![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Proximal nephron |
Activities vitamin D |
|
|
Kidney produce erthropoeitin |
Not be able to produce blood cells |
|
|
Renin |
Produce by juxtaglomerullary cells and cause increase in BP and perfusion pressure in kidney |
|
|
Renal medulla contain |
Only collecting ducts and loop of henle |
|
|
Collecting ducts function |
Passively absorb water by ADH due to 1200 osmolarity of solution |
|
|
Cortex more metabolically active |
Medulla more susceptible to ischaemia |
|
|
Maccula densa more NaCl |
Constriction of Afferent arterioles Dec RBF and GFR |
|
|
GFR control by |
Stretching and Tubular glomerular feedback |
|
|
Constriction of R2 |
Inc GFR results in diuresis |
|
|
Increase R1 |
Dec GFR, less will be delivered, higher will be recovery percentage Its done in order to conserve more water and substance |
|
|
R1 and R2 |
|
|
|
Normal GFR 120 ml /min if we remove 1 kidney |
GFR dec only by 25 percent because other nephrons compensate |
|
|
GFR factors |
|
|
|
If inject saline to a patient |
It doesn't contain plasma proteins but dilute plasma proteins and that increases GFR |
|
|
In vomiting and diarrhoea |
Loses water and increase plasma proteins that decreases GFR that induce the Diuresis |
|
|
GFR at afferent and efferent sites |
|
|
|
If Filteration fraction increase |
The plasma proteins contents increase at efferent site which cause of increase of reabsorption at peritubular capillaries |
|
|
Force promoting filtration |
Always takes as positive in addition And only PGC is positive that is 45 mmHg |
|
|
Capillaries have larger pores than proteins but it don't allows proteins to pass |
Because capillaries pores are negatively charged |
|
|
If we disrupt the membrane of the nephron |
It will filter the protein that will appear in urine I.e nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
If substance freely filtered by kidney then the ratio of plasma conc. / Filtrate conc.? |
TF/P=1 |
|
|
If increase the plasma conc. Of glucose or freely filtered substance the more glucose will be filtered |
But the percentage remains 20% |
|
|
If flow decrease |
Then the filtration increase and vice versa |
|
|
If we give angiotensin 2 blocker |
It mainly affects efferent and dilates thAt dec GFR and dec FF |
|
|
Kidney secrets |
Fixed acids and H+ |
|
|
Filteration load |
GFR*Px |
|
|
In pregnancy glucose appears in urine |
Because both GFR and Px increases Filteration load increases of glucose |
|
|
Plasma cretinin |

Is the clinical index of GFR that is index of renal Function Creatine is estimate of GFR |
|
|
GFR depends upon |
Capillaries permeability Surface area Both causes nephrotic syndrome in distorted situation |
|
|
Transport proteins |
Acquired defects in proteins are cause of kidney diseases and Transport proteins are important drug targets |
|
|
Tm |

|
|
|
Increase transporters proteins |
Increase TM |
|
|
Tm reached when u saturate the carriers |
Not under normal physiological conditions |
|
|
Transport medicated proteins |
Transport only natural isomers not others D glucose is natural but L glucose is not But this rule don't apply in simple diffusion |
|
|
Competition |

|
|
|
Secondary active transport |
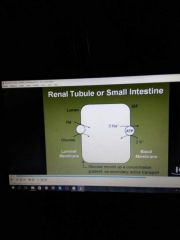
Will always indirectly depend on Atpase activity If we decrease Atpase pump in diagram secondary active transport will decrease because cell Na conc will increase |
|
|
Secondary active transport example |
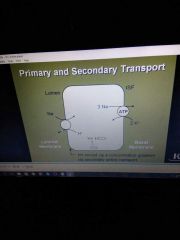
|
|
|
No reabsorption of glucose after proximal part |
All other is excreted then |
|
|
Glucose transport |

Splay is present because you don't saturate carrier at the same time At start of splay nephrons start to dump the glucose because some nephrons are saturated |
|
|
380mg/min is TM transport maximum normally |
And TM is a good and perfect index of functional nephrons.. |
|
|
If we remove one kidney |
The TM become half completely and it can be compensated... |
|
|
Reabsorption of glucose |
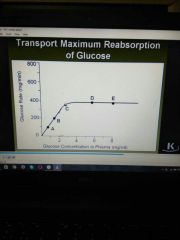
Minimum glucose appears in plasma at point C and reabsorption is below TM Point E??? |
|
|
If we increase GFR |
Renal threshold decreases In pregnancy renal threshold decreases |
|
|
Reabsorption |

Urea follows water if you excrete more water in diuresis more urea will be excrted |
|
|
Proximal reabsorption gradient |
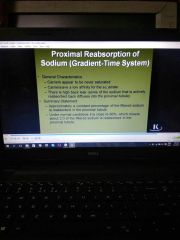
|
|
|
More GFR |
More metabolical rate of the kidney More Filteration is done of Na and more reabsorption is done.. |
|
|
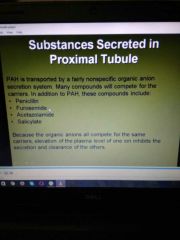
Tubular secretion |

Freely filtered substance are not reabsorbed and PAH is freely filtered... Protein carriers pump this PAH from peritubular capillaries to lumen |
|
|
PAH |
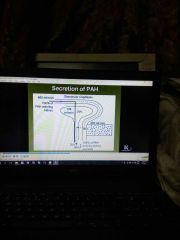
|
|
|
Asdf |
|
|
Imp formulas |

|
|
|
Filter load - Excretion rate = reabsorption |
Reabsorption |
|
|
Clearance |
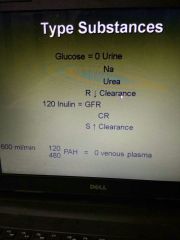
|
|
|
Clearance curve |

|
|
|
If drug stops the filtration of glucose |
The GFR will be equal to Clearance |
|
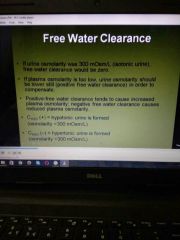
Water clearance |

|
|
|
Type 2 renal acidosis |

If Na H pump fail and there will be lose of bicarbonate ion that will cause renal acidosis type 2 |
|
|
2/3 water is absorbed in proximal tubules |
And all other are maximum absorbed in proximal tubes |
|
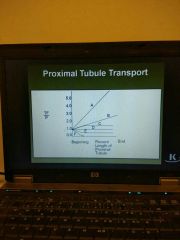
|
D is sodium F is glucose B is inulin A is PAH |
|
|
Inulin conc. |
Lowest at start of the bowman capsule Highest at the end of the system |
|
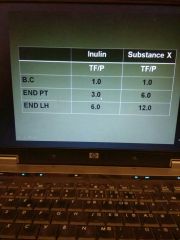
|
At Arrow side if value is 1.0 it means that water is not absorbed so value of inulin is constant |
|
|
All the reabsorption in proximal part is due to water absorption and all this is powered by Na K Atpase pump |
All is dependent on Na K pump.. |
|
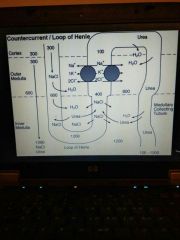
|
Osmolarity max at tip of loop of henle Osmolarity decreases in ascending thick limb Fluid leaving ascending limb is hypotonic Early part of distal tubule has lowest osmolarity |
|
|
Uncontrollable diabetics |
Proximal part don't works Results in large amount of urines |
|
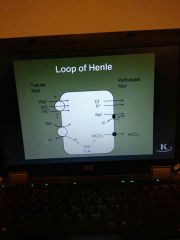
|
Loop |
|
|
Bicarbonate absorbed |
In late distal tubules is brand new |
|
|
Type 2 renal acidosis |
Due to diminished capacity of reabsorption of bicarbonate ion in proximal tubules |
|
|
Fanconi syndrome |
Proximal tubule gets defective and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. |
|
|
Renal acidosis type 1 |
Failure of distal tubule to secrete fixed acid... |
|
|
Acidosis in cell shrinkage promote hyper kalemia |
Alkalosis in cell swelling promote hyopkalemia |

