![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How thick is the cortex of the kidney?
|
~1 cm
|
|
|
What imaging tools can be used to view the kidney?
|
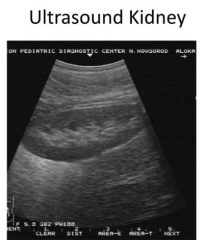
Ultrasound or CT
|
|
|
How does a kidney show up on an ultrasound?
|
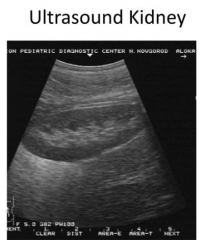
- Cortex = darker
- Medulla = lighter |
|
|
How many distal tubules combine and enter medulla to form Collecting Duct?
|
~6 distal tubules - form ducts of Bellini which drain into calyx
|
|
|
What is the organization of the glomerulus and mesangial cells?
|
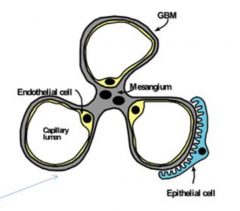
- Mesangium in center w/ 3 capillary loops of glomerular basement membrane
- Endothelial cells lines the inside of GBM - Epithelial cells on outside w/ podocytes |
|
|
What are the features of the glomerular endothelial cells as part of the filtration barrier?
|
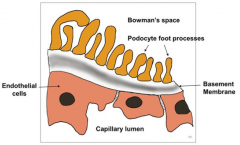
- Fenestrations: 70-100 nm
- Negatively charged surface - Form initial filtration barrier - Synthesize and maintain GBM |
|
|
What are the features of the glomerular basement membrane as part of the filtration barrier?
|
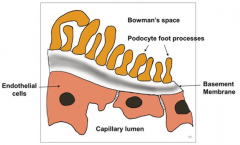
- Composed of type IV collagen
- Size and charge are main determinants of filtration - Heparan sulfate provides negative charge - Water and cationic proteins of LMW (<70,000) are permeable - Albumin permeability is limited by negative charge |
|
|
What are the features of the visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) as part of the filtration barrier?
|
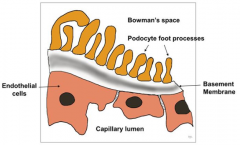
- Also synthesize and maintain GBM
- Cytoplasmic foot processes form filtration slit (slit pore) - Podocytes are negatively charged |
|
|
What is in the cell cytoplasm of mesangial cells?
|
Myosin filaments
|
|
|
What surrounds the mesangial cells?
|
Glomerular Basement Membrane like matrix
|
|
|
What are the functions of mesangial cells?
|
- Provides structural support
- Modulates glomerular filtration |
|
|
What are the congenital abnormalities associated with the kidneys?
|
- Aplasia, hypoplasia, dysplasia
- Ectropic kidneys - Fusion abnormalities - Duplication of ureters |
|
|
What is the most common congenital kidney disorder?
|
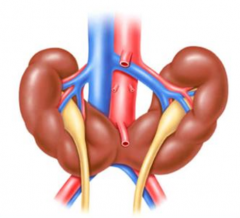
Horseshoe kidney
|
|
|
What percentage of horseshoe kidneys are fused at the lower poles?
|
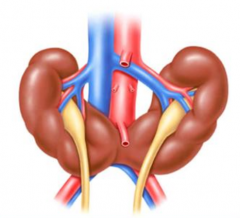
90%
|
|
What genetic issue is Horseshoe kidney associated with?
|
Turner's Syndrome
|
|
|
What are the complications of a horseshoe kidney anomaly?
|
- Increased risk of infection
- Kidney stones |
|
|
What cystic diseases are associated with the kidney?
|
- Renal dysplasia
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) - Medullary sponge kidney - Acquired cystic disease |
|
|
What is the most common cystic disease of the kidneys?
|
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
|
|
|
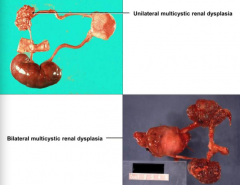
What are the types of Renal Dysplasia?
|
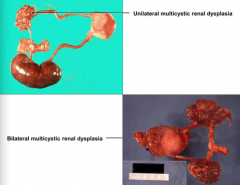
- Unilateral Multicystic Renal Dysplasia
- Bilateral Multicystic Renal Dysplasia (fatal) |
|
|
How do you detect Renal Dysplasia?
|
- Prenatal ultrasound
- Palpable mass - Asymptomatic (undetected into adulthood) |
|
|
What gene mutation / chromosome is responsible for Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
PKHD1 gene located on chromosome 6p21
|
|
|
How can you diagnose Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- In utero by ultrasound
- Large, hyperechoic kidneys - Oligohydramnios - decreased urine in fetal bladder |
|
|
How frequent is Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease? Who is it more common in?
|
- 1:20,000
- More frequent in caucasians |
|
|
What features are associated with Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Enlarged kidneys at birth
- Maternal oligohydramnios - Potter's facies - Pulmonary hypoplasia |
|
|
What is the prognosis for Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Serious cases are incompatible with life
- Perinatal mortality 30-50% |
|
|
What are the extra-renal manifestations of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Hepatic fibrosis
- Cholangitis (infection of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria) - Portal HTN (esophageal varices, GI bleeding) |
|
|
What are the morphological features of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Smooth kidney w/ numerous small cysts (cortical and medullary cysts)
- Cylindrical cysts extending radially through cortex - Microscopically cysts lined by cuboidal epithelium (may see epithelial hyperplasia) - Normal glomeruli |
|
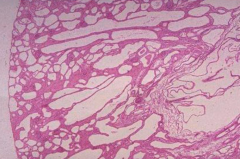
What does this histologically represent?
|
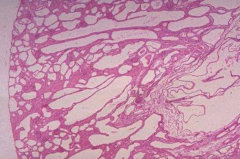
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
|
|
|
How frequent is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease? Who is it more common in?
|
- 1:400 - 1:1000 Americans
- Most common cystic disease of the kidneys |
|
|
How common is a LACK of family history in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Absent in 25-40%
- New mutations - Late onset renal failure |
|
|
What mutations commonly cause Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease? What chromosomes?
|
- 90% have mutation of PKD1 gene on chromosome 16
- Others have mutation of PKD2 gene on chromosome 4 |
|
|
How does the mutation you have for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease affect when you progress to renal failure?
|
- PKD1 (chr 16) progress to renal failure earlier (but in adulthood usually)
- PKD2 (chr 4) progress to renal failure at later age |
|
|
What are the possible causes of cyst formation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Abnormal differentiation of epithelial cells
- High proliferation rate - Secretion of fluid into cysts w/ loss of connection to functioning nephrons - Abnormal ECM |
|
|
What are the renal symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Hematuria
- Mild proteinuria - Hypertension - Progressive renal failure (50% reach ESRD by age 57-73) - Infections - Stones - Pain |
|
|
When do patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease get progressive renal failure? Implications?
|
- 50% reach ESRD by age 57-73
- They need to be on dialysis or kidney transplant to live |
|
|
What are the extra-renal symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Hepatic cysts (40%)
- Intracranial aneurysms (10-30%) - Cardiac valvular abnormalities - Arterial aneurysms (aorta, coronaries) - IVC thombosis - Inguinal and umbilical hernias - Pancreatic cysts |
|
|
What do 40% of patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease get?
|

Hepatic cysts
|
|
|
What do 10-30% of patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease get?
|
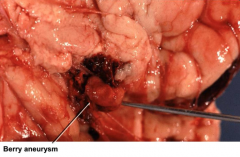
Intracranial Aneurysms
|
|
|
In what kidney disease do 40% get hepatic cysts and 10-30% get intracranial aneurysms?
|
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
|
|
|
How do you diagnose Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
Patients present in several ways:
- Symptomatic: flank pain and hematuria - Multiple bilateral cysts noted incidentally on imaging - Screening d/t family hx w/ ultrasound |
|
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease when a patient has a family history?
|
With ultrasound find:
- Age <30: at least 2 cysts - Age 30-59: at least 2 cysts on each kidney - Age >60: at least 4 cysts bilaterally |
|
|
What are the treatment goals of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
|
- Slow progression to ESRD (control BP and treat infections)
- Identify and manage extra-renal manifestations - Control pain - Dialysis / kidney transplant |
|
|
What are the common causes of acquired cystic disease?
|
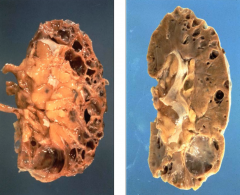
Develops in 50% of patients on dialysis and depends on duration of dialysis (the more years on dialysis, the more likely)
|
|
|
What symptoms are noticed with Acquired Cystic Disease?
|
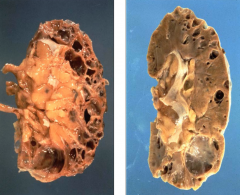
- Usually asymptomatic
- May present w/ bleeding or pain |
|
|
What are the morphological features of Acquired Cystic Disease?
|
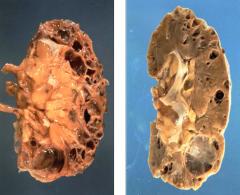
- Clear, fluid-filled cysts
- Uni- or multi-locular cysts - Cortex (usually) - May involve corticomedullary junction and medulla |
|
|
What type of cancer is Acquired Cystic Disease associated with an increased risk of?
|
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
When is a renal biopsy indicated?
|
- Persistent glomerular hematuria (need to rule out other causes of hematuria like cancer or kidney stone)
- Persistent nephrotic range proteinuria - Unexplained renal failure - Renal transplant rejection |
|
|
What are the contraindications for a renal biopsy?
|
- Bleeding disorders
- Anatomic abnormalities (eg, solitary kidney) |
|
|
What are the potential complications after a renal biopsy? How common?
|
- Self-limited gross hematuria (10%)
- Hematoma formation (80%) - Hemorrhage (1-2%) - surgery requiring (0.3%) - Death (1/8000) |
|
|
How do you do a renal biopsy?
|
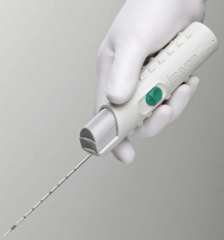
- Use long needle / instrument
- Real time guided by ultrasound (enter on side to avoid vessels) - Take 3 samples |
|
|
What tests are done to the tissue obtained from a renal biopsy?
|
- Light microscopy
- Direct immunofluorescence microscopy - Electron microscopy |
|
|
What do you do for light microscopy to study renal biopsy samples?
|
Silver, trichrome, PAS, and/or H&E stains
|
|
|
What do you do for direct immunofluorescence microscopy to study renal biopsy samples?
|
IgA, IgG, IgM, C3, C1q, albumin, fibrinogen, kappa, lambda (identifies patterns of immune-complex deposition)
|
|
|
What do you do for electron microscopy to study renal biopsy samples?
|
Identifies submicroscopic defects and sites of damage in glomerulus
|

