |
|
|
What FSH causes in granulosa cells |
Production of estrogen |
|
|
Amount if folicules that are recruited per cycle |
6-12 |
|
|
What happens to the non dominate follicle |
They atrophy and become graffian follicle |
|
|
What rising estrogen lvls cause on hupothslmus |
Increase GnRH causing a surge in LH and FSH |
|
|
What causes decline in estrogen before ovulation |
Graffian follicle stops produceing it |
|
|
What the surge in LH causes |
Progesterone release and plasma activity |
|
|
What progesterone causes |
Corona radiata to separate from granulosr cells stopping inhibition of maturation on folicille |
|
|
Length of time that a ovum is viable for after ovulation |
36 hr |
|
|
Formation of corpus lutrum |
Walls collapse and antral fluid is reabsorbed. Thecal blood vessels invade granulosa cells and antral cavity fills with blood. |
|
|
Corpus haemorragium |
When granulosa layers and antral cavity fills with blood |
|
|
What LH does to granulosa cells in corpus luteum |
Become lutenized. |
|
|
Luteinized |
Full of lipid/ steroids |
|
|
Cells that make up corpus luteum |
80% granulosa. 20% thecal cells |
|
|
How long corpus luteum lasts if not pregnant |
14 days |
|
|
What replaces corpus luteum if not pregnant |
Corpus albicans ( fibrous tissue) |
|
|
What luteinized granulosa cells respond to and produce |
LH and produce estrogen and progesterone |
|
|
What progesterone release causes for uterus |
Growth of endometrium and coiling of its spiral arteries |
|
|
Feed back loop of moderate estrogen and high progesterone |
Long loop negative feed back |
|
|
What causes luteolysis |
Lack of LH and FSH stopping production of steroids |
|
|
What causes menses |
Lack if progesterone |
|
|
What spiral arteries coils cause for menstration |
Imped blood flow causing tissue necrosis |
|
|
What PGs release cause for menstration |
Vasoconstriction leading to further tissue ischemia |
|
|
What necrosis if blood vessels cause |
Hemorrhage and endometrial sloughing which is helped by enzymes |
|
|
Blood and tissue volume lost during menstratiin |
25-76ml each (mostly arterial) |
|
|
What PGs cause for smooth muscle of uterus |
Rhythmically contractions and menstrual flow and cramps |
|
|
Menstrual abnormalities |
Amenorrhea. Oligomenorrhea. Menorrhagia. Metrorrhagia. Dysmenorrhea |
|
|
Amenorrhea |
Absent ovulation due to dysfunction if HPG |
|
|
Oligomenorrhea |
Infrequent light bleeding |
|
|
Menorrhagia |
Prolonged heavy bleeding |
|
|
Metrorrhagia |
Bleeding between periods |
|
|
Dysmenorrhea |
Painful period |
|
|
Effect of estrogen on breasts |
Fluid retention and ductal growth of breasts |
|
|
Progesterone effect on breasts |
Increase fluid retention and lobule growth |
|
|
What occurs to breasts prior yo Mendes |
Odema and swelling |
|
|
Two parts of penis involved in erection |
Corpus cavernosum and corpus sponglosum |
|
|
Type of tissue around the urethra |
Corpus. Spongiosum |
|
|
Blood flow that causes erection |
Pressureizes blood enters and veins constrict |
|
|
Where blood gets trapped in penis |
Corpus cavernosa |
|
|
What causes lubrication in penis |
Parasympathetic activation of the bulbourethral glands |
|
|
What causes ejaculation |
Intense sexual stimulation |
|
|
Where sympathetic impulses cause smooth muscle contractions for ejaculation |
Rhythmicly in bulbourethral glands. Prostate and seminal vesicles. And peristaltic contractions in testicular ductdd rpididimus. Vas defferns and ejqculatory ductv |
|
|
Movement to expel things out of the penis |
Rhythmic contraction in erectial column of penis |
|
|
Color change over erection |
It gets darker |
|
|
Four stages of an erection |
Excitment. Plateau. Orgasm. Resolution |
|
|
What causes excitation in females |
Paradympathetic impulses |
|
|
What occurs during excitment |
Vasocongestion of vaginal walls |
|
|
When peak vasocongestion of vaginal wall occurs |
Orgasm |
|
|
Agging issue with male penis |
Erection takes more time and stimulation and is less firm when fully erect and refractory period is longer |
|
|
Ejaculation volume as men age |
Volume decrease |
|
|
Testicular size during aging |
Smaller and signs of sexual arousal are reduceced |
|
|
What loss of estrogen causes in aging women |
Reduced vaginal flow. Resdudrd Vasocongrstion. Reduced lubrication. And may cause dyspareuria |
|
|
Dyspareuria |
Painful intercourse |
|
|
Effect on vaginal wall of ageing |
Vaginal wall loses elasticity and expansion reduces |
|
|
Sexual arousal signs and aging |
Reduce |
|
|
Endocrine issues with male |
Decreased testosterone causes decrease libido but not impair erection |
|
|
Endocrine issues with female |
Decrease in estrogen dryness of vagina and painful intercourse |
|
|
Neural issue for men and sex |
Impotence. Premature ejaculation |
|
|
Neural issues for females sexuaky |
Anorgasmia (1in14 psychological). Vaginismus. Dyspareuria |
|
|
Time it takes for sperm to get to fertilization site |
30 to 60min |
|
|
What helps sperm move through the cervix |
Glycoprotein channels in the mucus |
|
|
How the egg helps direct sperm |
Chenotactic factors |
|
|
Half identical twins (polar body twining) |
Egg splits on two and each egg I'd fertalized seperatly |
|
|
Causes for infertaikity in men |
Impaired spernatogenesis or seman production. Or impaired testicular or penile function |
|
|
Infertility in females |
Anovulation. Infection. Excess thick mucus |
|
|
When zygote begins mitotic division |
30 hr after fertilization |
|
|
How a zygote enters uterine cavity |
As a morula after 3-4 days |
|
|
Morula |
8 cells |
|
|
When a zygote implants |
7-8 days after fetulization |
|
|
What the zygote survives on till implantation |
Uterine milk secreted by endometrium |
|
|
Trophoblast secretion they increases endometrial permeability |
Estrogen |
|
|
What is made by trophoblast that allows for implantation |
Proteases |
|
|
Tropoblast |
Outer layer of cells around the zygote |
|
|
Blastocele |
Fluid filled pouch around the embryo contained by the teopoblast |
|
|
Parts of embryo during blastocyst |
Yolk sack and amniotic cavity |
|
|
Layers around amnonic fluid |
Chorion amnion |
|
|
When the placenta develops |
5 weeks after implantation |
|
|
What makes up the placenta |
Fetal chorionic frondosumn. Maternal decidual tissue |
|
|
What occurs at plecenta |
Exchange between fetal and maternal blood |
|
|
What maternal decidual tissue does |
Production of glycogon |
|
|
Where maternal blood pools form |
Chorionic excavation |
|
|
What forms chorionic frondosum |
From vascularized chronic villi |
|
|
Tissues that have decidual reaction |
Endometrial proliferation. Vascularization. Glycogen accumulation |
|
|
What makes up the placental barrier |
Endothelial cells of the blood vessels |
|
|
What crosses placental barrier by diffusion |
Oxygen. Co2. Ion. Lipids. Steroids |
|
|
What crosses placental barrier by 're rotor mediated endocytosis |
IgGs |
|
|
What gets amino acids across the placental barrier |
Amino acids |
|
|
How glucose crosses the placental barrier |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Functions of the placenta |
Gas exchange. Nutrient delivery. Antibody delivery. Removal of fetal waste. Secretion of hormones |
|
|
Hormones secreted by placenta |
HCG. hCS. Estrogen. Progesterone |
|
|
What hCG causes |
More progesterone and estrogen from corpus luteum |
|
|
What hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is like |
LH in structure and action |
|
|
What secretes hCG |
Syncitiotophs 6 days after fertilization. |
|
|
External use of hCG |
Pregnancy tests |
|
|
How concentration changes for hCG |
Doubles every two days till peak at 10 weeks when the placenta forms. Secondary peak in second trimester |
|
|
Hormones effected by hCG |
Increase relaxin. Decrease LH in mother. Increase DHEA in fetus. Decrease mother immune function |
|
|
Why a mother's immune function in decreased during pregnancy |
To avoid abortion |
|
|
What hCS is like |
GH in structte and action |
|
|
What hCS is produced and where it is found |
Syncitiotrophs 4 weeks after implantation. Mainly in maternal circulation |
|
|
Amount if hCS is proportional to |
Placenta size |
|
|
What hCS causes |
Direct nutrients to the fetus induceing a diabetic like state in mother |
|
|
Steroids that the placenta produces from the fetoplacental unit |
Pregnenalone and progesterone from materinal cholesterol |
|
|
What happens to placental prrgnenalone |
Enters fetus and gets turned to androgens |
|
|
Where fetal androgens go |
Into placenta and get converted into estrogen and get passed to mother |
|
|
Concentration change of progesterone over pregnancy |
Increases to term |
|
|
What progesterone causes in zygote |
Division |
|
|
Concentration change of estrogen over term of pregnancy |
Increases to term |
|
|
What causes cervical ripening at parturition |
Relaxin and prostaglandin |
|
|
Parturition |
Term (270 days after fertilization) |
|
|
Parts of myometrial contractions |
Braxton hicks. Labour. Amniotic rupture. Cervical dilation. |
|
|
What stimulates nyometrial contractions |
Oxytocin and prostaglandin |
|
|
How oxytocin causes effects if concentration does not drastical increase at term |
Uterus becomes more sensative due to receptor upregulation |
|
|
How Labour can be triggered with out hormones |
Once a critical size is reached the movement of the fetus triggers contraction |
|
|
Tubal/ectopic pragnancy |
Occurs in oviducts or outside uterus |
|
|
Psudopregnancy |
Emotionaly disturnbed and appear to be pragnant |
|
|
What prolactin causes in breasts |
Sysnthesis of milk in alveoli |
|
|
What oxytocin causes in breasts |
Secretion of milk from avleoli ducts |
|
|
Chiari frommel syndrome |
Persistent, inappropriate lactation |
|
|
Infertility |
Antigonadal actions of prolactin |

