![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
149 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is section 36 ? |
Emergency detention |
|
|
CN III palsy is caused by what ?
S/S |
Caused by vertebrobasilar aneurysms
S/S: down & out + ptosis + fixed dilated pupil |
|
|
What is section 44 ? |
Short-term detention |
|
|
CN VI (LR6) palsy is caused by what ?
What is this called ?
S/S? |
Caused by Raised ICP
Abduccens nerve
S/S: ipsilateral lateral gaze palsy/fixed convergent squint |
|
|
What is section 47 ? |
Adults with incapacity |
|
|
S/S of a CN IV (SO4) palsy ?
What is it called ? |
trochlear nerve
S/S: Up and IN |
|
|
What does SO4 nerve do ? |
Makes eye go down & out |
|
|
What eye Dx causes brown pigmentation of iris ? |
Latanoprost ( for chronic glaucoma) |
|
|
How long is an MI -cf. angina ? |
> 20 mins |
|
|
What are the side effects of sulphasalazine ? (DMARD) |
hepatitis Myelosuppression
Orange urine/tears Reversible oligospermia Macrocytic anemia SJS |
|
|
What are the side effects of methotrexate ? |
Hepatitis Myelosuppression
Pneumonitis teratogenic |
|
|
What are the side effects of penicillamine ( a copper chelator)
what is it used in ? |
Wilson's disease
Side effects: Glomerulonephritis, Worsens myasthenia gravis |
|
|
How do you Rx Crohn's disease |
If acute -> Steroids
1st. Azathioprine 2nd. Anti-TNF (Infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept) |
|
|
How do you Rx Ulcerative colitis ? |
If acute -> Steroids
1st. Sulphasalazine 2nd. Anti TNF ( infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab) |
|
|
What is definition of failure to thrive in a child ? |
Weight < 2nd centile |
|
|
What is the definition of child obesity ? |
Weight > 98th centile |
|
|
What is the definition for small for gestation age ? |
Weight < 10th centile |
|
|
Polyarteritis nodosa is associated with what infection ? |
HBV |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the pubic bones |
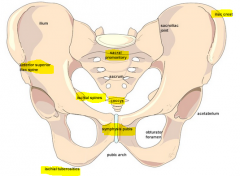
-Pubic bone ( pubic symphysis, Pubic arch, Superior/inferiour pubic Rami )
-Ischium ( Ischial tuberosity, Ischial spine)
-Ilium (ASIS/PSIS, Iliac crest)
-Pelvic brim -Sacral promontory |
|
|
What is IFN- alpha used to Rx ? |
HBV
HCV |
|
|
What is IFN- beta used to Rx ? |
MS |
|
|
What is Anti-TNF used to Rx ? |
RA
HLA-B27 & IBD & Psoriasis |
|
|
Which is commoner in Females
Primary biliary cirrhosis or Primary sclerosing cholangitis ? |
Primary biliary cirrhosis |
|
|
How do you calculate units of alcohol ? |
# units = volume (L) x Alcohol % |
|
|
By giving 1 unit of blood, how much will it increased the Hb (g/dL) ? |
1unit blood = 1 g/dL |
|
|
What causes delayed development/ failure to thrive in a child ? |
Malabsorption/illness
Hypothyroidism
Neglect (i.e non-organic failure to thrive) |
|
|
Erythema nodosum is caused by what ? |
(NODOSUM)
N-- Occult malignancy Dx - OCP Other infection (Strep, EBV) Sarcoidosis UC/Crohns Mycobacteria |
|
|
What does the Glossopharyngeal nerve do ? |
taste & sensation to posterior 1/3 of tongue
Sensation to oropharynx
Parotid innervation
Carotid baroreceptors |
|
|
What stimulates the aortic baroreceptor ? |
Vagus nerve |
|
|
What stimulates the carotid baroreceptor? |
Glossopharyngeal nerve |
|
|
What innervates the sensation to the nasopharynx ? |
trigeminal V2 |
|
|
What innervates the sensation to the laryngopharynx |
Vagus nerve |
|
|
What is the only aDductor of the vocal cord ? |
Posterior crycoarytenoid muscle |
|
|
What is the only laryngeal muscle not innervated by the recurrent laryngeal/vagus nerve ? |
Cricothyroid |
|
|
What is the only muscle of the tongue not innervated by the hypoglossal nerve ? |
Palatoglossal |
|
|
How & When do you test for eradication of H.pylori after Rx? |
1 month after Rx w/ Urea breath test |
|
|
What CN supplies the parotid gland ? |
Glossopharyngeal |
|
|
What CN opens the eyelid ? |
Oculomotor |
|
|
What CN makes the eye look down & out ? |
trochlear (SO4) |
|
|
what CN supplies the nasopharynx ? |
Trigeminal V2 |
|
|
What CN is sensory to the corneal reflex ? |
Trigeminal V1 |
|
|
What CN supplies the laryngeal muscles ? |
Vagus |
|
|
What CN supplies the trapezius muscle ? |
Accessory nerve |
|
|
What CN supplies the taste to the anterior 2/3rd of tongue ? |
Facial nerve |
|
|
What CN supplies senstation to anterior 2/3rd of tongue |
Trigeminal V3 |
|
|
What CN supplies the muscles of mastication ? |
Trigeminal nerve |
|
|
What are the indications for thyroidectomy ? |
Cosmetic
Pressure S/S
Refractory Hyperthyroidism after 2 Rx
CA
Planning pregnancy & Symptomatic |
|
|
How do you assess someones fluid status ?
(4) |
History: Intake/losses, thirst, Co-morbidities
Examination: Pulse, Cap. refill, HR, BP, JVP, Oedema
Charts: Fluid chart, SEWS
Ix: FBC, U&E
|
|
|
What is omalizumab ? |
Monoclonal antibody against IgE
Last line for asthma |
|
|
How do you Rx absent seizures ? |
Ethosuximab |
|
|
What are the causes of massive splenomegaly ? |
Malaria
CML
Myelofibrosis |
|
|
What is normal intra-ocular pressure ? |
10-22mmHg |
|
|
how do you Rx Sickle cell ? |
Vaccinations (Pneumovax, HiB,Meningococcus) Due to aplasnia
Hydroxyurea |
|
|
What does hydroxyurea do ?
used in? Side effects |
Alkylating agent (inhibits DNA synthesis) --> Increases HbF
For sickle cell, CML , polycythemia rubra vera
Side effects: Neutropennia |
|
|
How do you Rx Central retinal artery occlusion |
If <24 hrs --> Ocular massage |
|
|
How do you monitor thyroid Rx ? |
TSH ( aim for slightly lower than normal lvls) |
|
|
Rx for rosacea ? |
1) TOP metronidazole
2) PO tetracycline |
|
|
Rx diverticulitis |
IV metronidazole + Gentamicin |
|
|
HbA1C aim for DM ? |
6.5 % |
|
|
Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies are found in what disease? |
T1DM |
|
|
how do you Diagnose HTN ? |
2x 140/90mmHg
(malignant = 180/110 mmHg) |
|
|
How do you Rx vWF disease? |
Desmopressin (Releases vWF from wabel paladei bodies!) |
|
|
What is the commonest Thrombophilia ? |
Factor Leiden 5 (resistance against protein C) |
|
|
What is the commonest haemophilia ? |
vWF disease ( no platelet aggregation & no F8) |
|
|
What does side does SO4 supply ? |
Contralateral |
|
|
What does 0.5 % lidocaine mean ? |
5mg/mL |
|
|
What does 1:1000 adrenaline mean ? |
1mg/mL |
|
|
What does mycopheolate mofetil do ? |
Purine antagonist --> Inhibits T/B cell formation
(used against autoimmune dx, SLE, RA, post-transplant) |
|
|
How do you Rx moderate SLE ?
What do you need to do @ pregnancy ? |
Methotrexate
If pregnancy --> switch to sulphasalazine 3 months prio |
|
|
What is functional incontinence ? |
Mental/physical inability to get to the bathroom! |
|
|
What is Necrobiosis lipoidica associated w/? |
DM |
|
|
What is mycosis fungoides ? |
Cutaneous T cell Lymphoma |
|
|
Which rays are damaging to the skin ? |
UVB (Burns - DNA damage)
(UVA damages cell membranes) |
|
|
How do you Rx an irregular pigmented lesion ? |
Excision of entire lesion!
(For melanoma) |
|
|
How long does an infection usually present following skin excision ?
(Mins- Hrs- Days - weeks?) |
Days |
|
|
How do you Rx Shingles ? |
PO Acyclovir |
|
|
What cell in the skin is responsible for Vit D synthesis ? |
Keratinocytes |
|
|
What neurotransmitter is most involved in appetitive and approach system ? |
DA (Reward!) |
|
|
Rx for severe depression + Self-neglect |
ECT |
|
|
What antipsychotics are used in pregnancy ? |
olanzapine
Risperidone
Quetiapine |
|
|
What structures are within the retroinguinal space ? |
femoral artery/vein
Iliopsoas muscle
(Space deep to the inguinal ligament) |
|
|
When do you Rx chronic otitis media w/ effusion ? |
After 3 months |
|
|
What is chracteristic of an eosinophile? |
Bilobed nuclei
red granules |
|
|
What is characteristic of a basophil? |
purple/black granules |
|
|
Which is the only CN nerve that supplies the contralateral side ? |
CN IV (SO4) |
|
|
What is manipulation of fetus into cephalic presentation called ? |
External cephalic version |
|
|
What is the definition of
Post-term Pre-term Very preterm Extremely preterm |
Post term >42 weeks
preterm 32-37 weeks
very preterm 28-32 weeks
Extremely preterm < 28 weeks |
|
|
What is the bregma |
Anterior fontanelle in a neonate |
|
|
What is a sagittal view ? |
|
|
|
What is the commonest side effects of ACEi ? |
Cough
Angioedema |
|
|
What is HELLP syndrome in pregnancy ? |
DIC + Hepatic involvement |
|
|
When would you perform APGAR scoring ?
normal score? |
1 min
5min
10 min after birth
(Normal = 9-10) |
|
|
which hormone peaks before ovulation ? |
LH |
|
|
What defect would optic neuritis have ? |
Central scotoma |
|
|
What are the dimensions of family functionning |
CRP BAA
Communication Role allocations Problem solving
Behavior Affect involvement Affect response |
|
|
What are the signs of urethral injury ? |
butterfly peroneal haematoma
Blood from urethral meatus |
|
|
What is a basal cell papilloma ? |
Seborrheic keratosis |
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with what GN ? |
Amyloid GN !!
( Chronic dx + GN = amyloid) |
|
|
Side effects of beta blocker ? |
Worsens Raynauds - cold peripheries
Bradycardia
Worsens asthma
Postural hypotension |
|
|
side effect of NSAIDS? |
GI bleed
Renal injury
angioedema/fluid retention |
|
|
If a mom and dad have a child w/ CF , what are the chances that their next child is an unaffected carrier ? |
2/3 |
|
|
What is pars nervosa ? |
Posterior pituitary gland! |
|
|
What is couvelaire's uterus |
Placental abruption bleeding into myometrium/peritoneal cavity |
|
|
In PD, describe the Tone & reflex |
Increased tone
Normal reflex |
|
|
Rx Tachy AF ?
w/ CHF? |
beta blocker or diltiazem
If CHF - Digoxin or amiodarone |
|
|
Inheritance of hemophilia ? |
X-linked |
|
|
In the mouth, Painless yellow ulcer + red halo |
Aphtous ulcer |
|
|
What is the inheritability of schiophrenia |
80% |
|
|
Rx of fibroids |
1. Mirena 2. tranexamic acid , NSAIDS , COCP. depot
3. Myomectomy ( if fertility wanted) or uterine artery embolisation
4. Hysterectomy |
|
|
What cells are found in the fundus of the stomach ?
what do they secrete |
Parietal cells -H+ & Intrinsic factor
ECL cells - histamine
Chief cells - Pepsinogen |
|
|
What cells are found in the pylorus of the stomach ?
What do they secrete ? |
G cells - gastrin
D cells - somatostatin |
|
|
resting tremor + jaw tremor |
PD |
|
|
When are vitamin D supplements recommended to be taken? |
<5 yrs |
|
|
trauma which has then progressed to a blocked nose , What is diagnosis & how do you Rx it ? |
Septal haematoma
Septoplasty |
|
|
What is an idiosyncratic effect of a Dx |
Unique effect of a Dx |
|
|
What direction is DNA transcribed ? |
5'--> 3' |
|
|
what nerve supplies the groin |
L1
S2-4 |
|
|
What are the red flags for not reaching milestones ? |
Not sitting unsupported by 12 months Not walking by 18 months
Not grasping for objects by 6 months
No speech by 18 months
Asymmetry Regression ?hearing/visual disturbance |
|
|
what are the vaccines that elderly people get ? |
@ 65 pneumovax , Influenza (annually)
> 70 - shingles |
|
|
Risk factor for borderline Personality disorder |
Sexual abuse |
|
|
How long should you exhale for during CPR |
3 secs |
|
|
Imperforate hymen increases your risk of what ? |
Endometriosis |
|
|
Headaache after sex |
bening coital cephalgia |
|
|
headache + fever + worse w/ leaning forward |
frontal sinusitis |
|
|
Where is the surgical neck of humerus ?
Importance? Injury results in damage to what ? |
Below the greater & lesser tuberosity
More commonly # than anatomical neck of humerus
Damage to axillary nerve ( badge patch) |
|
|
Tinnitus + metabolic acidosis ??
Rx? |
ASA
Rx : NaHCO3 |
|
|
when does serotonin syndrome occur ?
Rx |
Within mins of Dx administration (SSRI)
Rx: Cyproheptadine |
|
|
Describe the ASA classification system |
Grade 1= no disease
Grade 2 = disease with no limitations
Grade 3=disease with limitations , but not life-threatening (e.g stable angina)
Grade 4 = Life-threatening disease (e.g unstable angina)
Grade 5= death < 24 hrs |
|
|
What are Reversible causes of Post-operative N&V |
Dx (opioids)
Pain
Ileus
NG tube obstruction
Metabolic disturbance |
|
|
When does neuroleptic malignant syndrome occur ??
With what Dx?
Rx? |
Within days of administering antipsychotics Dx
Rx: Bromocriptine |
|
|
Rx of antimuscarinic OD |
Physostigmine |
|
|
Rx of heparin OD |
Protamine sulphate |
|
|
Prescribe a fluid maintenance chart |
-0.9% saline + 20mmol potassium chloride ( 8hrly)
-5% dextrose + 20mmol potassium chloride (8hrly)
-5% dextrose + 20mmol potassium chloride (8hrly) |
|
|
What does Haartmann's solution contain |
NaCl
K
Lactate
Calcium |
|
|
2nd line HTN Rx for pre-eclampsia ? |
Methyldopa |
|
|
What are the side effects of methyldopa |
Post-partum depression
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Rx for a 55 yr old women + angina + HTN |
Calcium channel blocker |
|
|
Blue tinge in eyes , caused from what Dx? |
Sildenafil |
|
|
What is important advice to give on someone taking metronidazole |
No alcohol! can cause flushing (disulfiram rxn) |
|
|
Pulmonary oedema + tapping apex beat + normal LV function |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
What does pilocarpine do ?
indications |
Miosis (for glaucoma) |
|
|
How do you calculate predicted height in a child ? |
If girl ((Father -13) + mother) /2
if guy (father + mother + 13)/2 |
|
|
Altitudinal defect in vision ? |
Ischemic optic neuropathy |
|
|
What are the markers for syphillis
Active markers lifelong markers
|
Active = IgM + VDRL
Lifelong = IgG + TPPA |
|
|
What nerves do an epidural block |
T11-S5 |
|
|
What is Pica syndrome |
eating weird things ! like chalk |
|
|
What type of hearing loss is presbyacussis ? |
Sensorineural |
|
|
What are the indications for cochlear implant |
Bilateral deafness not improved by hearing aids |
|
|
Describe the changes in Pharmacology in elderly patients
Absorption, distribution, Metabolism, Excretion |
Absorption = Decreased gastric surface area, Decreased acidic dx absorption ( increased gastric pH)
Distribution = Increased free acidic drugs (decreased albumin) , Decreased free basic drugs ( increased acid glycoprotein) , increased fat (increased lipophilic Dx distribution) , decreased water volume ( decreased hydrophilic Dx distribution)
Metabolism & excretion - decreased |

