![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
causes of microcytic anemia, lab findings
|
low MCV, low rbc or low hgb
Iron deficiency anemia – Anemia of chronic disease – Thalessemia – Sideroblastic anemia "Anemia that ITSy" |
|
|
lab findings in megaloblastic anemia
|
low Hgb or low rbc, high mcv (>100)
|
|
|
calc of mcv
|
hct/rbc (rbc in fl=1 um3)
|
|
|
cal of mch
|
mean corp hem - hb/rbc
hem content of avg rbc (pg) |
|
|
calc of mchc
|
mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration =HB/HCT
Hemoglobin concentration within circulating RBCs (g/dL) |
|
|
mech of anemia of chronic dz
|
In anemia of chronic inflammation, iron cannot exit the macrophage.
Hepcidin blocks ferroportin in the macrophage so the iron can’t get out. |
|
|
mech of sideroblastic anemia
|
Iron can become trapped in the mitochondia of rbc
|
|
|
mech of thal
|
no globin chains
Iron makes it to heme synthesis, but globin chains are not made, so hemoblobin is not formed |
|
|
iron defic anemia lab findings
|
lower Fe
increased Tf lower % sat, lower ferritin, increased Tf-R |
|
|
iron stores in anemia of chronic dz
|
increased ferritin
reduced Tf nl tr receptor lower % sat |
|
|
causes of sideroblastic anemia
|
Alcohol, most common
– erythroid specific ALA-synthase (x-linked) – MDS/RARS – Drugs – Toxins (lead, zinc) |
|
|
lab findings in sideroblastic anemia
|
increased Fe in rbc precursors and in serum, inc ferritin,
nl TIBC, nl/low MCV Decreased pyridoxine |
|
|
causes of megaloblastic anemia
|
- B12 deficiency
– Folate deficiency – MDS – Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia (types I, III, IV) – Hereditary orotic aciduria – Lesch-Nyhan syndrome |
|
|
macrocytic anemias that are not megaloblastic
|
Alcohol
– Liver disease – Aplastic anemia – Hypothyroid (round shaped - not ovoid) |
|
|
peripheral smear findings for megaloblastic anemia
|
Macroovalocytes
• Hypersegmented PMNs |
|
|
bone marrow findings for megaloblastic anemia
|
Hypercellular
• Nuclear cytoplasmic dyssynchrony • Giant myelocytes • Dysplasia |
|
|
acanthocytes
|
heretidary abetalipproteinemia
cirrhosis hepatorenal failure anorexia chronic starvation |
|
|
where is Hb constant spring found and what can it be heterozygotic with
|
SE asian, with a-thal 1
|
|
|
beta+ means
|
reduced production of beta chains
|
|
|
lab findings in b thal minor
|
mild anemia, reduced MCV, reduced MCH (increased A2 and F)
|
|
|
beta thal major electrophoresis (if bo)
|
if b0: 5-10% A2, 90% F
|
|
|
electrophoresis in sickle cell dz
|
90-95% S
1-3% A2 5-10% F |
|
|
where is aa messed up in Hb C
|
same place as sickle cell but different substitution
|
|
|
homozygotes for Hb C
|
mild anemia, indirect hyperbilirubinemia, reduced MCV but increased MCHC
90-955 C 1-7% F |
|
|
what is HbE
|
southeast asion, change in position 26, mild microcytic
hz: 60-70 hb A, 30% E homo: 90% E, 3-5% A2 and 1-5% F |
|
|
findings on AIM hemolytic anemia peripheral smear
|
dense microspherocytes with no central pallor and polychromasia
|
|
|
findings on peripheral smear of oxidant hemolysis
|
bite cells, blisters
heinz bodies with supravital stains |
|
|
schistocytes, burr cells, helmet cells s/o
|
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
peripheral smear on HbH
|
recall: alpha thal with three missing globin chains)
target cells, microcytic cells and hypochromic cells |
|
|
peripheral smear on alpha thal trait
|
only mild microcytic, occ targets
|
|
|
basophilic stippling in younger polychromatophilic cells
|
lead
|
|
|
best test to id m7
|
glycoprotein IIIa (CD61)
|
|
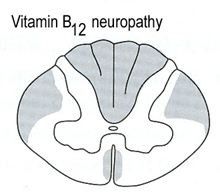
what
|
b12 deficiency -
|
|
|
folate in b12/folate deficiency
|
folate lowered in rbcs for b12 defii
folate lowered in serum for folate defi |
|
|
falsely low serum folate
|
pregnancy, myeloma,
haptocorrin deficiency |
|
|
in pernicious anemia, which is more specific and which is more sensitive
|
anti-intrinsic factor antibodies
– most specific, but insensitive (50 - 75% +) • anti-parietal cell antibodies – More sensitive, but less specific |
|
|
what is the retic index
|
retic ct x hct/nl hct
|
|
|
what is RPI
|
retic ct/maturation correction
|
|
|
causes of intravascular hemolysis
|
MAHA( DIC, TTP, HUS)
• PNH • PCH • Malignant hyptertension • Abnormal heart valve schistocytes appear |
|
|
causes of extravascular hemolysis
|
G6PD deficiency
• Hereditary Spherocytosis • Hereditary Elliptocytosis • Hemoglobinopathy • Thalassemia • Pyruvate kinase deficiency spherocytes |
|
|
red cell defects
|
Hereditary spherocytosis
• Hereditary elliptocytosis • Southeast Asian ovalocytosis • Stomatocytosis |
|
|
two causes of spherocytes
|
HS (anykrin mutation is most common)
aiha |
|
|
causes of elliptocytosis
|
-HE (Abnormal spectrin α or β, protein 4.1)
Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis (essentially a severe form of HE) cf to cigar shaped rbcs |
|
|
cause of stomatocyte
|
Hereditary stomatocytosis
– Autosomal dominant – Defect in Na/K permeability of rbc membrane • Alcohol and liver disease • Rh null disease |
|
|
where see heinz bodies
|
Seen in G6PD deficiency, unstable Hb, α thal (Hb
Barts, Hb H) |
|
|
what is Flourescent spot test,
|
NADPH flouresces, lost in G6PD deficency)
|
|
|
transmission of G6PD
|
x linked
|
|
|
settings for echinocyte
|
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
• air drying renal disease burns |
|
|
setting for acanthocyte
|
spur cell
Liver disease • Post splenecomy • McCloud syndrome • Abetalipoproteinemia (Mutated microsomal triglyceride transfer protein cannot absorb fat from food) |
|
|
two examples of unstable hb and effect on peripheral smear
|
Hb Zürich, Hemoblobin H disease
(see heinz bodies) |
|
|
high O2 affinity hb
|
Hb Chesapeake
|
|
|
name an ex methb
|
Methemoglobins, iron is in the Fe3+ ferric state, not Fe2+ ferrous (HbM Boston)
|
|
|
alkaline agar for hb
|
alkaline Cellulose acetate pH 8.5,
a fat santa claus (+ at A) |
|
|
acid agar for hb
|
Citrate Agar pH 6.0, acid gel
for a safe christmas |
|
|
globin chain in A2
|
delta
|
|
|
globin chain in F
|
gamma
|
|
|
what runs with Hb S on alk gel
|
Hb D, Hb G, Hb Lepore, india and hasharon
SDGL |
|
|
what runs with C on alk gel
|
A2, HbE and HbO run with Hb C on alk gel
“A CEO” |
|
|
what runs with A on acid gel
|
D, A2, G, E, N, I, H, Lepore
all run with Hb A on acid gel |
|
|
ultra fast moving on alk gel
|
NIH Barts
|
|
|
ultra slow on acid gel
|
constant spring
|
|
|
what is Dithionite solubility test
|
turbidity in sickle cell (cant see lines)
|
|
|
cancer that sickle cell patients are at increased risk fo
|
renal medullary ca
|
|
|
sickling test, who sickles
|
Metabisulfate sickling test - add agent, look for sickling
SS, SA (alpha thal and sickle) and Hb C Harlem |
|
|
another name for target cells
|
codocytes
|
|
|
osmotic fragility in codocyte
|
increased (too much membrane)
|
|
|
target cells seen in
|
HbC, HbE, HbS
• Liver disease • Hyperlipidemia • Thalessemia |
|
|
what are thal indices
|
Thalessemia indices
– Microcytic (MCV <75), erthrocytosis (RBC >5.5 x 1012) |
|
|
what hb shows thal indices
|
Hb E
|
|
|
golf ball inclusions on supravital dye
|
hb H
|
|
|
b thal major sx
|
Cooley’s anemia, severe, transfusion dependant
|
|
|
b thal major peripheral smear
|
Anisopoikilocytosis, nucleated rbcs, target cells, tear drop cells
• basophilic stippling |
|
|
flow for pnh
|
CD55, CD59, CD16, CD66, CD14
detects loss of GPI linked proteins |
|
|
hams test principle
|
acid urine causes hemolysis in PNH patients; heat resolves this (cuz kill complement)
|
|
|
criteria for aplastic anemia
|
absolute neutrophil count < 500/ml
– Platelets < 20 x 109/l – Reticulocytes < 1% – BM cellularity < 25% |
|
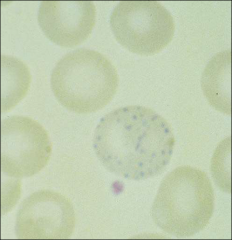
what settings does this arise
|
basophilic stippling
lead poisoning pyrimidine 5’ nucleotidase deficency MDS, infxn, sideroblastic anemia |
|
|
what are howell jolly bodies made of
|
DNA
|
|
|
where do howell jolly bodies occur
|
Seen in MDS, post splenectomy, sickle cell anemia,
|
|
|
what are pappenheimer bodies
|
iron
post-splenectomy/asplenia - iron overload |
|
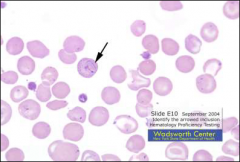
what, where
|
cabot ring
Ring shaped inclusion • Can look like 8 • Microtubule • Remnants of mitotic spindle • Seen in megaloblastic anemia, CDA and lead poisoning |
|
|
effect of autoagglutination on rbc indices
|
CBC incorrect values
– ↓RBC count – ↑ MCV |
|
|
Stomatocytosis assoc with
|
Rh null disease
|
|
|
Spherocytes assoc with
|
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
Target cells + Hb C crystals
|
= Hgb CC
|
|
|
when might you transfuse someone with scd
|
to avoid stroke
|
|
|
what's a false neg for g6pd
|
a recent hemolytic episode
|
|
|
common finding in hemolytic anemia (in lab)
|
Hemolytic anemia, low Hgb A1C levels
|
|
|
PNH mutations of
|
GPI proteins
|
|
|
unique fx of P malariae on peripheral smear
|
Plasmodium malariae, band form lacks stippling,
|
|
|
triad of PNH
|
hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia and thrombosis
|
|
|
decreased Lap score
|
CML and PNH
|
|
|
what is cause and what is result of pnh thrombosis
|
cause: lack of CD59 on plts
result: budd-chiari |
|
|
how is hemolysis caused in PNH
|
activation of complement alternate pathway (C3b) - not classic C1, C4, C2
|
|
|
what are downey cells
|
Cd8 t cells
|
|
|
what is 5q - syndrome
|
5q-syndrome is characterized by macrocytic anemia often thrombocytosis, erythroblastopenia, megakaryocyte hyperplasia with nuclear hypolobation and an isolated interstitial deletion of chromosome 5. The 5q- syndrome is found predominantly in females of advanced age.
|
|
|
three causes of petechiae with normal coag
|
- vit c def
- miningococcemia - CRF - depressing plt fxn |
|
|
marked splenomegaly (5 associations)
|
CML
myelofibrosis with myeloid hyperplasia Gaucher Kala-azar (visceral leishmaniasis) Hairy cell leukemia (mild forms with mono) |
|
|
mech of pml dic
|
release of granules/auer rods triggering coag cascade
|

