![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PDO vino |
PDO- Spanish DOP -Denominacion de Origen Protegita
Traditional terms under PDO *DO-Denominacion de Origen -This vines is certain minimum quality, permitet varieties, viticulture and location. There is 69 DOs *DOCa-Denoimicion de Origen Clasificada - prestigious category - there is only two DOCa , Rioja and Priorat use Catalan terminologu DOQ *VP - Vinos de Pago - Coverage estates with high reputation which previously been outside Spanish categories because of its focus on international grape variety but ist quality is equal ast DOs wines. - This eatates must use only its wines,vinificate and mature on their estates. *VCIG - Vino de Calidad con Indicacion Geografica - steping stone between VdlT and DO - must have VICG qualification at least 5 years to apply DO status. |
|
|
PGI vino |
PGI - Spanish IGP -Indication Geografica Protegida
Traditional terms under PGI status *VdlT - Vino de la Tierra - mostly covers area that not have VICG or DO status - most important of this clasification is *Vino de la Tierra de Castilla *Vino del la Tierra de Castilla y Leon |
|
|
Ageing
|
*Joven
- may or may not have spent some time i oak, idmediate release. *Crianza - Reds minimum 24 months in oak barrel of which 6 months in small barrels -Whites and Rose minimum 18 months before relese with no minimum rquirement for oak ageing *Reserva - selsctet vats of better vintage -Reds minimum 36 months of which 12 months in small oak barrels -White and Rose minimum 18 months of which 6 months in small oak barrels *Gran Reserva - exceptional vintages - Reds minimum 60 months accounting 18 months in small oak barrels - White and Rose minimum 48 months account 6 months in small oak barrel |
|
|
Geography and Climate
|
Three broad climatic zones
- NW Maritame climate with high influence of Atlantic ocean, anual rainffall excess of 1500 mm, summer days 24 C and mild winter - NE-S Mediterranian climate with warm summers and mild winters moderated by sea. - Continental climate (Meseta plato), moderate summers and cold winters. Anual rainfall can be low 300 mm |
|
|
Tempranillo
|
- Spain's premier black grape variety
- Vineyards are spreead on northen and central Spain - Thick skinned grape, low acidity, - often used carbonic maceration for fresh strawbery flavoured joven wines for early drinking, but also play key role in production age worthy, oaked wines or in blends with Garnacha, Graciano or Mauzelo |
|
|
Granacha Tinta
|
- (Grenache), high alcohol
- its widely used for rosados (Rose) - Important in Priorat where low yielding, old vineyards produced intense, complex and full-bodied wine. |
|
|
Monastrell
|
- (Mourvedre) , dark powerfull spicy wines, high in tannin and alcohol, and medium to low acidity.
- thick skinned grape more resistend to drought - ist grow SE DOs vineyards as Yecla and Jumilla - Its also grown in Catalunya, where is used for Cafa and some fortified wines. |
|
|
Graciano
|
- growing mainly in Rioja where is used for finest wines
- small quantities is used to add powerfull black fruits flavour, acid and tannin to help wine ageing. |
|
|
Carinena or Mazuelo
|
(Carignan), gives a wine dark colour, high acid and taninn
- small proportion with Tempranillo give ideal blend |
|
|
Mencia
|
- suits cooler condition give a wine fresh fruit, medium to high acidity and somethimes herbaceousness.
|
|
|
Verdejo
|
- high sensitive to oxidation, so ist mostly used for Sherry style wines
- with anaerobic winemaking can produce light bodied, chrispy, peach, melon flavoured, or with skin contact or barrel fermentation can produced fuller-bodied wines |
|
|
Alarino
|
- aromatic variety, high acidity with stone fruit flavours
- grow in the N of Spain - thick skinned grape and resist to fungal disease - it can be made in fuller and richer bodied style |
|
|
Airen
|
- most planted variety in Spain especialy in La Mancha
- resist to heat and drought - most of yields is using for production of brandy de Jerez |
|
|
Macabeo - Viura
|
(Maccabeu), chrisp with subtle herb and spicy wines
- its used for both still or sparkling wines - In Rioja is called Viura and can be used vor hevely oaked white wines. - also is grown in Catalunya for Cava together with *Parellada *Xarel-lo |
|
|
Viticulture and Vinification
|
- with exceptions of NW Spain rest of region have chalenge with heat and drought.
- low density, bush trained vineyard - Irrigation is legalised in 1996 - mechanical harvesting slow include where is vineyards wire trained. - grater care to grape during the harvest time, night harvest and in early morning is included to avoid oxidation. - oak retains a prominent role in production of reds - most of premium wines is aged in American oak, an have vanilla and spice character that combinied well with ripe. developed fruit flavours. - trend for using French oak is increasing, and younger wines have spice and toasty character. - |
|
|
Regions
|
- principal DO regions can be grouped into six geographical regions, which some of them have common climate and grape varieties.
Unofficialy they are: *Upper Ebro *Catalunya *Duero Valley *North-West *Levant *Castilla-La Mancha |
|
|
The Upper Ebro
|
Following the river Ebro from North-West to the medieterranian sea are spread a lot of vineyards and included in different regions
*Rioja *Navarra *Carinena *Calatayud *Somontano |
|
|
Rioja
|
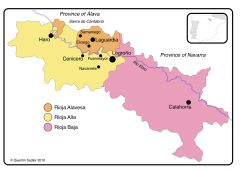
- First region awarded with prestigious DOC status.
- Bush trained vineyards, recently is permited wire training. - Eight white vine varieties are permited, most widely plantet is Viura (Maccabeu), recently is permited growing of Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc and Verdejo - Traditional red Riojas is defined by maturation and blending and giving very good results in long agening process at old oak barrels (barriques), which give very subtle oak flavour but alowed long controled oxidation. - Consejo Regulador rquires longer maturation for Rioja and Duero wines Red Crianza must be 12 months (from 6), Red Gran Reserva 24 months (from 18), white Gran Reserva 12 months (from 6) - New style of Rioja wines started from 1970, longer maceration still blended, particulary for Tempranillo shorter maturation in new French oak barrels. Results is deeply coloured, tanninic wine with primary fruit and oak flavours. - More recently white wines are produced with ageing in oak barrels, which wines have oxidative, oak character and fallen out of favour modern consumers. Modern white Riojas are made in stainless steel, on lower fermentation temperature and bottled young to preserve fruit character. - Principal city of Rioja is Lagrono and is used as point for three sub-regions *Rioja Alavesa - situed W of Lagrono on N Bank of Ebro river - vineyards altitude range is up to 800 m into foothils of Cantabrian Mountains - very chalky soil and wines are lightes of Rioja - share same climate with Rioja Alta *Rioja Alta - located W of Lagrono, mostly on S bank of Ebro river and retain region devide on two Rioja Alavesa at North bank of Ebro - altitude 500-800 m - largely limestone-based clay, but many is reddish with high proportion of iron. - Anual rainfall 500 mm - moderate continental climate, protected by Cantabrian Mountains from worst Atlantic weather (anual rainfall 500 mm) but are exposed to Atlantic winds which moderate climate. *Rioja Baja - situated E of Lagrono, mainly on south bank or Ebro river. - Climate is more continental with hot summers and severe winters, anual rainfalls of only 300 mm affect drought - heavy clay soil - the principal grape variety is Garnacha Tinta and wines tend to have less ageing affinity than at Rioja Alavesa and Alta - Increasing amount of Graciano is being planted and using for blending with Tempranillo from Alavesa and Alta |
|
|
Navarra
|
- in past its was known by alcoholic roses made from Garnacha which was often oxidised too. Uder support of Consejo Regulador most grower are switched to red wine production.
- Region is spread from northern borders of Rioja on North to foothills od Pyrinees - Divided to five subzones, all with different climate mainly affected from altitude, similar to Rioja Baja - Tempranillo is now more widely planted than Garnacha, there also significant vineyards of Cab. Sauvignon and Merlot - Whites account only 5% of production and are made from Viura, Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc. - Garnacha is mostly used for rose wines and is picked earlier to ensure high acidity, then handled anaerobically to produce refreshing, fruty wine with moderate alcohol. |
|
|
Carinena and Calatayud
|
- S and SW of Zaragoza is this two neibourgh DOs regions
- Low rainfall, warm continetal climate - Garnacha is main planted variety, although Consejo Regulador are promote Tempranillo in Krianza and Reserva styles. - inexpencive or mid-priced , soft and savory style wines - Carinena grape variety is not mostly plantet in DO region with the same name |
|
|
Somontano
|
- North of Ebro spread to the foothils of Pyrinees
- This region is affected under north cool winds from Pyrinees which are cooling hot continental climate to moderate. - Exellent and good valued reds, whites ad roses wines serving on international market. |
|
|
Catalunya
|
- has generic DO for still wines
- cover all of Cava production - Highlight Catalunyan's regions are: *Pendes *Priorat *Costes dei Segre |
|
|
Penedes
|
- SW of Barcelona following the coast
- three different climates results with wide range of wine styles - Mediterraneean, with hot dry summers producing mainly full-bodied red wines from Garnacha and Monastrell. - Inland climate is more temperate, vineyads suplying much of white wines using further fo producing Cava - Higher into the hills climate is more cooler and suitable for growing the international grape varieties such as Riesling, Gewurztraminer and Pinot Noir. |
|
|
Priorat
|
- located on inland in hills SW from Barcelona
- amazing tranformation, from blackwater to one of two awarded regions with prestigious DOC clasification - steep slopes often teraced - the best soil known localy as Llicorella, consist red slate and particles of mica which sparkle on sun and retain the warmth required for grape ripening. Also retain sufficient water for growing season. - 1980 group of pioners prsent to the world new style of wine, with high price wich ensure income of new investments for replanting and new vineyards. - Garnacha and Carinena vines is planted here, very low yields ensure concentration of fruit in wines. - Cabarnet Sauvignon also find its place in Priorat increased its role in traditional blends. |
|
|
Costers del Segre
|
- Inland, W of Barcelona
- continental climate with low rainfall, so irrigation is wide used - Main grape varieties are Cabarnet Sauvignon, Chardonnay and Tempranillo |
|
|
Duero Valley
|
- spring of River Duero are located in Sistema Iberico, and follows through Spain into Portugal called Douro world known by Port.
- Should be highlighted followed regions *Ribera del Duero *Toro *Rueda |
|
|
Ribera del Duero
|
- cut off maritime influence by ring of mountains, vineyards situed on a highest part of the Meseta plato
*Vega Sicilia - important producer which improve viticulture and result with high quality red wines that affect to whole region. Creditable for DO status, historicaly plantings of Bordeaux varieties Cab. Merlot and its permited since 1980s in DO reqirement. - DO status only for red and rose wines - Tempranillo dominant grape variety and is single ingredient in most of the best red wines. - Cab. Merlot and Malbec are permited - wide diurnal range helps to full ripening to the Tempanillo and retain acidity and fruity flavour. *Tinto Fino clone of Tempranillo more powerfull and tanninic than Tempranillo from Rioja |
|
|
Toro
|
-simillar climate as Ribera del Duero
* Tinto de Toro clone to Tempranillo, thick skineed grape - Joven wines is produced from Garnacha |
|
|
Rueda
|
-Situed between Toro and Ribera del Duero
- Continental climate - Chalky soil - Difference of other two neighbour DOs is focus to production of white wines - DOs imige is rebourn when Rioja-based company invest in moder anaerobic tehnology for production fresh and fruit wines. - Traditional grape variety is Verdejo, and must be present in blend with minimum 50% - Sauvignon Blanc is permitet and important variety of Rueda. |
|
|
North-Western Spain
|
- cooler climat
- results with best white wines from Spain - highlight regions *Rias Baixas *Bierzo |
|
|
Rias Baixas
|
- spread under separate sub-zones
- Maritime climate - pergola or big vine trained systems is used - Albarino is sominat grape variety here |
|
|
Bierzo
|
- lies in boundary between Galicia and Meseta
- warmer climate than Galicia with combination maritime influence. - Focus on red wines - Mencia is key variety here even though its capable produce dilute wines |
|
|
The Levante
|
- Region on mediterranean coast, south of Catalunya
- Regions *Valencia *Jumilla *Yecla |
|
|
Valencia
|
- Bulk wines was produced in past
- Now produced value-for-money, uncomplicated reds or whites made in style to meet the needs of a market - Conesjo Regulador encourage Tempranillo to be dominant grape variety but they are a lot of international varieties *Marseguera is dominant white variety but there is significant plants of *Mucat of Alexandria and sweet and usualy fortified highly araomatic white wine from *Moscatel de Valencia |
|
|
Jumilla and Yecla
|
- Located furter inland
- Main grape variety Monastrell - Yecla is simillar to Jumilla |
|
|
Castilla-La Mancha
|
- Half of Spain production comes from this part of Maseta south of capital Madrid
- Most extrime continental climate, hot summers over 40C, svere winters no maritime influence at all. - low density bush trained vineyards - anual rainfalls under 300 mm - Highlighted regions *La Mancha *Valdepenas |
|
|
La Mancha
|
- world's most planted white grape variety, Airen
- Now planting of Airen is decline as Consejo Regulador encouraging planting of Tempranillo known here as Cencibel and also int. varieties as Cab. Merlot, Syrah even Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc - La Mancha now is source of inexpencive well made reds and whites for export market and top pagos (VP) wines *Vinos de Pago |
|
|
Valdepanas
|
- lies south of La Mancha
- identical climate such as La Mancha has - built a higher reputation than northern neighbour - pale thin reds, fruty, soft, made as Tempranillo variety vine or in blends with int. varieties, often with wanila oak influence - As La Mancha more plantet grape variety is Airen |
|
|
Viñedos Singulares
|
Rioja, Spain June 7, 2017 New Sub-category for single estate designations with higher quality attributes, including 20% lower yields, manual harvesting, twice sensory evaluations before going to market |
|
|
Viñedos Singulares |
Single vineyard designations allowed in Rioja since June 2017 embraces the idea of terroir and creates a geo-based quality system focus on singular, rather than single also brings the notion of terroir more into play in Rioja, which is a region that traditionally was a region of geo-blended wines, rather than Burgundy style single site wines |
|
|
Ribera del Duero: ageing for Crianza |
2 years, minimum 12 months in oak |
|
|
Ribera del Duero: Ageing for Gran Reserva |
5 years, minimum 24 months in oak |
|
|
Ribera del Duero: Ageing for Reserva |
3 years, with minimum 12 in oak |
|
|
What are the three sub-regions of Rioja? |
|
|
|
What is Tinto del Pais? |
AKA - Tempranillo local name for Tempranillo in Ribera del Duero |
|
|
1988
|

