![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some of the major functions and characteristics of the kidneys? (There are 4 of them)
|
1. Regulates composition of body fluids (i.e., water balance)
2. Rids body of wastes of metabolism 3. Removes foreign chemicals, drugs and food additives 4. Minor endocrine organs (i.e., renin-angiotensin system and erythropoietin) |
|
|
What is the outer portion of the kidney called and what does it contain?
|
1. Renal Cortex
2. Contains capillary tufts and convoluted tubules |
|
|
True or false: One collecting duct can serve several nephrons
|
True
|
|
|
Describe the make-up a the glomerulus
|
A network of 50 capillaries with many circular fenestrations (pores)
|
|
|
Why is the glomerulus more permeable than typical capillaries and by how much?
|
The pores have a diameter of 50-100 nm.
100-1000 times more permeable |
|
|
Describe the Bowman's capsule (glomerular capsule)
|
It is a double-walled cuplike structure composed of squamous epithelium.
|
|
|
What is unique about the proximal convoluted tubule?
|
It is continuous with the epithelium of the glomerular capsule and consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells containing microvilli to greatly increase the surface are
|
|
|
Where is the thick segment of the nephron loop located?
|
It runs between the afferent and efferent arterioles
|
|
|
What is the Pathway of vessels to kidneys
|
Aorta->Renal Artery->Afferent arteriole->Glomerular capillaries->efferent arteriole->peritubular capillaries->Renal Vein->IVC
|
|
|
Ureter
|
Goes from hilum of the kidney down to bladder
|
|
|
Types of glomeruli
|
1. Superficial
2. Juxtamedullary |
|
|
Bowman's Capsule
|
Composed of podocytes.
One end covers the glomerular capillaries, other end forms tubules. |
|
|
Renal Tubules
|
Used for reabsorption or secretion of ultrafiltrate components.
Hollow tube made up of a single layer of epithelial cells. Inside surface=luminal/apical Outside surface=basolateral/peritubular |
|
|
Excretion
|
Products must be outside body and measured directly from urine.
Excretion=Amount filtrated-amount reabsorbed+amount secreted. |
|
|
Renal tubule components
|
1. Proximal Nephron (Convoluted and straight)
2. Loop of Henle (thin descending, thin ascending, thick ascending) 3. Distal nephron (Distal convoluted tubule, connecting duct, collecting tubule) |
|
|
Proximal nephron
|
1st part of renal tubule.
Consists of convoluted and then straight tubules. Used for bulk reabsorption of water and solutes. |
|
|
Loop of Henle
|
2nd part of renal tubule
1. Thin descending limb 2. Thin ascending limb 3. Thick ascending limb Used for dilution or concentration of urine through water. |
|
|
Distal nephron
|
Last part of the renal tubule, used for fine tuning of urine composition.
Has 1. Distal convoluted tubule 2. Connecting duct 3. Collecting tubule |
|
|
Where are the renal columns?
|
Renal columns are portions of cortex between pyramids
|
|
|
Which renal vein receives it's adrenal and gonadal vein?
|
Left - because the left renal vein is longer than the right (IVC lies anterior and to the right of Aorta). On right, these enter IVC
|
|
|
Why would a fetus with renal agenesis not die of azotemia?
|
Mother's kidneys and placenta filter out fetal blood
|
|
|
What can happen to kidneys after dialysis?
|
Cysts may form, even after transplant, probably due to fibrosis or oxalate crystals
|
|
|
T\F One nephron per collecting duct? What does this mean?
|
False, multiple nephrons use the same collecting duct, nephrons operated in parallel
|
|
|
What controls the permeability of the collecting duct?
|
Vasopressin\ADH
|
|
|
How many layers must a filtrate pass through at the glomerulus to enter Bowman’s capsule?
|
3, Capillary endothelium, basal lamina, podocytes(slits between feet with diaphragms)
|
|
|
What modulates the effect of the sympathetic nervous system?
|
Simultaneous release of PGE2 and PGI2 opposes SNS and minimizes SNS effect
|
|
|
Why does angiotensin II differentially affect the afferent and efferent arteriole?
|
Efferent arteriole more sensitive
|
|
|
What are the Vasodilators that regulate RBF?
|
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), glucocorticoids, NO, prostaglandins: increase RBF and GFR
|
|
|
T\F Lots of protein enter filtrate at renal corpuscle?
|
False, almost no protein
|
|
|
What 2 chemical properties allow filtration at the glomerulus?
|
Electrical charge (negative charges in basal lamina) repel negative proteins, molecular size
|
|
|
The urinary consists of 4 parts of the body. What are the 4 parts and what are each of their functions?
|
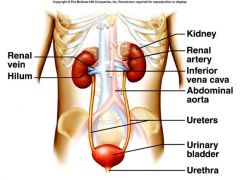
1. Kidneys - Form Urine
2. Ureters - Transport Urine 3. Urinary Bladder - Store Urine 4. Urethra - Carries Urine to Outside of Body |
|
|
What factors can alter the Kf of the glomerular capillaries?
|
Mesangial cells (sympathetic, beta receptor)
|
|
|
What is the definition of clearance?
|
the VOLUME of plasma that is cleared of solute x PER MINUTE
|
|
|
T\F respiratory acidosis can be completely compensated by the kidneys
|
True, slow but effective
|
|
|
What are the 2 ways that diuretics work?
|
Increase GFR and decrease reabsorption of electrolytes
|
|
|
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
|
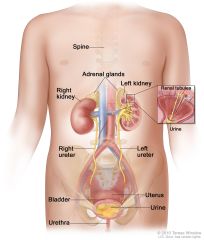
Either side of vertebral column in abdominal cavity between 12th and 3rd lumbar vertebrae.
|
|
|
What is the inner portion of the kidney called and what is it composed of?
|
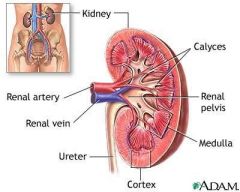
Renal Medulla
Composed of a series of triangular masses (renal pyramids) which are separated by renal columns |
|
|
What are the six parts of the nephron?
|
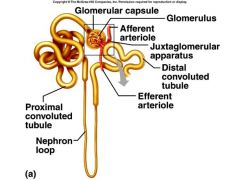
The Glomerulus
Bowman's Capsule (glomerular capsule) Proximal Convoluted Tubule Loop of Henle (Nephron Loop) Distal Convoluted Tubule Collecting Duct |
|
|
Glomerular Anatomy
|
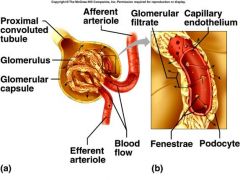
Layers:
Filtration barrier 1. Glomerular capillary endothelial cells 2. Glomerular Basement Membrane 3. Podocytes (forms Bowman's Capsule) Supported by mesangeal cells. |
|
|
Which renal artery is longer?
|
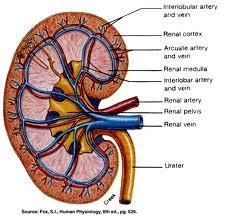
Right (aorta sits to the left and posterior to IVC)
|
|
|
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
|
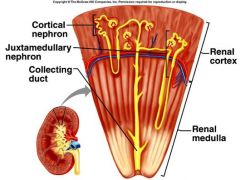
Where the thick ascending loop of Henle passes through the afferent and efferent arterioles
|

