![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Main kidney functions (4) |
Regulate water, electrolyte balance Excrete waste products: urea, creatinine, drugs Regulate acid-base balance Produce hormones: renin, calcitriol, Epo |
|
|
Filtrate modification: big picture |
Reabsorption of useful things Secretion of unwanted things |
|
|
Kidney anatomy |
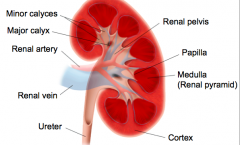
|
|
|
Renal artery to renal vein: vessel names |
Renal artery --> interlobar --> arcuate --> interlobular --> afferent arteriole --> glomerular capillaries --> efferent arteriole --> peritubular capillaries/vasa recta --> interlobular vein --> arcuate vein --> interlobar vein --> renal vein |
|
|
Nephron: # per kidney, structures |
1-1.3 million/kidney Renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman's capsule), proximal tubule, Loop of Henle, distal tubule, collecting duct |
|
|
Glomerular filtration barrier |
Fenestrated capillary endothelial GBM: glycoproteins, heparan sulfate proteoglycans Podocytes: foot processes, filtration slit diaphragms between (nephrin, podocin, others) --> size selectivity |
|
|
Mesangium: constituents, function |
Mesangial cells, mesangial matrix Structural support for glomerular capillaries, secrete ECM, smooth muscle --> influence filtration rate |
|
|
Juxtaglomerular apparatus: cell types, function |
Macula densa: specialized cells for NaCl sensing Extraglomerular mesangial cells Granular cells: produce and store renin |
|
|
Proximal tubule: main function, specialized structure |
Main function: reabsorbs 55-60% filtrate (primary site for NaCl and water reabsorp) Only tubule segment with apical brush border (increase surface area for reabsorption) Many mitochondria for active transport |
|
|
Loop of Henle: main roles |
Reabsorbs 25-35% of NaCl Critical role in urine concentration |
|
|
Distal tubule: main roles |
5% NaCl reabsorbed Primary site for calcium regulation |
|
|
Collecting duct: main sections, main functions |
Cortical collecting duct - principal cells: NaCl reabsorption, K+ secretion - intercalated: acid-base balance Medullary: ADH regulated water, urea transport |
|
|
Classes of nephrons |
Cortical nephrons: short LOH, peritubular capillaries Juxtamedullary nephrons: glomerulus adjacent to medulla, long LOH, peritubular capillaries and vasa recta |
|
|
Kidney innervation: efferent, afferent |
Efferent: sympathetic ONLY: vasoconstriction, increase Na+ reabsorption, stimulate renin secretion Afferent: baroreceptors in interlobular, afferent; chemoreceptors in renal pelvis |

