![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does "dysuria" mean?
|
Painful urination
|
|
|
What does "polyuria" mean?
|
Increased urine flow
|
|
|
As urine sits, several changes can occur. What happens to
A. the pH B. glucose C. Ketones D. bilirubin E. nitrites F. bacteria G. RBCs and RBC casts |
A. the pH : increases (due to breakdown of urea to ammonia by urease-producing bacteria)
B. glucose : decrease (due to glycolysis and bacterial utilization) C. Ketones : decrease (due to volatization) D. bilirubin : decrease (from exopsure to light) E. nitrites : increase (due to bacterial reduction of nitrate) F. bacteria : increase G. RBCs and RBC casts : disintegrate |
|
|
True or False:
Urine pH can only be between 4.4 to 9. |
True
|
|
|
Just for fun:
Nonpathologic causes of proteinuria are fever, exposure to cold, strenuous exercise, dehydration, and orthostatic proteinuria. Real question: Pathalogic causes of proteinuria include... (5 examples) |
gloemrular membrane damage, impaired tubule reabsorption, multiple myeloma, preeeclampsia and diabetic nephropathy.
|
|
|
Assessing nitrite urine levels is a rapid screening test for UTI, but is NOT a replacement for urine culture.
True or False: A negative nitrite test does NOT rule out the presence of a UTI. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Regarding urine microscopic examination, RBCs can originate from anywhere in the urinary tract from the kidney to the urethra. The presence of RBC casts, though (and any cast, for that matter), indicates origination from...
|
the kidney
|
|
|
Three types of epithelial cells can be present: squamous, transitional and renal tubular. Describe where each is found.
|
Squamous: derived from lining of the vagina and lower portions of the male and female urethras
Transitional: from the lining of the bladder, renal pelvis and upper urethra Renal tubular cells (self explanatory) |
|
|
RBC casts can indicate...
A. glomerulonephritis B. Pyelonephritis C. Renal tubular nephritis D. UTI |
A. glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
WBC casts can indicate...
A. glomerulonephritis B. Pyelonephritis C. Renal tubular nephritis D. UTI |
B. pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Epithelial cell casts can indicate...
A. glomerulonephritis B. Pyelonephritis C. Renal tubular nephritis D. UTI |
C. Renal tubular nephritis
|
|
|
Granular casts can indicate...
A. glomerulonephritis B. Pyelonephritis C. Renal tubular nephritis D. UTI |
D. UTI
|
|
|
Match the following with the appearances listed. Uric acid, Calcium oxalate, triple phosphate, calcium carbonate, cystine.
1. Envelopes 2. Rosettes 3. Dumbbells 4. Coffin lids 5. 6 sided |
1. Envelopes - Calcium oxalate
2. Rosettes - Uric Acid 3. Dumbbells - Calcium carbonate 4. Coffin lids - Triple phosphate 5. 6 sided - cystine |
|
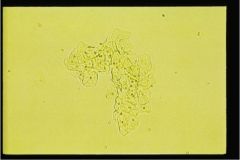
A. squamous cells
B. transitional cells C. renal tubule cells |
A. squamous cells
|
|
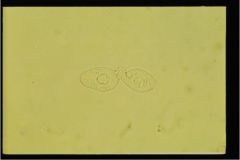
A. squamous epithelial cells
B. transitional cells C. renal tubule cells |
B. transitional cells
|
|
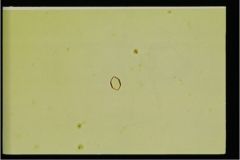
What type of crystal is this?
A. uric acid B. Calcium oxalate C. Calcium phosphate D. Triple phosphate E. Calcium carbonate F. Cystine |
F. Cystine
|
|
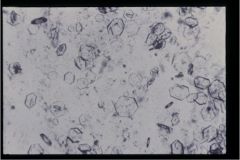
What crystal is pictured?
|
Cystine
|
|
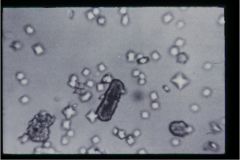
hint: "envelopes"
|
Calcium oxalate crystals
|
|
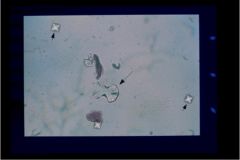
What two crystals are shown?
|
Calcium oxalate (envelopes) and Calcium carbonate (dumbells)
|
|
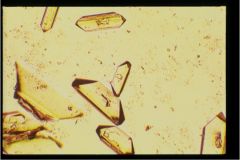
hint: "coffin lids"
|
Triple phosphate crystals
|
|
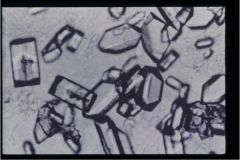
hint: "coffin lids"
|
Triple Phosphate Crystals
|
|
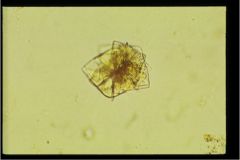
"rosette"
|
uric acid
|
|
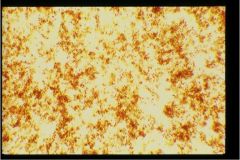
"crud"
|
Amorphous urates
|
|
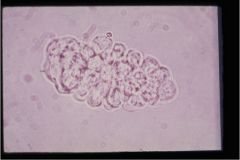
What type of cast is this?
|
WBC cast
|
|
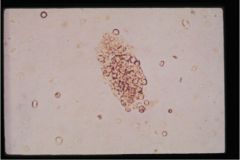
What type of cast is this?
|
RBC Cast
|
|
|
What is the significance of coarse muddy brown granular casts?
A. Acute Tubular Necrosis B. pyelonephritis C. allergic interstitial nephritis |
A. Acute Tubular Necrosis
|
|
|
What is the differential of “red” urine?
|
RBCs, Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Beets, Rhubarb
|
|
|
Pt. comes in complaining of dysuria (usually described as burning), frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain, and hematuria. What are your differentials?
|
Cystitis, urethritis, vaginitis, pyelonephritis.
Workup: If no CVA tenderness, prolly cystitis. If yes CVA tenderness then it is an upper urinary tract infection. |
|
|
True or False:
If acute cystitis is uncomplicated, then urine culture is not necessary. |
True
|
|
|
What is the treatment for acute cystitis?
|
Fluoroquinolone for 3 days
|
|
|
Urethritis symptoms are similar to cystitis (dysuria) but usually also present with social history of....
|
new, recent sexual partner
Urethritis is commonly caused by STDs chlamydia and gonorrhea. Diagnosis made by culture of urethra or DNA amplification for chlamydia. |
|
|
Acute pyelonephritis is an infection of the upper urinary tract (ureters, kidneys). Symptoms include ....
|
fever, CVA TENDERNESS, nausea/vomiting, DYSURIA, suprapubic pain, frequency
must differentiate from PID, and ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
What is treatment for acute pylonephritis?
|
can use SMX/TMP for 14 days,
Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin or Gatifloxacin If signs of sepsis, vomiting or pregnant, then admit to the hospital for IV antibiotics - Ceftriaxone and Aminoglycoside |
|
|
When is a UTI considered "complicated"?
|
An infection in a pregnant or immunocompromised patient, if dealing with multi-drug resistant organisms, patient with anatomical abnormality of the kidneys or genitourinary tract, or the extremes of age (<2 or > 70)
|
|
|
When do you image kidneys? (4)
|
a.Infection persists despite tx with antibiotic organisms should be sensitive to
b. Yeast infection c. Recurrent infection d.Two or more episodes pyelonephritis in one year |
|
|
Asymptomatic bacteruria is common and can lead to symptomatic infection but treatment is not shown to prevent infection so only treat under what 2 conditions?
|
pregnant women or patient that has post instrumentation of the bladder (catheter or cystoscopy)
|

