![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Psoriatic arthritis is classified with the spondyloarthropathies because
|
Psoriatic arthritis is classified with the spondyloarthropathies because of the potential axial involvement, the contribution of enthesitis in its pathogenesis, and its increased association with HLA-B27.
|
|
|
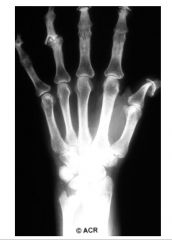
This radiograph shows “pencil-in-cup” deformities of the distal interphalangeal joints of the thumb and middle fingers. These deformities are caused by erosive changes associated with psoriatic arthritis.
|
|
|
|
dd
|
|
|
|
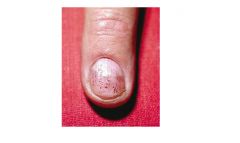
nail pitting
|
|
|
Psoriatic arthritis most commonly presents with a
|
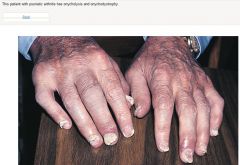
Psoriatic arthritis most commonly presents with a symmetric polyarticular arthritis that resembles rheumatoid arthritis in distribution except that psoriatic arthritis also is associated with increased involvement of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints (Figure 17 ). In a small subset of patients with psoriatic arthritis, the arthritis is limited almost exclusively to the DIP joints and is often associated with psoriatic fingernail changes with pitting and onycholysis
|
|
|
Up to 40% of patients with psoriatic arthritis have evidence of
|
Up to 40% of patients with psoriatic arthritis have evidence of either sacroiliitis (which may be asymmetric) or spondylitis, most often accompanying a peripheral arthritis. In a small percentage of these patients, involvement is limited to the spine.
|
|
|
A diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis should be suspected in patients with
|
A diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis should be suspected in patients with dactylitis, marked DIP joint involvement, asymmetric joint involvement, symptoms of enthesitis, or joint ankylosis. In these patients, a thorough skin examination should be performed to evaluate for nail changes or undetected small patches of psoriasis in areas such as the scalp, periumbilical area, and intertriginous skin folds to verify the diagnosis.
|
|
|
definition
|

|
|
|
tx
|

|

