![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Internal balance refers to the distribution of patoassium in the body. Due to Na-K ATPase, most potassium is where?
|
Intracellular
|
|
|
|
Insulin stimulates K uptake by...
|
both hepatic nad skeletal muscle cells by stimulating the Na-K ATPase (indirectly) to transfer K+ into cells!
|
|
|
|
True or False:
Regarding internal K+ balance, Beta-2 stimulation increases entry of K+ into cells. |
TRUE
Beta-2 agonists are epinephrine and albuterol. These increase intracellular K+ / decreases extracellular K+ |
|
|
|
Regarding internal K+ balance, what do the following do to K+ movement into cells?
A. Epinephrine B. Albuterol C. Propranolol, sotalol D. alpha-adrenergic stimulation E. Beta-2 stimulation |
A. Epinephrine : is a beta-2 agonist, decreases plasma K+ / increases intracellular K+
B. Albuterol: same as Epi C. Propranolol: is a beta-2 antagonist thus increases plasma K+ D. alpha-adrenergic stimulation: increases plasma K+ E. Beta-2 stimulation: decreases plasma K+ / increases intracellular K+ |
|
|
|
Regarding internal K+ balance, of the following options (elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis, normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis), which results in:
1. Low plasma K 2. Elevated plasma K 3. lack of transcellular shift of K |
1. Low plasma K: metabolic alkalosis
2. Elevated plasma K: normal anion gap metabolic acidosis 3. lack of transcellular shift of K: elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis |
1. Low plasma K: metabolic alkalosis --> H+ leaves cells to buffer extracellular pH and K+ shifts intracellularly to maintain electroneutrality.
2. Elevated plasma K: normal anion gap metabolic acidosis --> excess H+ moves inside the cell adn K+ ecits to maintain neutrality 3. lack of transcellular shift of K: elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis --> H+ enters the cell with organic anion thus remaining electroneutral so transcellular shift of K does not occur see syllabus p. 105 for your drawing |
|
|
True of False:
Regarding internal K+ balance, if you give too much digoxin for, say CHF, you could potentially inhibit the Na-K ATPase |
True
|
|
|
|
Regarding internal K+ balance, name things that shift K+
A. out of the cell (3) B. into the cell (2) |
A. Shifting K+ out of the cell: Hyperosmolarity (via solvent drag), exercise, cell lysis
B. Shift K+ into the cell: Insulin, beta-agonists |
|
|
|
Regarding external (renal) K+ balance, what do the following do to K+ secretion?
A. acidosis B. alkalosis C. presence of other luminal anions D. Thiazide diuretics E. Loop diuretics F. K sparing diuretics |
A. acidosis: decreases K+ secretion because H+ enters the cell, K leaves the cell, decreased intracellular K concentration and thus decreasing secretion
B. alkalosis: stimulates K+ secretion b/c opposite of above C. presence of other luminal anions: increased K+ secretion D. Thiazide diuretics: increased E. Loop diuretics: increased F. K sparing diuretics: decreased |
|
|
|
What are the clinical symptoms for
A. hypokalemia B. hyperkalemia |
for BOTH hypo and hyper,
- generalized muscle weakness, - muscle cramps - cardiac ectopy / arrhythmias |
|
|
|
What are the effects of hypokalemia on the EKG?
|
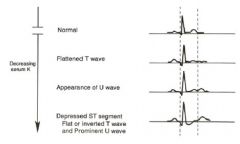
|
|
|
|
Hypokalemia is often associated with a prominent ___ -wave.
|
Prominent U0wave.
|
|
|
|
What are the hyperkalmia readings on an EKG?
|
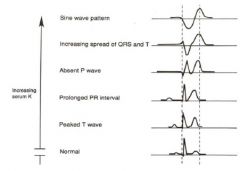
|
|
|
|
How do you determine the cause of hypokalemia?
|
1. History
2. Urinary potassium to creatinine ratio. If > 22 mEq of K per gram creatinine, then it is urinary potassium wasting. Otherwise, poor intake, excess GI loss or tranascellular shift prob. |
|
|
|
Which of the following is/are not cause(s) of hyperkalemia?
A. strenuous exercise B. metabolic acidosis C. primary hyperaldosteronism D. excess insulin E. beta adrenergic antagonist |
C. primary hyperaldosteronism
D. excess insulin are causes of HYPOkalemia, the rest are causes of hyperkalemia |
|
|
|
When hyperkalemia is reported, what is the first thing to do?
|
Obtain an EKG to check for changes.
|
|
|
|
What drugs cause hypokalemia? (3)
|
Diuretics, Amphotericin B, Aminoglycosides
|
|
|
|
Which types of Renal Tubular Acidosis cause hypokalemia?
|
RTA Type 1 and RTA Type 2
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hyperkalemia?
|
1. Calcium to stabilize heart membrane!
2. redistribution of patssium into the cell (glucose and insulin bolus, beta-2 agonist like albuterol, or if they are acidic sodium bicarbonate 3. Removal of potassium from the body: kayexalate, sodium polystyrene, diuretics or dialysis |
|
|
|
True or False:
If you are hypomagnesemic, can't reabsorb K+ and thus lose K+ in urine. |
True
|
|
|
|
What is NOT reabsorbed primarily in the proximal tubule portion of the nephron?
A. Na+ B. K+ C. Ca++ D. Mg++ E. P |
D. Mg++
It is primarily reabsorbed in the thick ascending limb of the loop of henle! |
|
|
|
In the thick ascending limb of the loop of henle, what two cations compete for reabsorption?
|
Mg++ and Ca++
Thus, hypercalcemia decreases Mg reabsorption; hypermagnasemia decreases Ca reabsorption |
|
|
|
What are possible causes of hypermagnasemia?
|
Magnesium infusion (to treat preeclampsia), magnesium ingestion (laxatives, Epsom salts), near drowning in the Dead Sea, DKA, Lithium ingestion
|
|
|
|
What are possible causes of hypomagnesemia?
|
*Poor dietary intake
*GI losses like 1. diseases assoc with generalized malabsorption like diarrhea, steatorrhea, small bowel bypass surgery 2. Congenital defect in Mg reabs 3. Acute pancreatitis 4. Proton Pump Inhibitors (anything that prevents Na+ reabs prevents Mg++ reabs too since Mg++ pretty much follows Na+ around) *Renal losses 1. inhibition of sodium reabs 2. primary defect in Mg reabs |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of hypomanesemia?
|
Very similar to effects of hypocalcemia and hypokalemia which frequently accompany it.... Tetany, numbness and tingling, positive Chevostek's and Trousseau's sign.
|
|
|
|
What are the cardiac effects of hypomagnesemia?
|
Widening of the QRS, Peaked T waves, Prolongation of the PR interval, Increased risk of toursade de pointes
|
|
|
|
Magnesium is a calcium channel blocke and high intracellular magnesium blocks potassium channels in the heart. Thus, milkd hypermagnesemia yields ______ and _______ while severe hypermagnesemia yields _______ and ________.
|
Mild hypermagnesemia yields bradycardia and hypotension;
severe hypermagnesemia yields complete heart block and cardiac arrest |
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hypermagnesemia?
|
Depends on the renal function. If normal or improving renal function, then stop Mg ingestion adn simply observe and Mg should come down on its own. BUT if pt has renal failure, then dialysis is treatment. Calcium chloride IV can antagonized some of the actions of hypermagnesemia.
|
|
|
|
Hypomagnesemia is frequently accompanied by what three other conditions?
|
Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and metabolic alkalosis.
|
|
|
|
What are symptoms of hypermagnesemia?
|
Nausea and vomiting, hyporeflexia, hypotension, somnolence, heart block, paralysis
|
|
|
|
When can you use Winter's formula to calculate renal rules for compensation?
|
For metabolic acidosis!
Winter's formula: Expected pCO2 = (HCO3 X 1.5) + 8 |
|
|
|
What are the 7 causes of respiratory alkalosis Dr.D wants you to know?
|
Sepsis
Anxiety Aspirin toxicity Pneumonia Asthma Prengancy Cirrhosis |
|
|
|
What are the differential diagnosis for respiratory alkalosis that you need to know? (8)
|
Hysteria/Anxiety
Salicylate Toxicity Pneumonia High Altitude Pregnancy Cirrhosis Asthma (v. similar list to the 7 causes of respiratory alkalosis Dr.D wants us to know: Sepsis, Anxiety, Aspirin toxicity, Pneumonia, Asthma, Prengancy, Cirrhosis |
|
|
|
The following are differential diagnoses for which acid base condition:
COPD, narcotics |
respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
|
The following are differential diagnoses for which acid base condition:
hysteria/anxiety, salicylate toxicity, pneumonia, high altitude, pregnancy, cirrhosis, asthma |
respiratory alkalosis
|
|
|
|
The following are differential diagnoses for which acid base condition:
salicylate toxicity, pneumonia, high altitude, pregnancy, cirrhosis, asthma |
respiratory alkalosis
also hysteria and anxiety |
|
|
|
The following are differential diagnoses for which acid base condition:
pneumonia, high altitude, pregnancy, cirrhosis, asthma |
respiratory alkalosis
also hysteria and anxiety, as well as salycilate toxicity |
|
|
|
The following are differential diagnoses for which acid base condition:
Saline responsive: vomiting, volume contraction, diuretics Saline unresponsive: primary hyperaldosteronism bilateral hyperplasia, adenoma, renal vascular disease |
metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
|
What are possible differential diagnoses for:
A. normal anion gap metabolic acidosis B. elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis |
A. normal anion gap MA: diarrhea, RTA (Type 1: Distal –acidifcation defect ; Type 2: Proximal –defective bicarbonate reabsorption ; Type 4 –Hyperkalemia causing inhibition of ammonia synthesis and too little buffer found in the urine) , Renal failure
Elevated anion gap MA: MUDPILES (methanol, Uremia, DKA, propylene glycol, isoniazid, lactic acidosis, ehtylene glycol, ethanol. salicylates) |
|
|
|
Regarding MUDPILES, methanol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to _________ and ________.
|
methanol is metabolized to formaldehyde and formic acid. It is the formic acid which is toxic and causes blindness and basal ganglion infarcts.
|
|
|
|
Regarding MUDPILES, ehtylene glycol is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to _______ and ______.
|
glycolic and oxalic acids, which can injure the kidney
|
|
|
|
Renal tubular acidosis is a group of disorders in which the kidney is unable to maintain acid-base balance despite normal or near normal glomerular filtration rate. Match the defect to the type of RTA.
1. defect is in hydrogen ion secretion or inability to acidify the urine 2. defect is ammonia excretion 3. defect is in deficient bicarbonate reabsorption from the filtrate. |
1. Type 1 RTA (distal)
2. Type 4 RTA: primary problem is hyperkalemia which turns off ammonia synthesis 3. Type 2 RTA (proximal) |
|
|
|
What is the "delta-delta" calculation?
|
It compares the anion gap value to the bicarbonate value. If your anion gap is increased, there should be an equal number decrease of bicarbonate since that bicarb buffers the additional anions. If the two are not matched, then it tells you what additional acid base disorder is present.
|
|

