![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
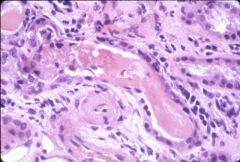
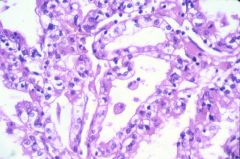
What is this disease?
Morphology - tubular cells detached from basement membrane and sloughed into the lumen - skipped areas in renal tubules - eosinophilic casts (Tamm-Horsefall protein) |
ischemic tubular necrosis
|
|
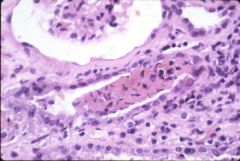
What is this disease?
Mophology - tubular epithelial cell necrosis - basement membrane intact - see crystals |
toxic tubular necrosis
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of acute tubulat necrosis.
|
- tubular cell injury: high metabolic rate and O2 requirement to maintain charged surface
- intrarenal vasoconstriction: increased Na delivery -> renin release; sublethal injury -> endothelin release and decreased vasodilators (NO, PGI) production |
|
|
Which phase of acute tubular necrosis is this?
- rising BUN - oliguria |
initiating phase:
- first 3 hours |
|
|
Which phase of acute tubular necrosis is this?
- sustained oliguria - salt, water overload - hyperkalemia - metablic acidosis |
maintenance phase
|
|
|
Which phase of acute tubular necrosis is this?
- increase in urine volume - hypokalemia - nomal BUN, creatinine |
recovery phase
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of pyelonephritis.
|
- ascending endogenous infection: ex catherization
- obstruction of urine outflow: prostatic hypertrophy, stone, tumors, pregnancy - hematogenous infection from bacteremia - vesicoureteral reflux: abbormal angle of ureter |
|
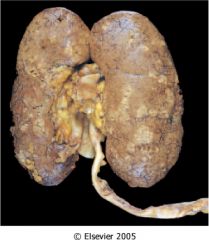
What is this disease?
|
acute pyelonephritis
- cortical surface: gray-white zones of inflammation and abscess |
|
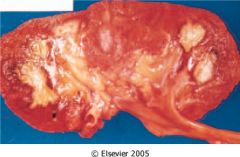
What is this called? what disease is this associated?
|
Papillary necrosis associated as a result of acute pyelonephritis
- demarcated zones of pale gray necrosis limited to renal papillae - associated with diabetes mellitus, analgesic nephropathy, sickle cell disease, obstruction |
|
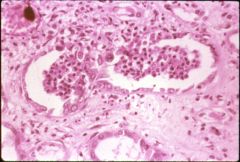
What is this disease?
- flank pain, fever, malaise - dysuria, frequency - glomeruli not affected |
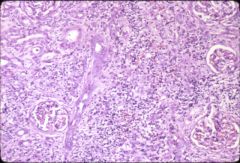
Acute pyelonephritis
- neutrophils filling tubule with epithelial necrosis - interstitial inflammation, bacterial aggregates |
|
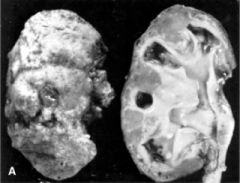
What is this disease?
|
chronic pyelonephritis
- small, irregular scarred kidney - corticomedullary scar over dilated deformed calyx - dilated cortical tubules filled with acellular protein (thyroidization) |
|
|
Etiology of pyelonephritis.
|
gram negative bacilli
- E.Coli (most common) - protus - klebsiella - enterobacter - strep fecalis |
|
|
What is this drug?
- causes drug-induced interstitial fibrosis, minimal GN, and membranous GN |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of drug-induced interstitial fibrosis.
|
hypersensitivity reaction
- hapten (drug) - IgE mediated |
|
|
Etiology of drug-induced interstitial fibrosis.
|
- antibiotics: methicillin
- NSAIDs |
|
|
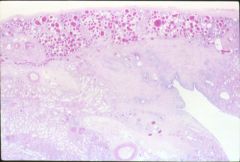
What is this disease?
- fever, hematuria - eosinophilia, rash |
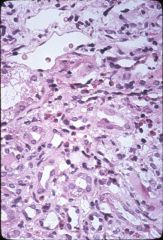
acute drug induced interstitial fibrosis
- intersitial edema, inflammation: monocyte, lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils |
|
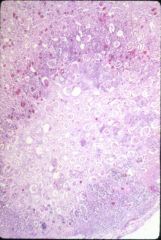
What is this disease?
|
analgesic abuse nephropathy
- necrotic papilla with overlying scar: ghost papilla - columns of Bertin spared |
|
|
What is this disease?
- headache, anemia, HTN - renal stone formation - kidney lose concentrating ability |
analgesic abuse nephropathy
- phenacetin - ASA - acetaminophen - caffeine - codeine |
|
|
Pathogenesis of acute urate nephropathy.
|
- precipitation of uric acid crystals in tubules: obstruction and acute renal failure
- chemotherapy: abundant uric acid from disintergrating tumor cell nuclei |
|
|
List three urate nephropathy.
|
- acute uric acid nephropathy: obstruction, acute renal failure, chemotherapy
- nephrolithilasis: usric acid calculi - chronic urate nephropathy: gout, lead exposure |
|
|
What kidney problem will this cause?
- lead exposure: "moonshine whisky" |
chronic urate nephropathy
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of chronic urate nephropathy.
|
- chronic hyperurecemia: monosodium urate crystals in distal tubules and collecting duct
- tophus: lymphocytes, foreign body giant cell, fibrosis - lead exposure: moonshine whisky |
|
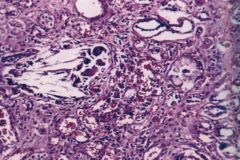
What is this called? what disease is this associated with?
|
tophus
- seen in chronic urate nephropathy - lymphocytes, foreign body giant cell, fibrosis |
|
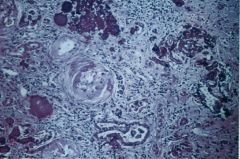
What is this disease?
|
- deposition of excessive Ca2+ in the kidney
- secondary to: hyperparathyroidism, multiple myeloma, VitD intoxication, metastatic malignancy in bones, excess Ca2+ intake |
|
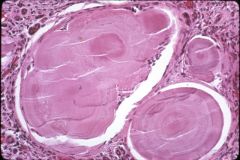
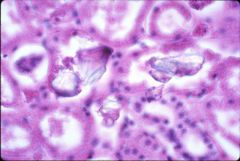
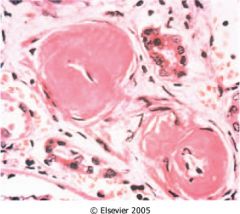
What disease is this disease?
- cast in the picture contains monoclonal free light chain with Tamm-Horsfall protein |
multiple myeloma
- laminated paraprotein casts: obstruct urine outflow - associated with amyloidosis, light chain nephropathy, hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, vascular disease and infection |
|
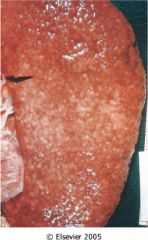
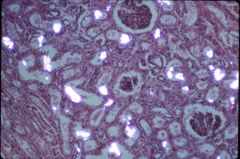
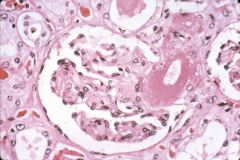
What is this disease?
- punctate granularity of surface |
benign nephrosclerosis
|
|
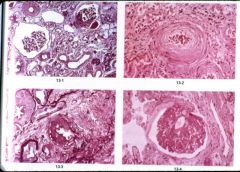
What is this disease?
- shruken glomerulus - thick vessel - elastic proliferation |
benign nephrosclerosis
- sclerosis of renal arterioles and small arteries |
|
What is this? what renal disease is this seen in?
|
benign nephrosclerosis
- universal with aging - accelerated by diabetes, hypertension |
|
|
What is this disease?
- medial, intimal thickening - hyaline deposits - fibroelastic hyperplasia |
benign nephrosclerosis
|
|
|
What renal disease would this cause?
- diastolic pressure>130mmHg |
malignant nephrosclerosis
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- retinopathy, papilledema - elevated plasma renin - proteinuria, hematuria - headache, nausea, vomit |
malignant nephrosclerosis caused by uncontrolled HTN
- eye problem - headache, nausea, vomit caused by increased intracranial pressure |
|
What is this disease?
|
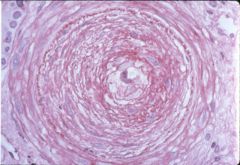
malignant nephrosclerosis
- hyeprplastic arteriolitis - fibrinoid necrosis |
|
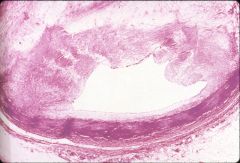
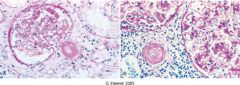
What is this disease?
|
renal artery stenosis
- irregular and asymmetric media hyperplasia - disordered medial smooth muscle |
|
|
What are some causes of renal artery stenosis?
|
- atherosclerotic plaque (most common): men, old age, DM
- fibromuscular dysplasia: young women - constriction of one renal artery -> renin secretion, AngII |
|
|
What is "goldblatt kidney"?
|
constriction of one renal artery leads to HTN via secretion of renin by JG cells and production of AngII
|
|
|
What drug can be used for renal artery stenosis?
|
ACE inhibitors
|
|
|
Name some thrombotic microangiopathies that affect the kidney.
|
- HUS (hemolytic uremic syndrome): E.Coli(O157:H7)
- TTP (thrombocytopenic purpura) |
|
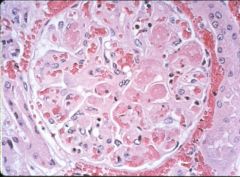
What is this disease?
|
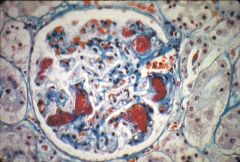
thrombotic microangiopathies
- HUS: mainly renal - TTP: mainly CNS |
|
|
HUS or TTP?
- mainly CNS involvement |
TTP
|
|
|
HUS or TTP?
- mainly renal involvement |
HUS
|
|
|
Possible caueses adult HUS/TTP?
|
- idiopathic
- infections: endotoxin from E.Coli, shiga toxin from shigella - SLE: anticoagulant syndrome - post partum failure - vascular renal disease: scleroderma, malignant HTN - chemotherapy: mitomycinC, cyclosporin, bleomycin, cispalin |
|
|
What is this disease?
- schistocytes in peripheral blood smear - thrombocytopenia - renal failure |
thrombic microangiopathies
|
|
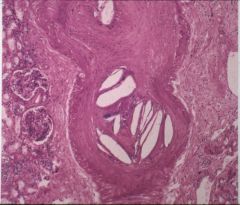
What is this? what can cause this?
|
cholesterol clefts
- seen in athero-embolic renal disease - often after surgery on abdominal aorta or angiopathy |
|
|
Pathogenesis of sickle cell nephropathy.
|
hypoxic and hyertonic envionment -> accelerated sickling -> increased viscosity -> plugging of vessels -> proteinuria, hematuria, papillary necrosis, impaired concentrating ability
|
|
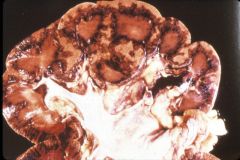
What is this disease? pathogenesis?
|
diffuse cortical necrosis
- secondary to disseminated intravascular coagulation -> ischemic necrosis of renal cortex - after placental abruption, septic shock, extensive sugery |
|
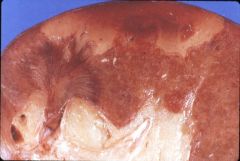
What is this disease?
|
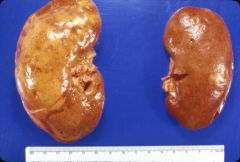
renal infarct
- wedge shaped pale areas - emboli from left ventricle (post MI) or left atrium (atrial fibrillation) |
|
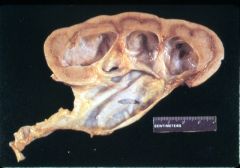
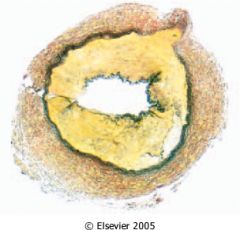
What is this disease?
|
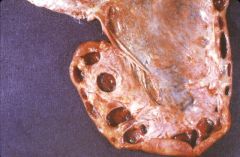
hydronephrosis
|
|
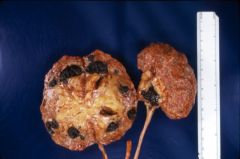
What is this?
|
renal stone
|
|

What is this? what is the composition?
|
struvite stone
- magnesium ammounium phosphate salt |
|
|
Etiology for hydronephrosis.
|
obstruction
- pelvic obstruction - ureter(intrinsic) - ureter(extrinsic): pregnancy, tumors, retroperitoneal fibrosis - vesicoureteral reflux - bladder - urethra: posterior valve stricture |
|
|
Name some types of renal stones.
|
- calcium oxalate: hypercalcemia, hyperoxaluria
- struvite: assoiciated with protus (urea splitting) - uric acid: gout, chemotherapy - cystine |
|
|
Pathogenesis of struvite.
|
urea pliting protus -> urea converted to ammonia -> alkaline urine -> precipitation of magnesium ammonium phosphate salts
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of uric acid stones.
|
- gout
- chemotherapy - acid urine (pH<5.5): uric acid less soluble - radioluscent |
|
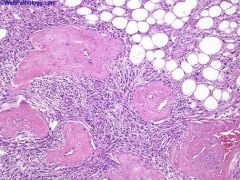
What is this disease?
|
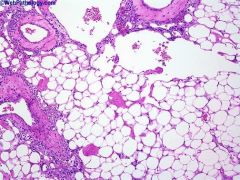
angiomyolipoma
- prominent vessels - fat cells - muscles |
|
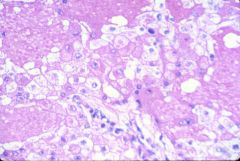
What is this renal tumor?
- eosinophilic cells with prominent granular cytoplasm |
oncocytoma
- eosinophila because of abundant mithochondria |
|
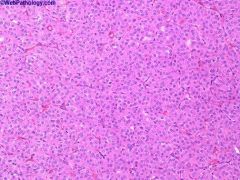
What is this disease?
|
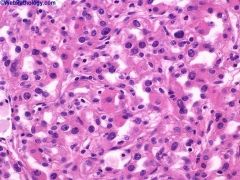
Clear cell carcinoma
- chromosomal translocations: t(3:6), t(3:8), t(3:11) |
|
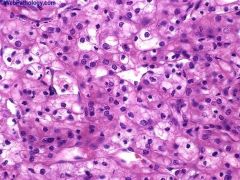
What is this disease?
|
Clear cell carcinoma
- chromosomal translocations: t(3:6), t(3:8), t(3:11) |
|
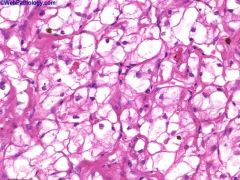
What is this disease?
|
Clear cell carcinoma
- ancinar type: gland forming |
|
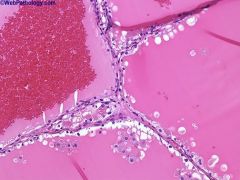
What is this disease?
|
Clear cell carcinoma
- cystic pattern |
|
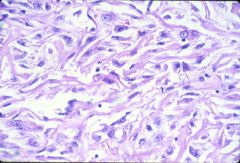
What is this disease?
Gross - fleshy, solid tumor Histo: see picture |
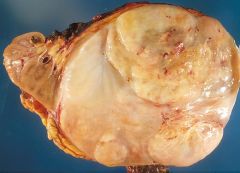
Clear cell carcinoma
- sarcmatoid variant: spindle shaped cells |
|
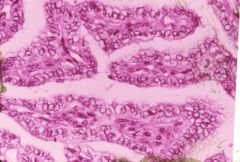
What is this disease?
- trisomies - mutations in MET oncogene |
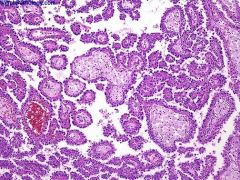
hereditary papillary carcinoma (chromaphil)
- multiple bilateral carcinimas |
|
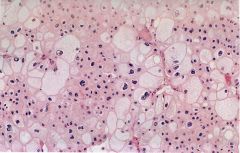
What is this disease?
- chromosome losses - hypodiploidy |
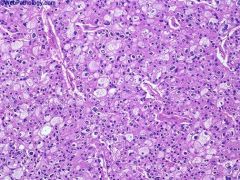
chromophobe renal carcinoma
- lines up vasculature |
|
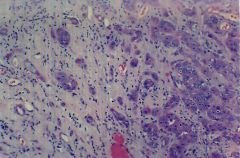
What is this disease?
|
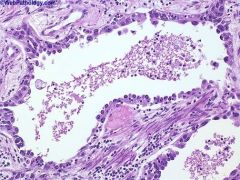
collecting duct carcinoma
- fibrotic |
|
|
What type of cells are renal cell carcinoma derived from?
|
renal tubular cells
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- hemangioblastoma of cerebellum and retina - renal cysts or bilateral renal cell carcinoma |
von Hippel_Lindau syndrome
|
|
|
What is the 4th most common pediatric malignant tumor in the US?
|
Wilms tumor
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- aniridia - genital anomalies - mental retardation |
WAGR syndrome
- 33% chance of developing wilms tumor |
|
|
What is the genetic defect in WAGR syndrome?
|
germline deletion of 11p13
- WT1 and PAX located here |
|
|
What is this disease?
- male pseudohermaphrodism - early mesangial sclerosis |
Denys-Drash syndrome
- germline mutations in WT1 - 90% risk of developing Wilms tumor |
|
|
What is this disease?
- germline mutations in WT1 - 90% risk of developing Wilms tumor |
Denys-Drash syndrome
- male pseudohermaphrodism - early mesangial sclerosis |
|
|
What is this disease?
- organomegally - macroglossia - omphalocele - renal medullary cysts - adrenal cytomegaly |
Beckwith-Wiedmann syndrome
- chromosome allelic loss in 11p15.5 (WT2) |
|
|
What is this disease?
- chromosome allelic loss in 11p15.5 (WT2) |
Beckwith-Wiedmann syndrome
- organomegally - macroglossia - omphalocele - renal medullary cysts - adrenal cytomegaly |
|
|
What is this disease?
- germline deletion of 11p13 (WT1 and PAX) - 33% chance of developing Wilms tumor. |
WAGR syndrome
|
|
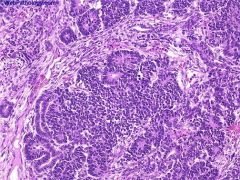
What is this disease?
|
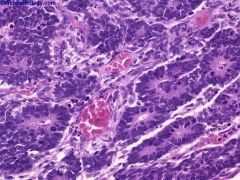
Wilms tumor
- blastema cells - epithelial cells - stromal cells |
|
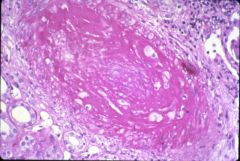
What type of transplant rejection is this?
|
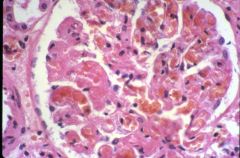
hyperacute rejection
- circulating antibodies to graft in recipient - acute renal failure leading to anuria |
|
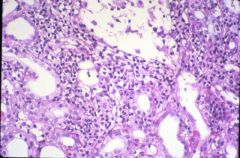
What type of transplant rejection is this?
|
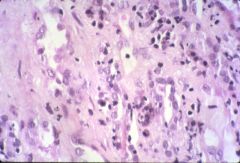
acute rejection (celluar)
- interstitial inflammation: CD8, CD4, moncyte, plasma cells - interstitial edema and tubulitis |
|
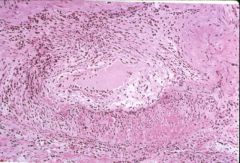
What type of transplant rejection is this?
|
acute rejeciton (vascular)
- antibody, humoral - vasculitis - endothelial swelling, luminal narrowing - thrombosis - medial layer not involved |
|
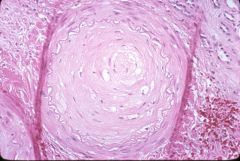
What type of transplant rejection is this?
|
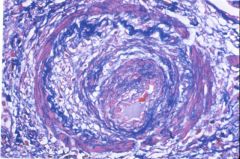
chronic rejection
- severe stenosis of large and medium arteries (intimal fibrosis) with secondary ischemia - tubular atrophy, glomerulosclerosis - interstitial fibrosis |

