![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
GFR usually is constant in a single subject (without progressive renal failure) when measured under constant conditions. What will cause physiologic alterations in GFR?
|
- Diurnal variation: highest values in afternoon and lowest in middle of night.
- exercise transiently lowers filtration rate because shifts to other muscles - GFR increases during pregnancy - GFR increases with over hydration and decreases with water restriction. - GFR changes with age. Newborns have <50% GFR than that at 1 year. Over age 1 year, GFR in children is same as young adults and is constant until about 40s, when it starts to decline. |
|
|
We can estimate GFR by using endogenous markers. Name the four present.
|
Serum creatinine, BUN, plasma cistatin C, other biomarkers (NGAL, IL-18, KIM-1)
Most commonly used ones are creatinine and BUN. |
|
|
Why is creatinine not a perfect glomerular marker?
|
- Varies 10% day to day normally
- Not sensitive for detection of minimal impairment. GFR must be substantially reduced before serum levels are clearly abnormal. - GFR could be reduced by more than 50% in some individuals before serum creatinine is clearly elevated. - Can be increased by medications, which compete with creatinine secretion (cimetidine, trimethoprim) |
|
|
True or False:
Just looking at the BUN or creatinine value alone is not an accurate way of determining GFR. How can we use these markers and determine GFR? |
24 hour urine collection in which creatinine clearance is measured. A blood sample is also taken during that time period and analyzed for creatinine concentration.
Advantages: - endogenous substance (cr is a metabolite of creatine, a major muscle component - production is fairly constant and proportional to muscle mass - excretion primarily by glomerular filtration, a small amount is secreted by tubules Disadvantages: - slightly overestimates GFR (since some is secreted in tubules) - As GFR decreases, the percentage of creatinine in the urine due to secretion increases - subject to collection errors - Cr excretion increases after a meat meal |
|
|
How can we estimate creatinine clearance (Ccr) WITHOUT a 24 hour urine collection study?
|
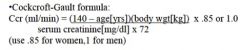
The other two equations are the abbreviated MDRD formula and new CKD-EPI equation. And for children, we use the Schwartz formula or Counahan-Barratt Equation.
|
|
|
Name the GFR ranges for the 5 stages of Chronic Kidney Disease.
|
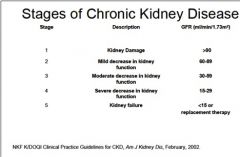
|
|
|
What is the equation for fractional excretion of sodium (FENa)?
|

Note: FENa is of limited value in the following condiitons: Chronic Kidney failure, use of diuretics, acute volume expansion, acute kidney failure due uto contrast, when prerenal azotemia is changing to acute tubular necrosis, and in early glomerulonephritis when glomerular filtration is decreased but tubular function is still maintained.
|
|
|
Under what conditions is the fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) not valid/useful? (7)
|

|
|
|
How do you write the short hand bone structure of chemistry values?
|
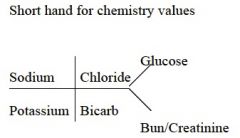
|
|
|
Men usually excrete _______ mg creatinine/kg in a 24 hour period whereas women usually excrete _______ mg creatinine/kg in a 24 hour period.
|
Men: 15-20 mg creatinine/kg
Women: 10-15 mg creatinine/kg |
|
|
What is the normal creatinine level (kind of arbitrarily set for this class)?
|
< 1.2 mg/dL
|

