![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what to see in P
|

|
|
|
most accurate test
|

|
|
|
what is shirmer test
|

|
|
|
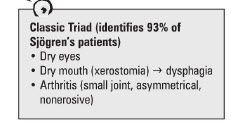
when to think that this is shogren
|

|
|
|
tx
|

|
|
|
What HLA type is Sjögren syndrome associated with?
|
What HLA type is Sjögren syndrome associated with?
HLA-DR3 |
|
|
What type of cancer are patients with Sjögren syndrome at high risk for?
|
What type of cancer are patients with Sjögren syndrome at high risk for?
Lymphoma |
|
|
What autoantibodies is Sjögren syndrome associated with?
|
What autoantibodies is Sjögren syndrome associated with?
Anti-single stranded (SS)-A (Ro) and anti-SS-B (La) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Sjögren syndrome?
|
What is the treatment for Sjögren syndrome?
Corticosteroids |
|
|
confirmatory test
|
parotid gland byopsy
|
|
|
Additional systemic features of Sjögren syndrome include c
|
Additional systemic features of Sjögren syndrome include cutaneous vasculitis, peripheral neuropathy, vasculitis that may be associated with mononeuritis multiplex, and interstitial nephritis with associated distal renal tubular acidosis. Pulmonary involvement may develop in patients with Sjögren syndrome and most commonly manifests with interstitial lung disease; however, bronchial and bronchiolar disease also may occur.
|
|
|
In addition to Sjögren syndrome, the differential diagnosis of parotid gland enlargement includes
|
In addition to Sjögren syndrome, the differential diagnosis of parotid gland enlargement includes bacterial, mycobacterial, fungal, or viral infection; lymphoma; sarcoidosis; amyloidosis; alcohol abuse; bulimia; and HIV infection.
|
|
|
Patients with primary Sjögren syndrome have up to a 44-fold increased incidence of lymphoma, particularly non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and should be monitored closely
|
Patients with primary Sjögren syndrome have up to a 44-fold increased incidence of lymphoma, particularly non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and should be monitored closely for lymphadenopathy. This patient’s firm enlarged left axillary lymph node and pancytopenia particularly raise suspicion of lymphoma, and an excisional axillary lymph node biopsy is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management.
|
|
|
a
|

|
|
|
j
|
|

