![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
417 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
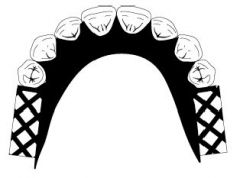
MASTER CAST: What are parameters for trimming it?
|
- Keep land area fairly low (no more than 2-3 mm above depth of vestibule)
- land area shouldnt be wider than 4 mm - base should be trimmed parallel to the alveolar ridge - borders should be smooth and rounded (NOT SHARP) - undercuts must be adequate |
|
|
What are some areas of undercuts that may need to be blocked out on COMPLETE MASTER CAST?
|
- MAXILLARY: Labial undercuts, frenal areas, tuberosities, rugae
- MANDIBULAR: thin ridges, labial undercuts, retromylohyoid region |
|
|
What is the purpose of making WAX OCCLUSAL RIM?
|
- to make jaw relation record (JRR)
|
|
|
What are the dimensions for WAX OCCLUSAL RIM?
|
- 7 mm anterior
- 10 mm posterior Mandibular rim centered over the ridge MAX RIM: 22mm anterior, 18mm posterior MAN RIM: 18 mm anterior |
|
|
How far should the mandibular wax rim extend up the retromolar pad?
|
1/2 to 2/3's up the retromolar pad
|
|
|
Describe the clinical adjustment / check points of maxillary wax rims:
|
1. Adjust length of anterior portion of rim
- should be stable and retentive - may need to stabilize with denture adhesive - check extensions - 1-2 mm of display when lip is at rest - check existing denture 2. Adjust labial contours to establish lip support - palpate/feel lip overlying rim to ensure not strained - naso-labial angle 90-120 degrees - good indicator of lip support 3. Check orientation of occlusal plane - use a fox plane - it should parallel interpupillary line - occlusal plane should be parallel to ala-tragus line 4. Place mandibular wax rim 5. In CR position the rims should contact evenly, if not they will need to be adjusted - check that heels of record base are not contacting - scribe 3 separate lines in patient's mouth on the max and mand rim - check outside the mouth to be sure adequate clearance posteriorly. - once wax rims contact evenly in CR, then vertical dimension can be established 6. Determine vertical dimension - establishes patients lower facial height - vertical height of the face determined by tooth contact - centric relation recorded at VDO - patient should be sitting upright 7. Determine VDR - vertical height of face while the mandible is at rest - usually 2-4 mm of space between teeth - VDO minus VDR = interocclusal distance = freeway space 8. Determine VDO: - place two dots (nose and chin) and measure distance when teeth are together and mandible at rest - determine interocclusal distance (IOD) - if large > 7mm due to loss of VDO as a result of resorption or occlusal wear, may need to restore some of the lost VDO - DO NOT INCREASE VDO BY MORE THAN 5mm - Generally patients tolerate insufficient VDO better than excessive VDO - interocclusal distance will determine how much space is available between the alveolar ridges for setting teeth - 2 mm of overlap 9. Mark midlines on wax rim 10. Record CR - place 2-3 notches on rims - Aluwax or PVS bite registration material - Trim PVS 11. Mount mandibular cast 12. Set pin to +1mm on articular when mounting. Then set to 0 so rims touch. 13. Make protrusive record. Aluwax or Regisil - patient should protrude no less than 4 mm and no more than 8 mm 14. Set horiz condylar guidance - loosen centric and condylar locks - rotate condylar housing until record fully seats - record condylar inclination - set lateral condylar guidance - H/8 + 12 = LCG (12-15 degrees) |
|
|
What things does Vertical dimension affect?
|
- esthetics
- phonetics - mastication - muscle function - comfort |
|
|
Define "Freeway space"?
|
VDO - VDR = interocclusal distance
|
|
|
What are three methods of determining VDO?
|
1. Boley guage method
2. Palpate for interocclusal distance with fingers on chin 3. Closest speaking space - rims should not touch when speaking "S" sound should have 1mm apart. |
|
|
Mandibular teeth on wax rim should be no further than:
|
depth of the vestibule
|
|
|
Where do you make marks on the wax rims?
|
- midline
- cuspid line - high lip line` |
|
|
Occlusal plane of maxillary rim should parallel what two lines?
|
- interpupillary line
- ala-tragus line |
|
|
What is the ala-tragus line?
|
- the line running from the inferior border of the ala of the nose to the superior border of the tragus of the ear.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of doing a protrusive record?
|
- to determine your horizontal and condylar guidance (inclination)
|
|
|
Provide a brief summary of the steps in adjusting wax rims and mounting master casts:
|
1. adjust length of anterior portion of maxillary
2. adjust labial contours to establish lip support 3. check orientation of occlusal plane 4. place mandibular wax rim 5. adjust wax rims until even contact in CR 6. establish vertical dimension of occlusion 7. After VDO established, rims contact evenly, proper amount of horizontal overlap should be established 8. mark landmarks on wax rims 9. facebow transfer record 10. mount maxillary master cast 11. record CR position 12. mount mandibular cast 13. make protrusive record 14. |
|
|
Define CHROMA:
|
- amount of hue in a colour (saturation)
|
|
|
Define HUE:
|
- principle modification of colour
|
|
|
Define VALUE:
|
- brightness of a hue
- value increases as an object becomes lighter or nearly white |
|
|
What are the pros/cons to using PORCELAIN TEETH?
|
PROS
- resistant to abrasion - very aesthetic - mechanically retained in denture with pins CONS - prone to breakage - discolouration around necks of teeth - need adequate inter-occlusal space |
|
|
What are the pros/cons of using ACRYLIC TEETH?
|
PROS
- easy to adjust - more resilient CONS - wear more easily than porcelain - bonds to denture base |
|
|
In what order do you set the teeth?
|
- Max centrals
- laterals canines - mandibular teeth |
|
|
What are the ideal properties of a reline material?
|
- Compatibility with oral tissues
- Compliance and resilience - Dimensional stability in moist environment - Rupture resistance - Adhesion to denture base - Wetability - Inhibition of bacterial/fungal growth |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of reline material?
|
- lack of long term stability/resiliency
- rough surface, harbors microorganisms - cleaning |
|
|
Describe the procedure of doing tissue conditioning / denture reline:
|
- Clean denture with scalers, burs, pumice, ultrasonic as necessary
-Reduce denture base as necessary - Place temporary soft liner - Trim/adjust - Home care instructions - Recall - Polish or send to lab |
|
|
How much overjet and overbite do you want?
|
2 mm overjet
1 mm overbite |
|
|
How much base reduction do you do on a denture prior to relining?
|
- If VDO adequate then 2 mm reduction
- if VDO insufficient then just roughen up the surface |
|
|
What are home-care instructions for relined denture?
|
- no brushing for 24 hours , rinse only
- brush external surface, wipe liner with cotton - eat soft foods - remove at night, keep immersed in water - massage tissues - use water only - avoid denture adhesives - |
|
|
Lynal must be replaced every how many weeks?
|
4-6 weeks
|
|
|
Why do you take a panoramic radiograph on a complete denture case?
|
- residual roots
- pathology - ridge - |
|
|
Which is more traumatizing to tissues:
Excessive VDO Insufficiente VDO Incorrect Occlusion |
Excessive VDO
|
|
|
Why do you take a protrusive record?
|
To get horizontal condylar inclination (for mounting purposes)
|
|
|
What is the best method for finding CR?
|
- tongue to the roof of the mouth
- tell the patient to swallow - |
|
|
What is the purpose of making a custom tray?
|
- improve retention
- minimize impression material distortion - adequate thickness - minimize tissue distortion - decrease cost due to less material used |
|
|
Describe the markings made on a diagnostic cast for guidance during custom tray fabrication?
|
- BLUE PENCIL: depth of vestibule
- BLUE PENCIL: 2-3 mm away from vestibule line - RED PENCIL: 5-6 mm away from 2nd line , 2-3 mm away from vibrating line |
|
|
How thick should your border moulding be?
|
4-5 mm
|
|
|
What are the types of complete denture occlusion?
|
- bilateral balance
- neurocentric |
|
|
What are the goals of complete denture occlusion?
|
- minimize trauma to supporting tissue
- increase stability - preserve remaining structurs - facilitate esthetics and speech - restore mastication efficiency to a reasonable level - in addition - decrease lateral forces to the residual ridges |
|
|
What is HANAU's QUINT?
|
Five factors affecting occlusal balance
- condylar guidance - incisal guidance - occlusal plane inclination - compensating curves - cuspal inclination |
|
|
Which factors of HANAU'S QUINT can't be altered by dentist?
|
CONDYLAR INCLINATION
OCCLUSAL PLANE |
|
|
Why would you choose lingualized occlusion for complete denture?
|
- high esthetic demands
- severe mandibular ridge atrophy - displaceable supporting tissues - malocclusion - previous successful occlusion with Lingualized teeth Advantages - good esthetics - freedom of non-anatomic teeth - potential for bilateral balance - centralizes vertical forces - minimizes tipping forces - facilitates bolus penetration |
|
|
What is the single most important factor in the successful manipulation of complete dentures under function?
|
NEUROMUSCULAR CONTROL
- coordination of tongue and previous denture experience |
|
|
What are the indications for NON-ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- Poor Residual Ridges
- Poor Neuromuscular control (Bruxers, CP etc.) - Previously successful with Monoplane Dentures or Severely worn occlusion on previous denture - Arch discrepancies - Class II or III or Cross-bite - Immediate Dentures except when opposing natural dentition - Potential poor follow-up |
|
|
What are the indications for ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- Good Residual Ridges
- Well Coordinated Patient - Previously successful with anatomic dentures - Denture opposes natural dentition - When “Lingualized” occlusion is desired |
|
|
What are the advantages of NON-ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- Reduction of horizontal forces
- CR can be developed as an area instead of a point - Freedom of movement - Can develop solid occlusion despite arch alignment discrepancies - Easily adapted to situations prone to denture base shifting - Easy to set and adjust teeth |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of NON-ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- No vertical component to aid in shearing during mastication
- Occlusal adjustment impairs efficiency unless spillways and cutting edges restored - Patients may complain of lack of positive intercuspation position - Somewhat esthetically limited (don’t look like natural teeth) |
|
|
What are some INDICATIONS for TISSUE CONDITIONERS?
|
- abused or irritated denture supporting tissues
- diagnostic / adjunctive provisional procedures (increase VDO, correct occlusion) - chronic pain - temporary liner for immediate dentures - reline cleft palate speech aids - reline during implant healing - functional impression |
|
|
If a patients tissues exhibit signs of abuse, these tissue should be restored to health prior to making the new denture in what ways?
|
- tissue rest
- occlusal correction - oral hygeine instruction - tissue conditioning |
|
|
What are some SYSTEMIC causes of INFLAMMATION / DISCOMFORT under dentures?
|
- hormonal
- metabolic disturbances (diabetes) - xerostomia |
|
|
What are some DENTURE CAUSES of inflammation / discomfort?
|
- denture trauma
- poor OH |
|
|
What is really important to do before NEW DENTURES are made?
|
Any adnormalities of the soft tissues must be recognized and treated
|
|
|
Tissue recovery takes place in how much time?
|
48-72 hours
|
|
|
What are the steps of TISSUE CONDITIONING?
|
- HYGEINE - make sure denture surfaces are clean
- TISSUE REST - patients instructed to remove dentures at night - OCCLUSAL CORRECTION - stable occlusion - USE OF TEMPORARY SOFT LINERS - gives tissues some relief |
|
|
What are some proper oral hygeine tips for edentulous patients?
|
- Brush all surfaces of the denture (but don't scrub inside surface)
- Massage tissues in circular motion with textured soft cloth using warm water |
|
|
What is the most overlooked cause of tissue trauma in denture patients?
|
OCCLUSION
|
|
|
How will adjusting occlusion before beginning treatment make fabrication of a new denture easier?
|
- prevents difficulty in making jaw relation records
- perpetuating problems caused by denture wear and ridge resorption - perpetuating previous errors |
|
|
What are some techniques of OCCLUSAL CORRECTION?
|
- Clinical remount (irreversible)
- add acrylic to occlusal surfaces (irreversible) - soft mouthguard over denture (reversible) |
|
|
Define CONDITIONING MATERIAL:
|
soft material which is applied temporarily to the fitting surface of a denture for the purpose of allowing a more equal stress distribution of the load which allows the mucosal tissues to return to their normal position
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of the ideal tissue lining materail?
|
- compatibility with oral tissues
- compliance and resilience - dimensional stability in moist environment - rupture resistance - adhesion to denture base - wetability - inhibition of bacterial/fungal growth |
|
|
What are some of the DISADVANTAGES of temporary soft liner material?
|
- lack of long term resiliency
- rough surface, harbours microorganisms - cleaning |
|
|
How does one achieve "Tissue Recovery"?
|
- Patient should leave denture out for 12 hours previously
- disclosing paste PIP will help identify areas of gross pressure - over-extensions are relieved and under-extensions can be built up with self cure acrylic - if freeway space is insufficient - occlusal surfaces of teeth should be reduced - tissue conditioner is applied to internal surface of the denture - when complete patient is dismissed and advised to adopt a fairly soft diet for 1 week and massage the tissue - several treatments may be necessary - improves fit of denture - compensates for loss of vertical dimension - less effective after 4-6 week period |
|
|
Give a quick list overview of the TISSUE CONDITIONING procedure:
|
- clean denture with scalers, burs, pumice, ultrasonic as necessary
- reduce denture base as necessary - place temporary soft liner - trim/adjust - home care instructions - recall - polish or send to lab |
|
|
How much denture base reduction should be done when RELINING a denture?
|
- if VDO is adequate relieve 2mm (thickness for resiliency)
- if VDO insufficient may only need to roughen up the base |
|
|
What are some important points to remember when seating a denture for a LINER?
|
- treat ONE DENTURE at a time
- treat LEAST STABLE first - most stable denture should be used to orient the position via occlusion - patient closes LIGHTLY - assess occlusal contacts - move/tilt denture to orient |
|
|
How does one develop LINER contours?
|
- border mold after 2-3 minutes
- allow patient to talk while setting - remove gross excess early (finger sweep or cotton roll) - leave intraorally for 8-10 minutes |
|
|
Trimming of LINER should be done with what?
|
HOT SCALPAL BLADE
|
|
|
What are the HOME CARE INSTRUCTIONS for LINER?
|
- no brushing for 24 hours - rinse only
- teach patient to scrub with good denture brush, wipe liner with cotton - use water only, avoid commercial cleaners - avoid denture adhesives - remove at night - keep immersed in water |
|
|
How does one FINISH a temporary liner?
|
- Patient returns in 2-3 days for adjustment / polish
- discomfort (use PIP paste and adjust) - trim flush with denture - polish with pumice (NO HISHINE) |
|
|
LYNAL must be replaced how often?
|
Every 4-6 weeks until permanent reline or new denture is complete
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a CUSTOM IMPRESSION TRAY?
|
- Improve retention
- minimize impression material distortion - uniform thickness - rigid tray - cost effective (less impression material used) - accurately adapted tray |
|
|
What are some effects of a poorly adapted impression tray?
|
- vestibular distortion
- underextended borders |
|
|
What is the procedure for making a CUSTOM TRAY?
|
- mark depths of vestibule on diagnostic casts with BLUE PENCIL
- mark 2nd blue line that is 2-3 mm from first blue line (except between max hamular notches) - mark 3rd line in RED pencil 5-6 mm from first blue line - 2-3 mm short of vibrating line |
|
|
During CUSTOM TRAY PROCEDURE where does the wax extend?
|
- one thickness of baseplate wax trimmed to red line
- no wax over undercut areas - provide vertical stops |
|
|
Where can vertical stops be made for CUSTOM TRAYS?
|
- palate or tuberosities if high palate
- buccal shelf and anterior ridge |
|
|
Tray material (Triad or Hygon) should extend to which line when fabricating custom tray?
|
MIDDLE line (BLUE)
|
|
|
What are the border molding segments in the MAX area?
|
BUCCAL - hamular notch to buccal frenum (bilaterally)
LABIAL - buccal frenum to buccal frenum POST-PALATAL area |
|
|
What are the border molding segments in the MAND?
|
BUCCAL - retromolar pad to buccal frenum (bilaterally)
LABIAL - buccal frenum to buccal frenum POST LINGUAL - retromolar pad to retromolar area ANT LINGUAL - premolar to premolar |
|
|
What is the purpose of a HANAU ALCOHOL TORCH in border molding?
|
- to re-soften new additions
- to blend in new additions with existing segments - keep junctions smooth and continuous |
|
|
What is the adequate thickness of border mold?
|
4-5 mm
|
|
|
What are some important things to check for with your BORDER MOLDING?
|
- adequate thickness 4-5 mm
- compound not overlapping onto wax - no burn through of the tray - should be stable at rest or during manipulation - should be no space apparent in vestibule during tissue manipulation - should be resistance to dislodgement when pulling on handle of tray (maxillary mainly) |
|
|
How does one prepare BORDER MOLDED TRAY for final impression?
|
- blend compound into periphery of the tray
- blend internal surfaces well - remove wax spacer - grind away any sharp edges inside of tray - place 2-3 holes in maxillary tray to reduce hydraulic pressure - dispense small amount of adhesive into medicine cup - use cotton applicator or brush to spread adhesive over internal surface |
|
|
What is the PATIENT PREPARATION for taking a final impression?
|
- Dry tissue with gauze
- advise patient to relax mouth - practice insertion of tray - make sure you can see |
|
|
What is the seating direction for FINAL IMP of the maxilla?
|
- FRONT to BACK seating of the tray is best
|
|
|
What is the purpose of POST-PALATAL SEAL?
|
Compensates for polymerization shrinkage of the denture
|
|
|
Describe MECHANICAL POST PALATAL SEAL:
|
- after master cast is poured, back of the cast is scraped in a butterfly shape
|
|
|
Describe FUNCTIONAL POST PALATAL SEAL?
|
- butterfly shape added with Korecta-wax to the final impression
|
|
|
What are the ideal dimensions of the LAND AREA of a master cast?
|
- fairly low (no more than 2-3 mm above depth of vestibule
- no wider than 4 mm - base trimmed parallel to alveolar ridge |
|
|
What are some common areas of undercuts in MAXILLA?
|
- labial undercuts
- frenal areas - tuberosities - rugae |
|
|
What are some common areas of undercuts in MANDIBLE?
|
- thin ridges
- labial undercuts - retromylohyoid region |
|
|
What are the WIDTH dimensions of OCCLUSAL WAX RIMS?
|
7 mm anterior
10 mm posterior |
|
|
What are the HEIGHT dimensions of OCCLUSAL WAX RIMS?
|
MAX - 22mm anterior
MAX - 18 mm posterior MAN - 18mm anterior |
|
|
How far should the wax rim extend up the retromolar pad?
|
1/2 to 2/3 up
|
|
|
What are the important adjustment points of WAX RIMS?
|
MAX FIRST
1) Adjust length of anterior portion 2) adjust labial contours to establish lip support 3) Check orientation of occlusal plane (Fox Plane), parallel interpupillary line, ala-tragus line 4) Place mandibular wax rim 5) In CR position rims should contact evenly 6) Establish vertical dimension 7) Proper horizontal overlap 8) Mark landmarks - midline ,cuspid, high lip 9) Facebow transfer 10) Mount maxillary cast 11) Record CR 12) Mount mandibular master cast 13) Make protrusive record 14) Set horizontal condylar guidance 15) |
|
|
What is the desired naso-labial angle one should have with a WAX RIM?
|
90-120 degress
|
|
|
How much display of wax rim should there typically be when the lip is at rest (upper)?
|
1-2 mm
|
|
|
Centric relation is recorded at which point?
|
VDO
|
|
|
How much space is usually between the teeth at VDR?
|
2-4 mm of space
|
|
|
Define FREEWAY SPACE:
|
VDO - VDR
|
|
|
What is the limit by which we should increase VDO?
|
no more than 5 mm
|
|
|
Patients tolerate which better, insufficient or excessive VDO?
|
Insufficient tolerated better
|
|
|
What is the CLOSEST SPEAKING SPACE?
|
- rims should not touch when speaking
- "S" sound should have them 1mm apart |
|
|
Mandibular anterior teeth on the wax rim should be no further forward than what?
|
Depth of vestibule
|
|
|
What are the important landmarks to mark on wax rims?
|
- midline
- cuspid line - high lip line |
|
|
What are the properties of CR?
|
Condyles positioned superiorly and posteriorly
|
|
|
What can be used to record CR?
|
aluwax
PVS bite reg material |
|
|
How far can patient protrude the mandible forward for a protrusive record?
|
At least 4mm , no more than 8 mm
|
|
|
What do the numbers on the DENTSPLY MOLDS represent?
|
45F
FIRST number = Shape (square, tapering, ovoid, etc) SECOND number = Proportion of the tooth (long, short, medium, curved, straight) LETTER = width of six anteriors on the curve |
|
|
Define HUE
|
Colour - principle modifications of a colour
|
|
|
Define VALUE:
|
brightness of a hue
|
|
|
Define CHROMA
|
- amount of hue in a colour
|
|
|
What are the features of PORCELAIN TEETH?
|
- very resistant to abrasion
- mechanically retained in denture with pins - very aesthetic - prone to breakage, discoloration around necks - need adequate interocclusal space |
|
|
What are the features of ACRYLIC DENTURE TEETH?
|
- easy to adjust
- wear easily - bonds to denture base |
|
|
What is the correct positioning of CENTRAL INCISOR tooth?
|
- flush with occlusal plane
- long axis of tooth slightly disto-angulation - mesial surface at midline - labial surface flush with wax rim contour - lower 2/3 maintains contour developed in wax rim |
|
|
What is the correct positioning of LATERAL INCISOR tooth?
|
- mesial surface contacts distal of central
- incisal edge is 1mm above occlusal plane - long axis at angle more distal than central - cervical portion more depressed than central - most of labial surface flush with wax rim contour |
|
|
What is the correct positioning of CANINE tooth?
|
- mesial surface contacts distal of lateral
- long axis at a more distal angle than lateral - middle third is flush with labial contour of wax rim - cervical is prominent - mesial plane follows curve of anterior teeth |
|
|
How much OB and OJ do we want?
|
1mm overbite
2 mm overjet |
|
|
What are the goals of COMPLETE DENTURE OCCLUSION?
|
- minimize trauma to supporting structures
- preserve remaining structures - enhance stability of the dentures - facilitate esthetics and speech - restore mastication efficiency to a reasonable level - in addition we would like to decrease lateral forces to the residual ridges |
|
|
What are the two types of COMPLETE DENTURE OCCLUSION?
|
- Bilateral balance
- Neutrocentric |
|
|
What type of COMPLETE DENTURE OCCLUSION do we prefer?
|
Bilateral balance - because it limits tipping of dentures during parafunctional movements
|
|
|
What are the FIVE FACTORS (Hanau's Quint) that affect occlusal balance?
|
- condylar inclination
- incisal guidance - occlusal plane inclination - compensating curve - cuspal inclination |
|
|
Which factors of the HANAU's QUINT are controlled by the dentist?
|
- Incisal guidance
- Compensating Curve - Cuspal inclination |
|
|
Which factors of the HANAUS QUINT can you NOT control?
|
- condylar inclination
- occlusal plane |
|
|
What should be minimized in HANAU's QUINT to minimize inclined tipping forces?
|
Incisal guidance
|
|
|
What is the criteria for selecting posterior teeth?
|
- resorbed or flabby ridges
- physical condition of the patient - patients who clench or brux - previous denture occlusion - ridge relationship - immediate dentures - opposing arch |
|
|
What are the INDICATIONS of NON-ANATOMIC teeth?
|
- poor residual ridges
- poor neuromusscular control - bruxers - previously successful with monoplane dentures or severely worn occlusion - arch discrepancies Class II or III or crossbite - immediate dentures (except when opposing natural dentition) - potential poor follow-up |
|
|
What are the INDICATIONS of ANATOMIC occlusion?
|
- good residual ridges
- well coordinated patient - previously successful with anatomic - denture opposes natural dentition - lingualized occlusion desired |
|
|
What are the ADVANTAGES of NON-ANATOMIC occlusion?
|
- reduction of horizontal forces
- CR can be developed as an area instead of a point - freedom of movement - can develop solid occlusion despite arch alignment discrepancies - easily adapted to situations prone to denture base shifting - easy to set and adjust teeth |
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of NON-ANATOMIC occlusion?
|
- no vertical component to aid in shearing during mastication
- occlusal adjustment impairs efficiency unless spillways and cutting edges restored - patients may complain of lack of positive intercuspation position - somewhat esthetically limited |
|
|
What are the ADVANTAGES of ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- definite point of positive intercuspation may be developed
- estheticall similar to natural teeth - tooth-to-tooh and cusp to cusp balanced occlusion - maintains some shearing ability after moderate wear |
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of ANATOMIC TEETH?
|
- difficult to set
- less adaptable to arch relation discrepancies - horizontal force development due to cusp inclinations - harmonious balance occlusion is lost with denture base setting - requires frequent follow-up and may require more frequent relines to maintain proper occlusion |
|
|
What are the INDICATIONS for use of LINGUALIZED occlusion?
|
- high esthetic demands
- severe mandibular ridge resorption - displaceable supporting tissues - malocclusion - previously successful |
|
|
What are the ADVANTAGES of LINGUALIZED occlusion?
|
- good aesthetics
- freedom of non-anatomic teeth - potential for bilateral balance - centralizes vertical forces - minimizes tipping forces - facilitates bolus penetration |
|
|
What are the steps in POST TOOTH SELECTION?
|
- mark landmarks on master cast
- finalize position of occlusal plane - finalize position of wax rims relative to each other - check incisor relationship - measure space available |
|
|
What LANDMAKRS should be marked on the master cast?
|
- MIDLINE
- incisal papilla - anterior land area - ridge crest - retromolar pad |
|
|
What three landmarks are used to determine the plane of occlusion?
|
- midpoint of retromolar pads bilaterally
- incisal edge of maxillary central incisors - lines indicating crest of the ridge |
|
|
What are the STeps in WAX TRY IN?
|
1) check vertical dimension of occlusion and rest
2) prove centric relation record 3) make protrusive record 4) evaluate estehtics and phonetics 5) check posterior tooth position and final contours |
|
|
What things should be assessed at WAX TRY IN regarding VDO?
|
- at least 2-4 mm interocclusal distance measured and felt
- posterior teeth should not contact during assessment of closest speaking space - modify VDO FIRST before other aspects |
|
|
What are some different methods of assessing VDO?
|
- physiologic rest position
- phonetics and esthetics - swallowing - comparison with the old denture - closest speaking space |
|
|
What are some methods used to verify whether mounting in CR was accurate?
|
- insert dentures and hold lower position with your index finger
- retrude mandible and close in centric relation - observe any shift in upper denture - look for even contact of the posterior teeth bilaterally |
|
|
How does one make the CENTRIC RELATION RECORD with a WAX TRY IN?
|
- vaseline posterior teeth on max denture
- use heated #7 wax spatula to pick up small amount of aluwax - place small cones of aluwax on four spots on occlusal surfaces of mandibular posterior teeth - quickly place mandibular denture, stabilize it against mandible, and have patient close into CR |
|
|
How are FRICATIVE SOUNDS evaluated?
|
patient should be able to make a clear "f" and "v" sound with maxillary incisal edges against the lower lip
|
|
|
How are SIBILANT SOUNDS evaluated?
|
- "s" or "z"
- anterior and posterior teeth should not touch - should be no hissing or air loss |
|
|
If there is not a half-tooth offset at Canines, then what things can the dentist do to achieve this?
|
- reducing or increasing overjet
- reducing or increasing facial arch circumference of one or both occlusal rims - altering vertical dimension - bodily moving teeth more facially or more lingually within esthetic limits - changing axial inclination of one or more teeth |
|
|
What should the external contours of the wax rim look like?
|
- slightly concave
|
|
|
What are the types of MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
MAXILLARY
- palatal plate - anterior-posterior strap - palatal strap MANDIBLE - lingual plate - lingual bar |
|
|
What is the posterior extension of MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
MAXILLARY
- point to hamulor notch (in edentulous areas) - does not cover tuberosity - beaded posterior border MAND - 2/3rds to retromolar pad - terminates prior to ascending ramus - tissue stop |
|
|
What is the proper distance from gingival margin of MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
Maxillary: 6mm
Mandibular: 2-4 mm Floor of mouth: 7 mm gingival margin to FOM |
|
|
What is the min WIDTH OF STRAP?
|
Maxillary: 8mm wide but thin
Mandible: 6mm narrow but thick (half pear shape) |
|
|
What is the RELIEF used under MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
MAX AND MAND distal extension = 2 thicknesses of 28 gauze wax
TOOTH BORNE = no relief MAND = 2 thicknesses of 30 gauge wax |
|
|
How thick should MINOR connectors be?
|
4mm
|
|
|
Minor connector corners should be (rounded/ squared?)
|
ROUNDED
|
|
|
What is the extension of the GRIDWORK on an RPD?
|
- Mandibular 2/3 up retromolar pad
- Maxillary up to (but not covering) tuberosity - posterior REINFORCED, anterior not - slightly more lingual than buccal to the ridge - extends approx 2mm buccal past crest of ridge |
|
|
What are the different types of DIRECT RETAINERS?
|
- Suprabulge
- Infrabulge |
|
|
What are some different types of SUPRABULGE DIRECT RETAINERS?
|
- Circumferential clasp
- Combination clasp - Ring clasp - Reverse action - Embrasure clasp |
|
|
How much of an undercut is needed for a CIRCUMFERENTIAL CLASP?
|
0.01
|
|
|
How much of an undercut is needed for a RING CLASP?
|
0.01
|
|
|
How much of an undercut is needed for a COMBINATION CLASP?
|
0.02
|
|
|
What is an INFRABULGE RETAINER?
|
I-bar
|
|
|
How much of an undercut does I-bar need?
|
0.01
|
|
|
Where should the rest be on an abutment if there is distal extension?
|
MESIAL
|
|
|
What is the purpose of INDIRECT RETAINER?
|
Prevents rotation of framework
|
|
|
What effects can DIABETES have on RMV treatment?
|
- poor tissue tone in uncontrolled diabetics
- poor wound healing - should be under control prior to prosthetic treatment |
|
|
What effects can PARKINSON'S have on RMV treatment?
|
- rhythmic contracture of musculature
- patient may find it difficult to insert and remove prostheses and perform oral hygeine - lots of saliva - difficult impression |
|
|
What are some questions to ask / assess when checking an existing RPD?
|
- is there rotation around the fulcrum line?
- is the major connector rigid - are the rests adequate - is the indirect retention adequate - are the direct retainers adequate - is the denture base coverage adequate |
|
|
What are some findings which may indicate the need for periodontal treatment?
|
- pocket depth in excess of 3.0 mm
- furcation involvement - deviation of normal colour, contour and texture of gingiva - marginal exudate - potential abutment with less than 2.0 mm of attached gingiva - muscle or frenal pulls |
|
|
What are some potential causes of mobility of a tooth:>
|
- trauma from occlusion
- periodontal ligament inflammation - loss of alveolar bone support |
|
|
Tooth with less than what crown ratio is not suitable as an abutment for an RPD?
|
1:1
|
|
|
What are "STRATEGIC TEETH"?
|
- canines
- single molar that bounds edentulous space - may wish to invest in periodontal therapy to improve the prognosis for these teeth |
|
|
What are NON-STRATEGIC TEETH?
|
- weigh benefits of treatment vs extraction vs prognosis if no treatment
|
|
|
What are some conditions which may cause periodontal ligament irritation?
|
- tooth movement due to a prosthesis or occlusion
- tooth or restoration in traumatic occlusion - acute pulpitis - gingivitis / periodontitis - cracked tooth |
|
|
What should one do about root fragments prior to construction of RPD?
|
- generally if deeply embeded and NO PATHOLOGY changes then can just monitor
|
|
|
What does a WIDENED PDL indicate?
|
- mobility
- occlusal trauma - heavy function |
|
|
What are the purposes of having MOUNTED DIAGNOSTIC CASTS?
|
- essential diagnostic aid
- treatment planning - allows superior visualization - allows for a detailed occlusal analysis - patient education and tx plan presentation - diagnostic casts are a permanent dental record of the patient's condition before treatment |
|
|
CENTRIC RELATION is the treatment position used for RPD in which circumstance?
|
- Coincident CR and MI
- Absence of posterior tooth contacts - all posterior tooth contacts are to be restored with cast restorations - anterior slide from CR and anterior teeth exhibit signs and symptoms of occlusal trauma |
|
|
How much time is needed for healing is SOFT TISSUE REDUCTION is done?
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
How much time is needed for healing if HARD TISSUE reduction is done?
|
up to 6 weeks
|
|
|
The decision to extract or correct a tooth's position relative to the occlusal plane is dependent upon which three factors?
|
- tooth's condition
- its position in the arch - severity of displacement |
|
|
If a tooth requires more than _____ of enameloplasty, then a crown is indicated.
|
2 mm
|
|
|
What are some signs and symptoms of TRAUMATIC OCCLUSION?
|
- excessive wear of the teeth include chipping, fracturing, facets
- a change or loss of the supporting structures of the teeth including increased mobility, tooth migration, and pain with occlusal contact - muscle splinting, tenderness, pain RADIOGRAPHIC - widened PDL - periapical or furcation radiolucency - root resorption |
|
|
What are some options for PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS PATIENTS?
|
- Fixed partial denture
- Removeable partial denture - implant supported / retained restoration - complete denture - removeable partial overdenture - complete overdenture |
|
|
What is the average area of the maxillary residual ridge?
|
24 cm squared
|
|
|
Normally, the maxillary residual ridge resorbs at what rate?
|
0.1mm per year
|
|
|
What may be a complication with an excessively thick MAXILLARY TUBEROSITY?
|
- coronoid process may dislodge CUD if buccal flange excessively thick
- can interfere with lower denture - can affect occlusal plane |
|
|
Define HAMULAR NOTCH
|
Notch formed between maxillary tuberosity and hamulus of medial pterygoid plate
|
|
|
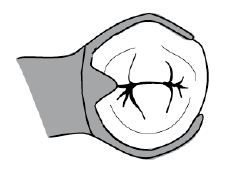
What are the FOVIA PALATINAE?
|
- two small pits / depressions
- posterior aspect of palate - one on each side of midline - near or at junction of hard and soft palate |
|
|
Define VIBRATING LINE:
|
- imaginary area at the junction of the immoveable and moveable tissues of the palate
- posterior CUD should end 1-2 mm PAST vibrating line |
|
|
How HIGH should the post-palatal seal area be?
|
1.0 - 1.5 mm
|
|
|
How WIDE should the post palatal seal area be?
|
3-4 mm
|
|
|
What is the INCISIVE PAPILLA?
|
Elevated tissue covering the incisive foramen
- used to help aid in location of denture teeth |
|
|
What is the primary stress bearing area in CUD?
|
Maxillary residual ridge
|
|
|
What is the primary stress bearing area in CLD?
|
Buccal shelf
|
|
|
What are the BOUNDARIES of the BUCCAL SHELF?
|
ANTERIOR: mental foramen
LATERAL: ext oblique ridge MDEIAL: crest of residual ridge POST: retromolar pad |
|
|
Which muscles attach to EXTERNAL OBLIQUE RIDGE?
|
Masseter
Buccinator (runs parallel to ridge) |
|
|
What are the contents of the RETROMOLAR PAD?
|
- glandular tissue
- muscle fibers of buccinator and superior constrictor - pterygomandibular raphe - terminal tendon of temporalis muscle |
|
|
What muscles attach to MYLOHYOID RIDGE?
|
- mylohyoid
- superior constrictor |
|
|
What are the borders of the RETROMYLOHYOID SPACE?
|
ANT: mylohyoid ridge
LATERAL AND SUP: retromolar pad INF: submandibular gland |
|
|
What is the purpose of RETROMYLOHYOID SPACE?
|
Provides border seal and retention
|
|
|
What is the purpose of MYLOHYOID RIDGE FLANGE?
|
- provide border seal
- guide tongue to rest on top of flange |
|
|
What attaches to the GENIAL TUBERCLES?
|
- genioglossus
- geniohyoid - suprahyoid |
|
|
What is the purpose of the LAND AREA OF THE CAST?
|
To aid in denture processing
|
|
![Identify [1]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932210_m.jpg)
Identify [1]
|
LABIAL FRENUM
|
|
![Identify [2]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932213_m.jpg)
Identify [2]
|
LABIAL VESTIBULE
|
|
![Identify [3]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932216_m.jpg)
Identify [3]
|
BUCCAL FRENUM
|
|
![Identify [4]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932219_m.jpg)
Identify [4]
|
BUCCAL VESTIBULE
|
|
![Identify [5]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932222_m.jpg)
Identify [5]
|
RESIDUAL ALVEOLAR RIDGE
|
|
![Identify [6]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932225_m.jpg)
Identify [6]
|
BUCCAL SHELF
|
|
![Identify [7]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932228_m.jpg)
Identify [7]
|
RETROMOLAR PAD
|
|
|
Identify [8]
|
PTERYGOMANDIBULAR RAPHE
|
|
![Identify [9]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932231_m.jpg)
Identify [9]
|
RETROMYLOHYOID FOSSA
|
|
![Identify [10]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932234_m.jpg)
Identify [10]
|
TONGUE
|
|
![Identify [11]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932237_m.jpg)
Identify [11]
|
ALVEOLINGUAL SULCUS
|
|
![Identify [12]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932240_m.jpg)
Identify [12]
|
LINGUAL FRENUM
|
|
![Identify [13]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932243_m.jpg)
Identify [13]
|
PREMYLOHYOID EMINENCE
|
|
![Identify [1]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932246_m.jpg)
Identify [1]
|
LABIAL NOTCH
|
|
![Identify [2]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932249_m.jpg)
Identify [2]
|
LABIAL FLANGE
|
|
![Identify [3]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932252_m.jpg)
Identify [3]
|
BUCCAL NOTCH
|
|
![Identify [4]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932255_m.jpg)
Identify [4]
|
BUCCAL FLANGE
|
|
![Identify [5]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932258_m.jpg)
Identify [5]
|
ALVEOLAR GROOVE
|
|
![Identify [6]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932261_m.jpg)
Identify [6]
|
BUCCAL SHELF AREA OF BUCCAL FLANGE
|
|
![Identify [7]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932264_m.jpg)
Identify [7]
|
RETROMOLAR FOSSA
|
|
![Identify [8]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932267_m.jpg)
Identify [8]
|
PTERYGOMANDIBULAR NOTCH
|
|
![Identify [9]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932270_m.jpg)
Identify [9]
|
RETROMYLOHYOID EMINENCE
|
|
![Identify [10]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932273_m.jpg)
Identify [10]
|
INCLINED PLANE FOR TONGUE
|
|
![Identify [11]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932276_m.jpg)
Identify [11]
|
LINGUAL FLANGE
|
|
![Identify [12]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932279_m.jpg)
Identify [12]
|
LINGUAL NOTCH
|
|
![Identify [13]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/871012/932282_m.jpg)
Identify [13]
|
PREMYLOHYOID EMINENCE
|
|
|
What is the sequence of MOUTH PREPARATION for RPD?
|
1) establishment of occlusal plane
2) re-contour proximal surfaces of posterior teeth 3) re-contour proximal surfaces of anterior teeth 4) re-contour facial and lingual surfaces of teeth 5) prepare rest preparations 6) smooth and polish all altered surfaces |
|
|
What is a quick sequence of mouth preparation?
|
Occlusal plane > proximal post > ant > facial lingual > rests > smooth
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of enameloplasty one can perform/
|
2mm
|
|
|
What is the IDEAL location of the RETENTIVE CLASP?
|
- no higher than the junction of the gingival and middle 1/3 of the crown
|
|
|
What is the shape of a rest in a posterior tooth/
|
ROUNDED TRIANGULAR shape
- follows outline of the fossa |
|
|
What are the M-D dimensions of posterior rest seats?
|
3-4 mm
1/3 to 1/2 MD width of tooth |
|
|
What are the FL dimensions of posterior rest seats?
|
1/3 F-L width
|
|
|
What is the design of the FLOOR of the rest seat on posterior tooth?
|
- concave
- inclined slightly towards center of tooth |
|
|
What are some things to look for when assessing RPD framework on master cast?
|
- master cast integrity
- has the surface been altered, fractured, abraded? - was the design followed carefully? - is there any rocking of the framework across fulcrum lines? - is the finish and polish of external and internal surfaces correct? |
|
|
What are some disclosing agents used to check REST SEAT FIT?
|
- occlude
- fit checker - PIP - articulating foil - chloroform and rouge |
|
|
Define PARTIAL DENTURE:
|
Prosthesis that replaces one or more, but not all of the natural teeth and supporting structures. It is supported by the teeth and/or the mucosa. It may be fixed (bridge) or removeable
|
|
|
Define RETENTION:
|
Resistance to removal from the tissues or teeth
|
|
|
Define STABILITY:
|
Resistance to movement in a horizontal direction
|
|
|
Define SUPPORT:
|
resistance to movement towards tissues or teeth
|
|
|
What are the objectives of RPD Treatment?:
|
- preserve remaining teeth and supporting structures
- restore esthetics and phonetics - restore and/or improve mastication - restore health, comfort, and quality of life |
|
|
What are the ALTERNATIVES to RPD's?
|
1. NO TREATMENT
- most patients can function with a shortened dental arch - requires anterior teeth + 4 occlusal units (symmetric loss) or 6 occlusal units (asymmetric loss) for acceptable function - opposing premolar = 1 unit, opposing molar = 2 units - RPD doesn't usually improve function if minimal occlusal units present ---------------------------------------- 2. FIXED PARTIAL DENTURE - requires abutments at opposite ends of edentulous space - more expensive than RPD, must grind down abutments, flexes and can fail if too long ------------------------------------------------------- 3. IMPLANT SUPPORTED PROSTHESIS - most costly, closest replacement to natural dentition - less costly over long-term ------------------------------------- 4. COMPLETE DENTURE - if few teeth left, with poor prognosis - if replacement of missing teeth is very complex or costly |
|
|
What are the INDICATIONS for RPD'S?
|
- lengthy edentulous span (too long for FPD)
- no posterior abutment for a fixed prosthesis - excessive alveolar bone loss (esthetic) - poor prognosis for complete dentures due to residual ridge morphology - reduced periodontal support of remaining teeth - cross-arch stabilization of teeth - need for immediate replacement of teeth - cost/patient desire considerations |
|
|
What are the clinical steps in RPD fabrication?
|
- Diagnosis, Treatment plan, Hygeine
- Diagnostic casts - DRAW DESIGN and LIST ABUTMENT MODIFICATIONS - Complete Phase I treatment - Abutment modifications - Preliminary impression to check abutment modifications - Crown or FPD's for RPD abutments - Final Framework impression (must include hamular notches / retromolar pads for distal extension - Make TWO casts - Draw design on 2ND CAST - Instructor approval / corrections - Complete Frame prescription - Inspect wax-up - Framework adjustment - Altered cast impression - Try in with teeth in wax - Process, deliver to patient |
|
|
What are the 5 components of a PARTIAL DENTURE?
|
- major connector
- minor connector - direct retainer - indirect retainer - denture base |
|
|
What is the principle function of MAJOR CONNECTOR?
|
- provide unification and rigidity to denture
- connect one side of dental arch to other |
|
|
What is the main function of the MINOR CONNECTOR?
|
- connects other components to the major connector
- provide unification and rigidity |
|
|
What is the primary function of a DIRECT RETAINER?
|
- provides retention against dislodging forces
- rest, retentive arm, reciprocal arm, minor connector |
|
|
What is the primary function of the INDIRECT RETAINER?
|
- prevents / resists movement or rotation of base away from residual ridges
- usually just a rest |
|
|
What is the purpose of the denture base?
|
- covers residual ridges
- supports denture teeth |
|
|
What may happen to the philtrum if the denture teeth are set too far facially?
|
Depression of the philtrum is lost
|
|
|
How does one evaluate an irreversible hydrocolloid impression?
|
- alginate should be properly mixed, smooth and creamy
- tray should be centered over ridge - no significant contact should occur between tray and soft tissues or teeth - no large voids in impression - all critical anatomy should be recorded |
|
How should the DIAGNOSTIC and MASTER cast be trimmed?
|
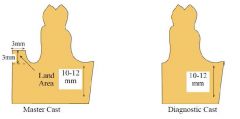
^
|
|
|
What is the advantage of having a SINGLE path of insertion?
|
- equalizes retention on all abutments
- provides bracing and cross-arch stabilization of teeth - minimizes torquing forces of the partial denture - allows the partial denture to be removed without encountering interferences - directs forces along the long axes of the teeth - provides frictional retention from contact of parallel surfaces on the teeth |
|
|
What should guiding planes be prepared for?
|
- proximal plates
- bracing arms - rigid portions of retentive clasps |
|
|
What is the purpose of the DENTAL SURVEYOR?
|
- diagnostic instrument
- select most favourable path of insertion - aid in preparation of guiding planes - designing RPD |
|
|
What are some SPECIFIC uses of a surveyor?
|
- locating soft tissue undercuts
- contouring wax patterns - machining parallel surfaces - blocking out undesireable undercuts on master casts - placing intracoronal retainers - recording the cast position (tripoding) |
|
|
Which should contact the tooth first RETENTIVE ARM or BRACING ARM?
|
Bracing arm
|
|
|
Guiding planes are most effective when they are:
|
- parallel
- include more than one common axial surface (ie proximal and lingual) - directly opposed by another guiding plane - placed on several teeth - cover a large surface area (long/broad) |
|
|
What is the minimum height of a GUIDING PLANE?
|
- minimum 2mm
- 1/2 to 1/3 of the axial height |
|
|
What should the design of LINGUAL guiding planes for bracing arms be?
|
2-4 mm
ideally in MIDDLE THIRD of crown |
|
|
What is the function of RESTS?
|
- to direct forces along the long axis of the abutment tooth
- to prevent the denture base from moving cervically and impinging gingival tissue - to maintain a planned clasp-tooth relationship - to prevent extrusion of abutment teeth - to provide positive reference seats in rebasing and/or impression - to serve as an indirect retainer by preventing rotation of the partial dneture (Class I or II) |
|
|
What is the shape of an occlusal rest seat?
|
ROUNDED TRIANGULAR - apex nearest to center
|
|
|
What is the B-L width of the rest seat at marginal ridge?
|
1/3 BL width of the tooth
|
|
|
How much bulk of metal height is needed for a rest seat?
|
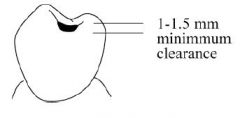
1 - 1.5 mm
|
|
|
What should the inclination of the floor of the rest seat look like?
|
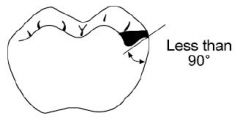
Inclined towards the centre of the tooth
|
|
|
Why is the floor of the rest seat designed to be CONCAVE?
|
- prevent horizontal stresses and torque
|
|
|
What is the design of a CINGULUM REST SEAT?
|
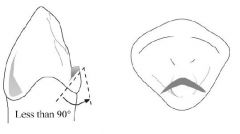
- broad inverted V
|
|
|
How does one test for a "positive" rest seat?
|
Tip of explorer should have resistance to dislodgement when removing it from rest seat
|
|
|
How far from the tooth contact should CINGULUM RESTS be prepared?
|
1.5 - 2.0 mm below
|
|
|
What is the most commonly used MANDIBULAR MAJOR CONNECTOR?
|
Lingual Bar
|
|
|
What is the shape and size of the LINGUAL BAR?
|
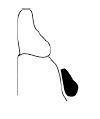
OG width = 4-6 mm
Thickness = 1.5-2mm |
|
|
What is the ideal position of the LINGUAL BAR?
|
As low as the lingual frenum and tissue reflections of the floor of the mouth will permit, as determined by observing functional movements of the tongue
- 1.5-2.0 mm below free gingival margin |
|
|
When is a LINGUAL PLATE usually used?
|
- high floor of mouth
- prominent lingual frenum - lingual tori - extensive distal extension cases with severe vertical resorption of ridges - reduce heavy calculus formation - stabilize mobile anterior teeth |
|
|
How much relief is placed on the LINGUAL BAR?
|
1 thickness of 30 gauge wax
|
|
|
What are some different MANDIBULAR MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
- lingual bar (most common)
- lingual plate - continuous bar - labial bar |
|
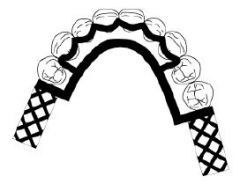
What kind of MAJOR CONNECTOR is here?
|
Continuous (lingual, double, kennedy)
|
|
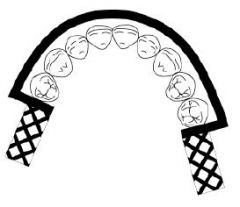
What kind of MAJOR CONNECTOR is here?
|
Labial bar
|
|
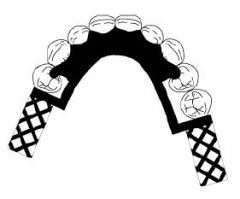
What kind of MAJOR CONNECTOR is here?
|
Lingual plate
|
|
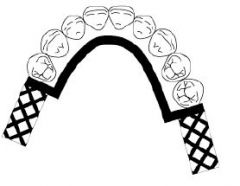
What kind of MAJOR CONNECTOR is here?
|
Lingual bar
|
|
|
What are the different types of MAXILLARY MAJOR CONNECTORS?
|
- Anterior-Posterior palatal strap
- Full palatal plate - palatal strap - anterior palatal plate (ushape) |
|
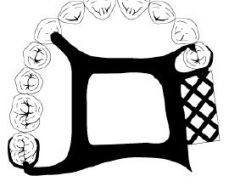
What kind of major connector is this?
|
Anterior-Posterior Palatal Strap
|
|
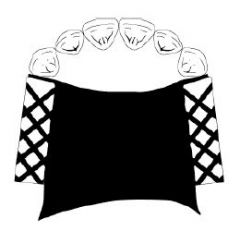
What kind of major connector is this?
|
PALATAL PLATE
|
|
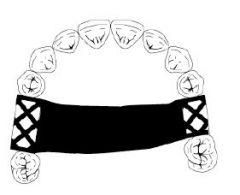
What kind of major connector is this?
|
Palatal strap
|
|
What kind of major connector is this?
|
Anterior palatal plate
|
|
|
When should a FULL PALATAL PLATE be used?
|
- long distal extension cases
- six or less anterior teeth remain - primary abutments are periodnotally involved - edentulous areas are covered with flabby tissue - shallow palatal vault |
|
|
All clasp assemblies should meet what requirements?
|
- SUPPORT: occlusal rests
- RECIPROCITY: use reciprocal arms - STABILITY: - RETENTION: - ENCIRCLEMENT OF GREATER THAN 180' of tooth - PASSIVITY at rest |
|
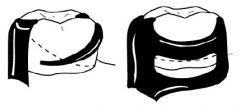
What kind of a clasp is this?
|
Aker's Clasp (circumferential)
|
|
|
What is the design of retentive arm, and what is design of bracing arm of an AKERS CLASP?
|
- retentive arm begins at the height of contour and curves and tapers to its terminal tip, in the gingival 1/3 of the tooth
- bracing arm is in middle 1/3 of tooth, broader O-G dimension, entirely above height of contour |
|
|
What are the advantages of an AKERS CLASP?
|
- excellent bracing qualities
- easy to design and construct - less potential for food accumulation below clasp compared to bar clasps |
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of an AKERS CLASP?
|
- more tooth coverage than bar
- more metal displayed - adjustments are difficult or impossible due to the half round nature of the clasp |
|
|
What are the different types of CLASPS?
|
- Aker's clasp
- Ring clasp - Embrasure clasp - C-clasp |
|
|
When is a RING CLASP used?
|
- encircles entire abutment tooth
- mesially and lingually tipped mand. molars (ML undercut) - undercut is same side as rest seat (edentulous span) - Use AKERS clasp with lingual retention and buccal bracing in preference to ring clasp |
|
|
What are the ADV. to ring clasp?
|
- excellent bracing (with supporting strut)
- allows use of an available undercut adjacent to edentulous area |
|
|
What are the DISADV. of RING CLASP?
|
- covers a large area of tooth surface
- very difficult to adjust due to extreme rigidity of reciprocal arms - lower bracing arm should be at least 1 mm from free gingival margin and relieve to prevent impingement of gingival tissues |
|
What kind of clasp is this?
|
RING CLASP
|
|
|
What are the advantages of an EMBRASURE CLASP?
|
- allows placement of direct retainers where none could otherwise be placed (especially contralateral to edentulous span on a class II case)
|
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of an EMBRASURE CLASP?
|
- extensive interproximal reduction is usually required
- covers large area of tooth surface / hygeine considerations |
|
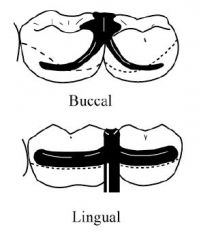
What kind of a CLASP is this?
|
EMBRASURE (Double Akers)
|
|
|
When is a C clasp indicated?
|
- retentive area is adjacent to the occlusal rest
|
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of a C CLASP?
|
- almost impossible to adjust
- non-esthetic - difficult to fabricate so the upper portion of the retentive arm clears opposing occlusion - covers extensive tooth surface - insufficient flexibility on short crowns due to insufficient clasp arm length |
|
|
What kind of clasps should be used in MOST tooth borne cases?
|
CAST SUPRABULGE
|
|
|
What kind of an undercut is needed for CAST clasps?
|
0.01
|
|
|
What kind of an undercut is needed for WROUGHT WIRE?
|
0.02
|
|
|
When are CAST SUPRABULGE clasps contraindicated?
|
- Esthetic concerns
- abutments are mobile - posterior abutment is mobile or questionable prognosis |
|
|
What are the components of the RPI clasp?
|
- REST (always MESIAL)
- Proximal plate - I-bar |
|
|
How far from the gingival margin should the inferior border of the I-bar be?
|
4mm
|
|
|
When there is insufficient vestibule depth or severe tissue undercuts, what can be used instead of an RPI?
|
-RPA (aker's)
|
|
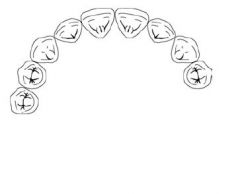
What Kennedy Classification is this?
|
Class I
|
|
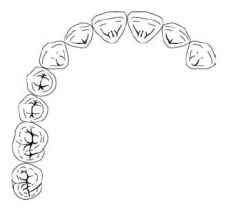
What Kennedy Class is this?
|
Class II
|
|
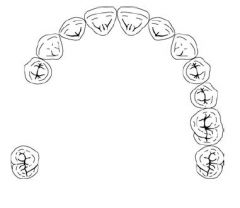
What Kennedy Class is this?
|
Class III
|
|
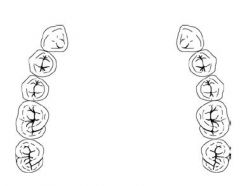
What Kennedy Class is this?
|
Class IV
|
|
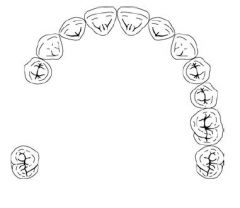
What Direct Retainer choice should be used for a case like this?
|
CLASP OF CHOICE: Akers > Double Akers
If abutment is severely tilted: - cast circumferential with lingual retention - ring clasp with support strat - rotational path RPD |
|
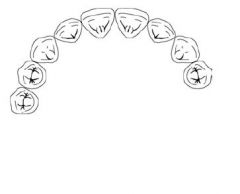
What Direct Retainer choice should be used for a case like this?
|
CLASP OF CHOICE: RPI
If can't use RPI, use RPA If can't use mesial rest, use Combination clasp (distal rest, buccal ww retention, lingual bracing) |
|
|
What is the MINIMUM number of direct retainers for CLASS I and II?
|
2 posterior abutments
|
|
|
What is the MAXIMUM number of Direct Retainers?
|
4
|
|
|
What are some ways of planning more retention and eliminating direct retainer for aesthetics?
|
- soft tissue coverage
- longer guiding planes |
|
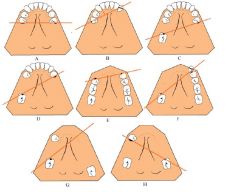
FULCRUM LINES
|
Know dis
|
|
|
What is the best way to prevent rotation about the fulcrum line?
|
INDIRECT RETAINERS
|
|
|
What are some examples of INDIRECT RETAINERS?
|
- Auxiliary cingulum rests
- Auxiliary occlusal rest - Continuous bar retainers and lingual plates |
|
|
Which ACRYLIC RESIN FINISH LINE should be placed FURTHEST from abutment teeth?
|
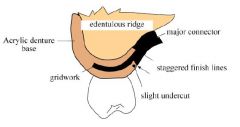
Internal finish line
|
|
|
Why should INTERNAL and EXTERNAL denture base finish lines be offset?
|
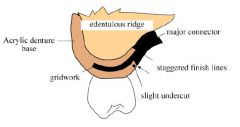
Improves strenght at the metal / denture base junction
|
|
|
The external metal finish line should be located how far from the replacement denture teeth?
|
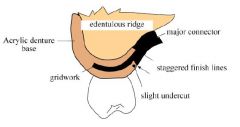
2mm lingual to the lingual surface of denture teeth
|
|
|
What kind of joint should the acrylic resin base make with the major and minor connectors?
|
Butt joint (or slightly undercut)
- NOT feather edge |
|
|
What is the advantage of ACRYLIC RESIN BASE?
|
- ability to reline base as supporting tissue changes
- esthetically superior to metal - ease of repair |
|
|
What are the DISADV of acrylic base?
|
- dimensional stability less than metal
- lower strength - porous - low thermal conductivity |
|
|
Why is THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY important?
|
Thought to maintain tissue health by ensuring patients do not swallow substances that are too hot. Some patients feel improved thermal perception lessens the feeling of the denture as a foreign object
|
|
|
What are some advantages of METAL base?
|
- thermal conductivity
- accuracy and permanence of form - hygeine - weight and bulk |
|
|
What is the minimum size of CINGULUM REST/SEAT?
|
1mm
|
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't stop whistling. |
- too much air escaping at midline
- treatment: adding papilla, moving centrals palatally, thinning behind laterals and canines |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
----------------------- My ear is aching. |
- TMJ pain actually from increased vertical
- Premature occlusion |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't swallow anything. |
- Upper posterior seal too long or too thick
- increased vertical - xerostomia - overextended lower lingual flange (especially in retromylohyoid zone) |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- Food sticks under my dentures |
- some is normal
- adaptation problems - short borders - unilateral tooth contact - poor posterior seal - unilateral premature occlusion |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- Saliva gets under my top plate. |
- Probably due to resorption or rebound of resilient tissues
- TREATMENT: adjust with PIP to decrease film thickness |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't taste my food anymore. |
- TREATMENT: flavour their food better
- atrophy of taste buds with age is normal - lack of heat transfer to palate (consider metal base) |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- Everything tastes funny (or odd). |
- worry
- menopause - nervous patient - poor OH - porous chairside liners - metallic taste - salty drainage of cyst - hemorrhage |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My plates come out when I sneeze. |
- teeth too far buccally
- over-extended hamular notch - poor posterior extension or seal - teach patient to cover mouth with hanky (polite / less embarrassing) |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- When I drink my dentures fall out. |
- normal to loosen at first
- poor peripheral seal - poor occlusion |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- Water drools out of the corners of my mouth. |
- pregnancy has been indicated
- TREATMENT: if vertical is correct then add resin on lower in modiolus area - increase or decrease vertical - afraid to swallow or spit - poor neuromuscular control - excessive salivation |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My plates are sharp and cut me. |
- xerostomia
- sharp borders or bubbles - elderly and debilitated (try soft liners) - chipped teeth - resorption causing epulis fissuratum |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My teeth are getting dull. |
- Hardy's need sharpening
- closed vertical due to resorption - lacks neuromuscular skill - teeth worn |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I bite my cheeks and tongue with these damn things. |
- poor occlusion
- decreased vertical - edge to edge horizontal set - poor neuromuscular control - insufficient buccal corridor |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My wife (husband) and friends say I have bad breath. |
- poor hygeine
- not soaking at night - systemic or oral disease |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My mouth is always dry. |
- cholera
- nephritis - high fever diseases - psychotic - drugs - age health - severe home stresses - xerostomia treated with sialogogue - radiation - Vit A deficiency - diabetes |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My teeth are noisy. |
- loose prosthesis
- increased vertical - poor neuromuscular skill - porcelain teeth used - over extended flanges pushing dentures away from seal |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- These things gag me. I'm throwing up. |
- long posterior seal
- poor seal or retention - increased vertical - mental health problems - insufficient pressure at post dam |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My lower lip tingles |
- pressure on mental foramina
- TREATMENT: relieve base - soft liner - surgery |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My mouth burns all over. |
- TREATMENT: large doses of vitamins or liver extract
- soft liners - poor hygeine - true monomer allergy - nerve pressure - avitaminosis - menopause - endrocrine imbalance |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't chew on either side. |
- normal habit
- poor retention - poor occlusion - 20 - 25 percent only, but patients expect more - poor neuromuscular control |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My teeth are staining and getting uglier. |
- poor hygeine
- old forms of plastic teeth |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My friends say I look horrible. |
- Class II
- poor selection / arrangement of teth |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- While I smile, my uppers fall down. |
- overextended labial flange
- reline needed |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My tongue won't move |
- crowded
- fear of tripping denture - undercut lingual flange |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- These teeth don't meet together. |
- decreased vertical
- poor occlusion |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't wear the bottoms (lowers). |
- typical
- short lingual flange - short of retromolar pad - resorption - poor occlusion |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I have to use powder to make them stick. |
- resorption
- habit from previous experience - incorrect extensions |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My nose and chin are coming together, corners of mouth are folding down |
- closed vertical originally
- resorption |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't see my front teeth anymore. |
- resorption
- fracture of teeth or wear of teeth |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- Why didn't you make me a set as good as Mrs. Jones? |
- Class II
- poor tooth selection - poor patient education |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- You didn't get rid of my wrinkles. |
- Class II or III
|
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I'm not going to be able to wear these. |
Class II
|
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- I can't talk with these. |
- increased vertical
- poorly positioned teeth |
|
|
What are some considerations and possible treatments when a patient presents with this statement:
--------------------------- My jaws are tired. |
- increased VDO
- poor masticating alignment |
|
|
What are the most common preparation procedures in the mouth for RPD Phase I?
|
- performing extractions
- modification of the existing occlusal scheme - definitive periodontal therapy - endodontics - operative dentistry - fixed prostho |
|
|
What are some requirements for a master cast?
|
- casts must be accurate
- neatly trimmed - dense - free of voids / blebs - should be extended to include all of the area available for denture retention and support - maxillary casts should indicate a definite posterior border for the appliance and display hamular notches and entire tuberosity - mandibular casts should include all of the retromolar pads and retromylohyoid fossa - base of maxillary casts should be 1/2 inch thick - lingual area of mandibular casts should also be 1/2 inch thick |
|
|
What are some common metal framework problems?
|
- Frame fits cast but not oral cavity
- frame pops up before a complete insertion is completed - teeter-totter of framework - bent major connector - broken cast-type clasp |
|
|
What are some solutions/ considerations for:
RPD frame fits cast but not oral cavity? |
- distorted master impression. remake case
- abutment teeth have drifted. place self-cure resin blocks into mesh area for temporary occlusion and have the patient wear the frame for several days. hope for orthodontic-like positional movement |
|
|
What are some solutions/ considerations for:
Frame pops up before a complete insertion is accomplished? |
- too much retention. reduce height of contour on teeth
- inflexible retentive clasps. thin and taper the clasp toward the tip - rigid parts of the framework ie major connector, bracing clasp, or guide plate are in harsh premature contact with teeth. Reduce frame thickness and/or height of contour of teeth. Also, check the cast for signs of abrasion and adjust the framework accordingle |
|
|
What are some solutions/ considerations for:
Teeter-totter of framework. |
- locate the fulcrum point with rouge-chloroform and reduce frame and/or tooth
- distal extensions only. expect slight posterior-downward rock on a distal extension frame. Essentially, you are usually observing mucosal compression under the soft tissue stop. If your impression was accurate then resin saddle will not allow this rocking after processing. If posterior downward rock persists at delivery then consider a reline. If the downward rock at framework-try in is gross, make an altered cast impression |
|
|
What are some solutions/ considerations for:
Bent major connector. |
- section major connector at the bend
- replace each part into oral cavity properly and make a full arch over impression - pore stone cast and send to lab for a weld repair - distorted master impression: remake case. |
|
|
What are some solutions/ considerations for:
Broken cast -type clasp |
- place clasp part and framework correctly into the mouth. Dura-lay parts together. Take a full arch impression pulling the framework with it. Pour cast and send it to the lab for weld
- consider the above except have the lab place a retentive wrought clasp into the adjacent resin base or weld the wrought clasp to the framework. |
|
|
What are some of the components of PREVENTION that we should be considering during case planning?
|
- proper design of the entire oral prosthesis
- massage of the remiaining mucosa - proper diet - recall for periodic checkups and treatment - occlusal adjustments - excellent oral hygeine for the prosthesis and the oral cavity - removing removeable appliances at least 6 hours every day - proper education of the patient |
|
|
What distance from the FREE GINGIVAL MARGIN should a LINGUAL BAR be?
|
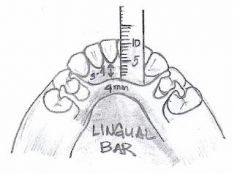
3.0 - 4.0 mm
|
|
|
What is the WIDTH of a lINGUAL BAR?
|
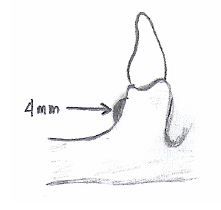
4mm
|
|
|
Where should the inferior border of a LINGUAL PLATE be?
|
- as close to the floor of the mouth as possible without interfering with normal movement
|
|
|
In an AP strap, how far from the free gingival margin should the ANTERIOR strap be?
|
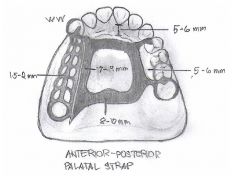
6.0 mm
- should not be placed any further anterior than the anterior rests - anterior and posterior straps should be perpendicular to the mid-palatine suture |
|
|
What should be the WIDTH of the ANTERIOR STRAP of an AP strap?
|
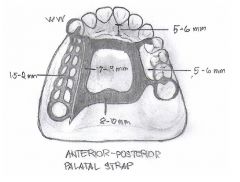
8-10 mm to prevent flex
|
|
|
What should be the WIDTH of the POSTERIOR STRAP of an AP strap?
|
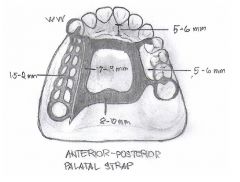
8-10mm
|
|
|
In an AP strap, what should be the width of the LATERAL straps?
|
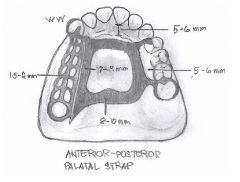
7-9mm
|
|
|
How big should the palatal opening of an AP STRAP be?
|
15mm or more in the A-P dimension
|
|
|
What are SINGLE PALATAL STRAPS usually designed for? What class of denture?
|
Kennedy Class III with or without modification spaces
|
|
|
What is the minimum width of the SINGLE PALATAL STRAP?
|
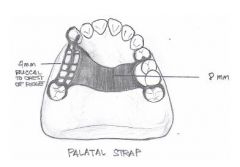
- 8 mm
- determined by edentulous space - posterior to rugae - perpendicular to mid-palatine suture |
|
|
What is the most POSTERIOR extension of Kennedy Class I or II lower RPD's?
|
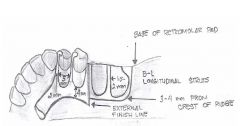
Retromolar pad beginning
- most distal strut will be placed at the base of the retromolar pad |
|
|
How wide should the STRUTS be in lower RPD base?
|
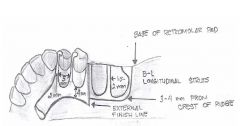
1.5 to 2.0mm wide
|
|
|
What should the buccal and lingual position of MANDIBULAR STRUTS of denture base be?
|
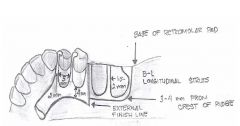
3-4mm lingual / buccal to crest of the ridge
|
|
|
How far BUCCAL should the denture base struts of a maxillary RPD be?
|
4-5mm buccal to crest of the ridge
|
|
|
What should be the width of minor connectors?
|
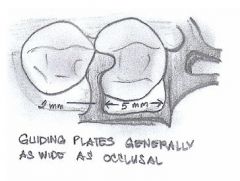
1.5 - 2.0 mm
|
|
|
What should be the distance BETWEEN minor connectors?
|
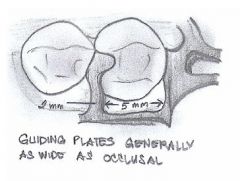
at least 5.0 mm
|
|
|
How wide should proximal plates be in Kennedy Class I or II?
|
4.0 mm buccal-lingually
|
|
|
Where should the approach arm for I-bar arise from?
|
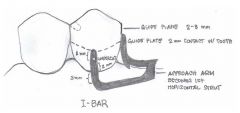
1st horizontal strut
|
|
|
How much tooth contact is needed on an I-Bar?
|
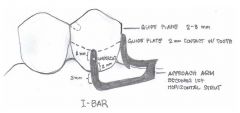
From terminus (tip at the height of contour) to 0.01 mid-buccal undercut is approximately 2.0mm
|
|
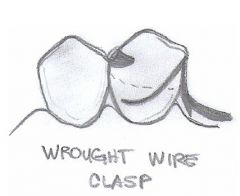
How much of an undercut is needed for a WROUGHT WIRE CLASP?
|
0.02"
|
|
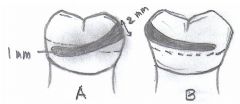
IDENTIFY A and B:
|
A: retentive arm
B: reciprocal arm |
|
|
Which part of a RETENTIVE ARM engages the undercut?
|
terminal 1/3 engages 0.01 undecut
|
|
|
What are some indications for an RPD?
|
- lengthy edentulous span
- no posterior abutment for fixed prosthesis - excessive alveolar bone loss - poor prognosis for complete denture due to residual ridge morphology - reduced periodontal support of remaining teeth - cross-arch stabilization of teeth - need for immediate replacement of extracted teeth - cost / patient desire considerations |
|
|
What are the three types of RPDs?
|
1) tissue / tooth borne
2) tissue borne 3) tooth borne |
|
|
What are the requirements of a MAJOR CONNECTOR?
|
- rigidity
- non-interference with soft tissues - food impaction - unobtrusive |
|
|
What is a brief treatment sequence for RPD fabrication?
|
1) Preliminary impression, diagnostic casts (mounted), design of RPD
2) tooth preparations, border molding RPD tray, final RPD impression 3) border molding CD tray, final CD impression 4) adjust the rpd framework 5) altered cast impression 6) maxillomandibular relations 7) setting of CD and RPD teeth, wax try in 8) delivery, adjustment, continuing care |
|
|
EXAMPLE OF WORK AUTHORIZATION:
|
- Please wax + cast a mand. partial denture framework:
I MAJOR CONNECTOR - lingual plate with mesial rest on #21 and #29 II RESTS - mesial #21 - mesial #28 - mesial #29 III GUIDE PLANES - 2-3 mm metal guide planes on distal of #21 and #29 IV CLASP RETENTION - #21 I bar engaging 0.015' mesial-buccal undercut Polish and return for try in. Thanks, L.D. NOTE: Case has been disinfected with NaOCl |
|
|
EXAMPLE OF WORK AUTHORIZATION:
|
Please set the teeth for a wax-try in:
I ANTERIOR - midline marked - set teeth to bite rims -> 3mm overjet + no overbite (vertical overlap) - plastic II POSTERIOR - 33 M rational flat plane teeth - set to 0' linear occlusion - plastic Thanks L.D. NOTE: Case has been disinfected with NaOCl |
|
|
What are some questions that must be asked in regards to RPD FRAMEWORK CONSTRUCTION PRIOR to submitting cases to the laboratory
|
- Has the case been properly disinfected and indicated on the prescription?
- Are casts free of imperfections? - Is the case properly designed? - are the instructions clear and complete for each abutment as to clasps, rests, etc? - is the type of major connector specified? - is the case tripoded? - is the jaw relation stable, accurate, and reproducible? - are the preparations for the rests , embrasures sufficient as to allow fabrication of strong clasp assembilies? - is there sufficient interocclusal or interridge space to allow for metal, acrylic, and artificial teeth? - does your occlusal plane need modification by extraction, occlusal adjustment, or overlay? - do you have sufficient undercut for the clasp you are using, or do you need to modify the abutment? - is your master cast poured with die stone? - are there any special instructions to include on the prescription? |
|
|
What are some questions that must be asked in regards to COMPLETE DENTURE MASTER CAST PRIOR to submitting cases to the laboratory
|
- has the case been properly disinfected and indicated on the prescription?
- are the casts free of imperfections? - is there a clearly defined peripheral roll and land area? - is there full extension in the retromylohyoid area? - are the casts extended to include the retromolar pad and hamular notch? - are all frenum attachments recorded? - any special instructions to the lab? |
|
|
What are some questions that must be asked in regards to MAXILLO-MANDIUBLAR RELATIONS PRIOR to submitting cases to the laboratory
|
- has it been properly disinfected and indicated on prescription
- are the wax rims neat so the technician knows where to place the teeth? - does the prescription state "set teeth" in Class I, II, III, edge to edge, or x-bite? - is the relation record stable, accurate, reproducible? - do you want the lower teeth set according to the lower rim or set over the ridge regardless of where the wax rim is - did you mark the midline? - are the shade and mould of anterior teeth and degree of posterior teeth indicated on the prescription? - any special instructions? |
|
|
What are some questions that must be asked in regards to PROCESSING DENTURE PRIOR to submitting cases to the laboratory
|
- has it been properly disinfected?
- is there a post-dam already on the cast? - do you want the full peripheral roll thickness on the cast or do you want it thinner in places? - did you check anatomic or smooth palate? - are there any special instructions for the laboratory? |
|
|
What are some problems that CONTRA-INDICATE fabrication of dentures?
|
- inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
- redundant tissue in the form of epuli - fibrous mobile ridges |
|
|
Why should final impressions be boxed before pouring?
|
- obtain a dense cast
- preserve the peripheral roll - determine a 1/2 inch thick base - develop a flasking ledge - eliminate distortion |
|
|
TRUE or FALSE: it is the lab tech's job to reduce bubbles, blebs, invaginations, etc?
|
FALSE. Responsibility of the dentist.
|
|
|
On evaluating MAXILLARY master cast, what are some requirements that must be met?
|
- both hamular notches
- posterior denture extension and post dam - undistorted peripheral roll with proper length and width - uncompressed rugae - frena - incisive papilla - proper 1/4 inch land area |
|
|
What are some MAXILLARY DETAIL requirements on a master cast?
|
- both hamular notches
- posterior denture extension and post dam - undistorted peripheral roll with proper length and width - uncompressed rugae - frena - incisive papillae - proper 1/4 inch land area |
|
|
What are some MANDIBULAR MASTER CAST DETAIL requirements?
|
- properly extended into disto-lingual (retromylohyoid) area
- show that retromolar pad has been completely captured iwthout distortion or compression - impress the entire buccal shelf - have 1/2 inch thick bases to prevent fracture in mail or during various lab procedures |
|
|
What are some "guides" to determining VDO?
|
- aesthetically, use amount of tooth exposure just described and also examining the facial contour to see if the patient appears "closed-down" or "stretched"
- ask the patient if the VDO seems to be about the same as they remembered their natural teeth to be (they can remember accurately after many years) - have the patient speak and make "s" sounds, being sure that there is 1 to 1.5 mm clearance in the premolar region for those sounds - have the patient make a prolonged "mmmmmm" sound and ensuring that there is freeway space ath te nd of the sound - measure against: old dentures, occlusal rim distance at VDO and VDR |
|
|
What is the purpose of the FACEBOW TRANSFER?
|
- used to position the maxillary cast in the same relation to the condylar mechanism on the articulatory as it exists between the patients max arch and TMJ
|
|
|
What is the function of the PROTRUSIVE BALANCE record?
|
- least important
- more for poor maxillary anterior ridge or shallow hard palate with little tissue for forming adequate post-pal seal |
|
|
What things need to be checked, and in what order, at the CLINICAL WAX TRY IN?
|
1) vertical dimension
2) centric relation 3) protrusive relationship 4) aesthetics |
|
|
What should you do as soon as you receive your processed dentures from da lab?
|
- visually and digitally inspect for sharp areas
- imperfections - adjust denture base - should have bilateral occlusal contact in centric and eccentric relations - |
|
|
What is the purpose of SURVEYING the cast?
|
- determine the best path of insertion / removal for RPD
- locate proximal surfaces that are or can be made parallel to act as guiding surfaces - locate undercuts for mechanical retention - identfify areas of potential hard / soft tissue interferences - determine path of insertion/removal considering aesthetics - determine restorative procedures needed - establish a formal RPD design |
|
|
The antero-posterior tilt of the cast on the SURVEYOR should be adjusted to what position?
|
- maximum parallelism of the proximal surfaces has been attained
|
|
|
What is the minimum thickness of rests for RPD?
|
1.0 mm
|

