![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why do you administer thiamine together with glucose for someone with hypoglycemia?
|
Pyruvate dehydrogenase, which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA, required thiamine as a cofactor.
Thiamine is also required for transketolase, an enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway. Some people have a genetically altered transketolase that has a weaker affinity for thiamine. These people, when given IV glucose, could have severe thiamine deficiency, and cause Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. It is not clear how this happens, but neuronal damage in the brain occurs. Wernicke encephalopathy: * encephalopathy * oculomotor dysfunction * gait ataxia Korsakoff syndrome * chronic amnesia. |
|
|
What is the name of the potassium binding resin used to treat hyperkalemia?
|
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
(Kayexalate). |
|
|
How do you decide whether to use ASA or warfarin to anti-coagulate a patient with a-fib?
|
CHADS2
CHF, 1 pt Hypertension, 1 pt Age > 75, 1 pt Diabetes, 1 pt Stroke, 2 pts If patient is 2 or more points, then use warfarin. Otherwise, use ASA. |
|
|
What is the anion gap formula? What is it used for?
|
AG = Na - (Cl + HCO3)
Normal AG is 7-13. It is important in differential diagnosis in metabolic acidosis. Tells you whether there are unmeasured anions in the blood. If there are, then AG will increase. |
|
|
Where does prostate cancer metastasize to?
|
Lymph nodes and bone.
|
|
|
What are the neurotransmitters of preganglionic neurons in the:
a) sympathetic nervous system? b) parasympathetic nervous system? |
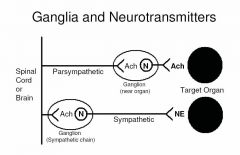
a) SNS - acetylcholine.
b) PNS - acetylcholine. |
|
|
What are the neurotransmitters of postganglionic neurons in the:
a) sympathetic nervous system? b) parasympathetic nervous system? |
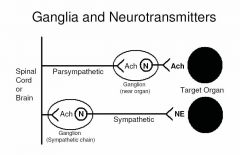
a) SNS - norepinephrine.
b) PNS - acetylcholine. |
|
|
Where do you find nicotinic receptors in the autonomic nervous system?
|
Parasympathetic and sympathetic pre-ganglionic receptors.
Aside note: also found on skeletal muscle, at the neuromuscular plate. |
|
|
Where do you find muscarinic receptors in the autonomic nervous system?
|
At the parasympathetic post-ganglionic site.
Aside notes: Also found at * heart SA node * Smooth and cardiac muscle, and glands. |
|
|
What are the features of Horner's syndrome, and what causes it?
|
Miosis, ptosis (drooping of eyelid), and anhidrosis.
Caused by a lesion in sympathetic pathway that supplies head, neck, or eye. |
|
|
What is Pancoast syndrome?
|
It is brachial plexus pathology due to a tumor (usually lung cancer in the sulcus of the lung).
Often includes symptoms of Horner's syndrome, but in addition, pt feels weakness in the hand muscles as well as pain in the shoulder and arm. |
|
|
What happens if hypertonic solution is administered too quickly to a human?
|
Brain cells will shrink, causing acute osmotic demyelinization, aka central pontine myelinolysis.
|
|
|
What spinal level is the umbilicus at?
|
L3/4.
|
|
|
What is the spinal level of the renal arteries?
|
L1, L2.
|
|
|
What vein drains into the left renal vein?
|
Left gonadal vein.
|
|
|
What organisms can cause infections that result in lymphadenopathy?
|
Bartonella henselae (cat scratch fever), TB, toxoplasmosis.
EBV, HIV, CMV. |
|
|
What is the treatment for Syphilis, Chlamydia and gonorrhea in a rape victim?
|
Cefixime 400 mg stat PLUS Azithromycin 1 g stat
|
|
|
What is the most appropriate treatment for early mastitis (due to breast feeding)?
|
Cloxacillin 500 mg qid, for 10 days.
|
|
|
What are the top 4 most common sites for metastases, in order of highest frequency to lowest.
|
Lung
Liver Bone Adrenal glands |
|
|
What are the equations for:
* sensitivity? * specificity? |
Sensitivity: TP/TP+FN.
Specificity: TN/TN+FP |
|
|
What is the difference of specificity and PPV?
|
Specificity = TN/TN+FP
PPV = TP/TP+FP Having a high specifiity does not guarantee a high positive predictive value. PPV changes with the prevalence of the disease in the population, but specificity does not. For example, testing a disease with low prevalence may have a large number of FPs compared to TPs, just because there are just so many more people without the disease. |
|
|
What is the primary function of these activated complement proteins: C3a, C5a?
|
C3a - increases capillary permeability
C5a - increases chemoattraction |
|
|
What BMI is considered normal?
Overweight? Obese? |
Normal BMI: 18.5 - 24.9
Overweight: 25 - 29.9 Obese: > 30 |
|
|
It is normal for a newborn infant to lose weight for the first 7 days. At what point is it a cause for concern of excessive weight loss?
|
When the baby loses > 10% of newborn weight.
They should also regain the weight by 10 days of age. |
|
|
When do you use a z-track injection technique?
|
When injecting iron, or any agent that might stain the skin or pose a toxicity risk.
|
|
|
What gauge and length needle do you use for a deltoid, gluteal, and thigh injection?
|
Deltoid - 25 gauge, 5/8 inch
Gluteus - 22 gauge, 1.5 inch Thigh - 25 gauge, 5/8 inch |
|
|
What areas of the body do you use these size of sutures?
6-O 5-O 4-O |
6-O for face.
5-O for upper extremities and chest. 4-O for back, scalp, lower extremities. |
|
|
How long do you leave sutures in for the...
Face and scalp? Chest, back and abdomen? Upper extremities? Lower extremities? |
3-4 days for face and scalp
7 days for chest, back and abdomen 7-10 days for upper extremities 10-14 days for lower extremities |
|
|
What is the difference between Th1 and Th2?
|
Th1
• IFN-gamma • Promotes macrophage and CD8+ T cells. Th2 • IL-4, 5, 6, 10, 13 • B cells -> humoral response |
|
|
Classification of immunologic reactions
|
* Type I: Immediate in onset and mediated by IgE and mast cells and/or basophils
* Type II: Delayed in onset and caused by antibody (usually IgG) mediated cell destruction * Type III: Delayed in onset and caused by IgG:drug immune complex deposition and complement activation * Type IV: Delayed in onset and T cell-mediated |
|
|
Complement proteins - what do they do?
|
C3b, iC3b, C4b - opsonization, which enhances phagocytosis.
C5a, C3a - increase vascular permeability, chemotactic, and activate PMNs and macrophages. MAC attack - destruction of microorganisms |
|
|
Which cells in the body have MHC I and which ones have MHC II?
|
MHC I
- all nucleated cells - T-cell function - killer-CD8 MHC II - APCs - T-cell function - Helper-CD4 |
|
|
How are calcium channel blockers categorized?
|
Dihydropyridines (vasculature > heart)
- Nifedipine Non-dihydropyridines (heart > vasculature) - Benzothiazepines (Diltiazem) - Phenylalkylamine (Verapamil) |
|
|
How does heart failure result in peripheral edema and pulmonary congestion?
|
From Lilly (pg 237).
Heart failure results in reduced forward CO. This in term activates the RAS and also increases ADH. RAS will cause both arterial and venous constriction. The venous constriction causes ↑venous return (preload). In addition, Na+ retention will result in ↑circulating volume, which contributes to ↑preload. ADH will cause ↑circulating volume, which contributes to ↑preload. |
|
|
What is the diagnostic criteria for diabetes?
Impaired fasting glucose? Impaired glucose tolerance? |
Diabetes
- casual PG of ≥ 11.1 mmol/L + symptoms - or FPG ≥ 7.0 without symptoms after confirmed twice - or 2h OGTT ≥ 11.1 without symptoms Impaired fasting glucose - FPG 6.1-6.9 Impaired glucose tolerance - 2h OGTT 7.8-11.0 |
|
|
What are early symptoms of diabetes mellitus?
|
Polyuria
Polydipsia Unexplained weight loss |
|
|
What is the HbA1C target for most patients?
|
For most patients including those with CVD: ≤ 7%
For patients with no CVD and in whom it can be safely achieved: ≤ 6% |
|
|
What are the self monitoring blood glucose target levels for most patients?
|
For most patients:
• Premeal: 4-7 mmol/L • 2h postmeal: 5-10 mmol/L For patients in whom it can be safely achieved • Premeal: 4-6 mmol/L • 2h postmeal: 5-8 mmol/L |
|
|
Describe the flow of the fetal blood from the umbilical vein onwards.
|
Splits into 2 - portal sinus to join with portal vein which supplies liver, and ductus venosus to join with IVC.
|

