![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the JNC VII Classification of Hypertension for:
A. Normal B. Prehypertension C. Hypertension, Stage 1 D. Hypertension, Stage 2 |
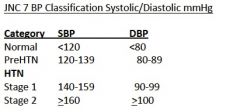
|
|
|
What are the consequences of HTN?
|
- stroke
- retinopathy - peripheral vascular disease - renal failure - heart failure |
|
|
True or False:
Hypertension is due to increased cardiac output and/ or increased peripheral resistance. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Differentiate the types of HTN.
1. Essential HTN 2. Secondary HTN 3. Isolated Systolic HTN 4. White Coat HTN 5. Acute severe HTN |
1. Essential HTN - no particular thing making you HTN
2. Secondary HTN - particular cause is identified and treatment of it can "cure" HTN 3. Isolated Systolic HTN - only systolic # is high (bottom isn't) 4. White Coat HTN - b/c of healthcare provider 5. Acute severe HTN - hypertensive crisis |
|
|
What is the JNC 7 definition of isolated systolic HTN?
|
greater than or equal to 140 mmHg systolic, and less than 90 diastolic
|
|
|
What is the most common form of HTN in the elderly? In general?
|
In the elderly : Isolated Systolic HTN
In general: Essential HTN |
|
|
True or False:
Systolic blood pressure increases with age and diastolic blood pressure tends to decrease. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Hypertensive [ Emergency / Urgency ] is blood pressure greater than 180/120 mmHg complicated by evidence of impending or progressive target organ dysfunction. Hypertensive [ Emergency / Urgency ] is BP > 180/110 or 120 mmHg but without the target organ damage.
|
Emergency, then Urgency
|
|
|
What are important secondary causes of hypertension (5-10% of all HTN) that you need to know for this course?
|
Primary hyperaldosteronism and renal vascular disease
|
|
|
Regarding treatment of HTN stages, what treatment is recommended for each?
1. Prehypertension, normal otherwise healthy adult 2. Prehypertension, diabetics with proteinuria 3. Stage 1 HTN 4. Stage 2 |
1. Prehypertension, normal otherwise healthy adult : lifestyle modification only
2. Prehypertension, diabetics with proteinuria: start on ACE inhibitor 3. Stage 1 HTN : start with one drug 4. Stage 2 : always need 2 drugs When treating with multiple drugs, choose drugs from different classes that attacks the hypertension from different sides of the BP regulatory mechanisms . When treating with multiple drugs, a diuretic should be one of them |
|
|
True or False:
Blood pressure normally increases in the mornign and decreases overnight. This is called dipping. Non dipping is associated with increased cardiovascular risk. |
TRUE
|
|
|
In which of the following conditions are ACE inhibitors AND ARBs CONTRAINDICATED?
A. Angioedema B. Bronchospastic disease C. Depression D. Liver Disease E. Pregnancy F. Second or third degree heart block |
A. Angioedema
E. Pregnancy |
|
|
When is a HTN condition considered "resistant" according to the JNC 7?
|
BP not controlled despite adherence to adequate doses of 3 antihypertensive medications, one of which is a diuretic.
|

