![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
356 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Normal IOP |
11-21mmHg |
|
|
What are the factors which regulate IOP |
Aqueous formation Aqueous outflow Episcleral venous pressure |
|
|
Glaucoma |
** |
|
|
Enucleation |
removal of the eye that leaves the eye muscles and remaining orbital contents intact. An intraocular tumor excision requires an enucleation, not an evisceration.
-Endophthalmitis - anophthalmia/microthalmia - uveal melanoma
|
|
|
Evisceration |
removal of the iris, cornea, and internal eye contents, but with the sclera and attached extraocular muscles left behind
-endophthalmitis |
|
|
Exenteration |
removal of the contents of the eye socket, including the eyeball, fat, muscles, and other adjacent structures of the eye. The eyelids may also be removed in cases of cutaneous cancers and unrelenting infection. -large orbital tumors -IO tumors spreading to orbit -mucormycosis |
|
|
Bones which form the orbit |
Maxillary. Frontal. Zygomatic. Ethmoid. Lacrimal. Sphenoid. Palatine. (Many friendly zebras enjoy lazy summer picnics) |
|
|
Optical canal |
Optic nerve opthalmic artery |
|
|
Enophthlamos |
Nerves Lacrimal. Frontal. Trochlear. Superior Oculomotor. Abducens. Nasal. Inferior Oculomotor. (Live frankly to see absolutely no insult) Vessels Superior opthalmic vein. Inferior opthalmic vein. Meningal artery. Lacrimal artery |
|
|
Inferior orbital fissure |
Maxillary nerve (V2) Infraorbital vessels Zygomatic nerve Emissary vein |
|
|
Annulus of Zinn |
fibrous tissue surrounding the optic nerve at its entrance at the apex of the orbit. It is the origin for the four rectus muscles |
|
|
Structures inside Annulus of Zinn |
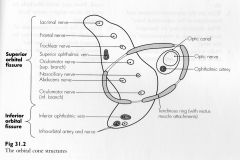
|
|
|
Normal optic disc size |
1.5mm to 2mm |
|
|
Normal optic cup size |
0.2 to 0.4 mm Central non-neural tissue in optic disc. Increased in myopes, decreased in hypermetropes. |
|
|
Normal cup/disc ratio? (CDR) |
0.3 (0-0.8mm range) >0.9 suggests glaucoma |
|
|
Abnormal CDR |
>0.8mm Or Difference of 0.2mm between eyes |
|
|
Circumcorneal injection |
Ciliary flush. Dilation of ciliary and conjunctival vessels near limbus - Uveitis - Keratitis - Angle closure glaucoma |
|
|
Causes of Epiphora |
Children: failure of recanalization of duct Mucocele & Dacrocystitis Elderly Infection & trauma |
|
|
Angle closure glaucoma |
Sp. Hypermetropes (small eye, far-sightedness) |
|
|
open angle glaucoma |
Sp. Myopes (large eye, short sighted) |
|
|
Floaters and flashers (photpsia) |
Post virteous detachment |
|
|
what is strabismus |
** |
|
|
Correction of myopia |
diverging lens |
|
|
correction of hypermetropia |
converging lens |
|
|
Correction of astigmatism |
cylindrical lens Toric lens (IOL) (difference power and different focal lengths perpendicular to each other) |
|
|
muscae volitans |
Old age floaters seen due to degeneration of the vitreous humor. Floaters>Entoptic Phenomenon>visual effects whose source is within the eye |
|
|
xanthelasma |
lipid deposits around the eye, seen in hyperlipidemia. Can be removed with green laser but recur. Usually found on the anterior surface of the eye, bilateral, near inner angle of the eye. Surgical removal for cosmetic reasons. |
|
|
Corneal arcus |
Grey-ish ring around corneal periphery. Esterified cholesterol Old age and dylipidemia |
|
|
Trachoma |
** |
|
|
Hirschberg test |
screening test for stabisumus/ocular misalignment. shining a light in the person's eyes and observing where the light reflects off the corneas. In a person with normal ocular alignment the light reflex lies slightly nasal from the center of the cornea
|
|
|
Esotropia |
Abnormal eye turned in |
|
|
Exotropia |
Abnormal eye turned outwards |
|
|
Hypotropia |
Abnormal eye lower than normal one |
|
|
Hypertropia |
abnormal eye higher than normal one |
|
|
Krimsky Test |
Prism reflex method Quantifies ocular misalignment. Patient fixates on a light, a prism is placed before the fixating eye, apex towards deviation, until the light reflexes are symmetrical, strength of prism required to center the corneal reflection in strabismic eye measures angle of deviation. |
|
|
Direct Ophthalmoscopy |
1. monocular 2. Limited field of view 3. Magnified 15 4. No stereopsis 5. Virtual erect image 6. affected by refractive errors 7. examination close to patient eye 8. easy to learn, cheap 9. low illumination 10. fundus send just beyond equator 11. 2 disc diameter focus |
|
|
Indirect ophthalmoscopy |
1. binocular 2. wide field of view 3. low magnification (3) 4 Stereopsis 5. Real, inverted image 6. not affected by refractive errors 7. examination from arms length distance 8. costly 9. bright illumination, possible to see thru hazy media 10 retina seen unto ora seratta 11. 8 disc diameter focus |
|
|
Foster Kennedy syndrome aka Kennedy syndrome aka Gowers-Paton-Kennedy syndrome |
Findings associated with frontal lobe tumors: * optic atrophy in the ipsilateral eye Optic nerve & olfactory nerve compression. High ICP due to a mass (meningioma) |
|
|
Pseudo FKS |
pre-existing one-sided optic atrophy with papilledema in the other eye but with the absence of a mass.
Seen in ischemic optic neuropathy (optic disc swelling – new episode, optic atrophy – old episode) e.g. Giant cell arteritis. |
|
|
Cataract |
Opacification of crystalline lens of eye. -age -dermatitis -congenital (rubella) -trauma -steroids -diabetes |
|
|
Band calcific keratopathy |
** |
|
|
Myopia |
Parallel rays of light entering the eye are focused in front of the retina in the un- accommodated eye. In this case the optical power is too high mostly due to increased axial length of the eyeball. Concave lens used for correction. |
|
|
hypermetropia |
Parallel rays of light entering the eye are focused behind the retina with accommodation at rest. Optical power is too low mostly due to decreased axial length. The reduced refractive error can be increased by increased accommodation hence increased convergence leading to esotropia (crossed eyes) and monocular amblyopia. Convex lens used for correction. |
|
|
Astigmatism? |
Optical power of cornea and lens in different planes is not equal hence parallel rays of light focus on different points on the retina. Cylindrical lens used for correction (toric lens) |
|
|
presbyopia |
Loss of accommodation with age because of decrease in elasticity of the lens. Occurs earlier in hypermetropes, is worse in dim light and morning (fatigue). Corrected by converging lens (+ve lens |
|
|
emmetropia |
There is no refractive error and with accommodation at rest, image forms on retina. |
|
|
Ametropia |
Condition where light not focusing on retina. Refractive error myopia (short-sightedness) hypermetropia (long-sightedness) |
|
|
Aniseikonia |
Disparity in image size between the two eyes unequal size and shape of image
|
|
|
Anisocoria |
Unequal size of pupils |
|
|
Anisometropia |
Disparity in refractive error of the two eyes can lead to amblyopia (lazy eye) hyperopic eye is chronically blurred. |
|
|
Aphakia & pseudophakia? |
After cataract extraction, the eye is rendered highly hypermetropic. This is because the lens provides 1/3 of the refractive power of the eye. Corrected by IOL, contact lenses or aphakic spectacles. After cataract, eye in aphakic IOL makes it psedophakic
|
|
|
How to calculate far point? |
Far point is the point at which an object must be placed on the optical axis for the image to be formed on the retina without accommodation. AKA farthest point from the eye at which clear image is formed.
Lens Power = 1/f(meters) inverse relationship with power |
|
|
what is the most common cause of registerable blindness? |
20-60 years - diabetes >60 years - ARMD |
|
|
Most common cause of preventable blindness |
Trachoma |
|
|
Most common cause of treatable blindeness |
Cataract |
|
|
Retinitis Pigmentosa (Rhodopsin mutation) |
Group of hereditary disorders characterized by slowly progressive pigmentary retinal dystrophy affecting rods more than cones. |
|
|
Inheritance pattern of RPA |
Isolated Autosomal dominant (best prognosis) Autosomal recessive (intermediate prognosis) X-linked (worst prognosis)
|
|
|
Progress of RPA |
Photoreceptor dystrophy starts at equatorial region--ring scotoma-central & peripheral extension -- tunnel vision-- blindness.
Presents as night blindness (early) & tunnel vision. Decreased visual acuity, normal color vision. |
|
|
Fundoscopic findings of RPA |
-Attentuated vessels -waxy pale optic disc - pigmentary bony corpuscles -maculopathy |
|
|
Tx of RPA |
None. Use Vit A and E to delay blindness reduce exposure to sunlight |
|
|
Syndromes associated with RPA |
Also seen in Usher’s syndrome, mitochondrial diseases, Abetalipoproteinemia |
|
|
Amblyopia |
Amblyopia AKA lazy eye is decreased visual acuity of un-identifiable organic disease. It is rarely bilateral. It occurs below 8 years of age, due to any cause, congenital or acquired during critical period of development (first 6 months of life – nerve pathway to brain does not develop) |
|
|
Types of Amblyopia |
1. strabismic 2. anisometropia difference 1D 3. visual deprivation (ptosis, congenital cataract, corneal opacity) 4. Hypermetropia >5D; bilateral 9 (aka isometropic amblyopia) 5. Meridional (astigmatism) >1D difference 6. Bilateral amblyopia (alcohol tobacco poisoning) 7. Toxic (Methanol) |
|
|
Tx Amblyopia |
1. remove organic cause, if any 2. cataract 3. anisometropia/refractive error 4. Occlusion therapy 5. Correct stabismus |
|
|
Benign Lid Lumps |
** |
|
|
Chalazion |
common, painless, obstruction in meibomion gland--granuloma within tarsal plate. Resolves in 6 months if not then surgical (incision + curettage) |
|
|
Internal horedeolum (abscess of meibomian gland) |
painful abscess of meibomion gland. Topical antibiotics and excision. |
|
|
External hordeolum (stye) |
Painful abscess of eyelash follicle. Removal of eyelash + hot compression + systemic antibiotics. |
|
|
Molluscum contagiosum |
umbilicated lesion on margin of eyelid caused by pox virus, irritation of eye (red eye) with follicular conjunctivitis (increased lymphoid tissue on tarsal conjunctiva). Surgical excision. |
|
|
Cysts |
Sebaceous (obstruction of pilosebaceous structure; opaque, painless, excision) - Cyst of Moll (translucent, obstruction of sweat gland) - Dermoid (hair follicle) |
|
|
Squamous cell papilloma |
common frond-like lid lesion with fibrovascular core & thickened squamous epithelium, asymptomatic, excision. |
|
|
Xanthelasmas |
lipid containing, bilateral, hypercholesterolemia. |
|
|
Keratoacanthoma |
brownish pink, fast growing, central crater filled with keratin, treat by excision careful histology (DDX-SCC) |
|
|
Naevus (mole) |
arrested epidermal melanocytes, no treatment necessary. |
|
|
Malignant Tumors of eyelid |
** |
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
Most common (90% of eyelid malignancies) Slow growing Locally invasive No Mets
Rodent ulcer, (nodular, ulcerative, sclerosing with pale margins)
Tx Excision biopsy with clear margins
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Malignant, Mets to lymph node.
Hard nodule or scaly patch. Rapid growth. Check cervical lymph node
Tx Excision biopsy with clear tissue margin. |
|
|
Causes of Ptosis (blepharatosis) |
Mechanical Lid lesions, lid edema, scarring Neurological CN III palsy, Horners, Marcus Gunn Myogenic Myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, external ophthalmoplegia Congenital – maldevelopment Aponeurotic – senile, trauma (pregnancy) Involutional - disinsertion of levator palpebrae muscle (elderly) |
|
|
Priniciple of applantation tonometery |
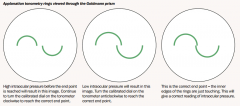
|
|
|
Method of Applantation tonometery |
determined by the force required to flatten the cornea, for the Imbert-Fick law, the force required to flatten the cornea is directly proportional to the IOP.
local anesthetic (topical – proxymetacaine) fluorescein drop (stain tear film) force applied until two hemicircles interlock calibrated into mmHg |
|
|
Cause for Leukocoria (cat eye reflex) |
congenital cataract - retinopathy of prematurity (retrolental fibroplasia) - uveitis - persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV) [primary vitreous & hyaloid vasculature do not regress] - endophthalmitis |
|
|
Latanoprost |
Prostaglandin analogue (F2 α) enhances uveoscleral outflow. Prodrug, hydrolyzed by esterases in cornea. |
|
|
Keratoplasty aka corneal graft |
Patient’s diseased cornea is replaced by donor’s healthy cornea. |
|
|
Types of keratoplasty |
1) Penetrating keratoplasty (full thickness corneal replacement) |
|
|
early Complications of keratoplasty |
- wound leak (seidel positive) |
|
|
late complications of keratoplasty |
graft rejection (immune) - microbial keratitis - recurrence of disease - astigmatism (contact lenses may be required) |
|
|
Corneal graft rejection |
Early: Late (immune; 6 months - 1 year): |
|
|
psuedoexfoliation syndrome (PEX)? |
Age related systemic disease (>65 years) manifesting itself primarily in the eyes; characterized by the accumulation of microscopic granular amyloid-like protein fibers. Buildup of protein clumps can block normal drainage of aqueous humor and can cause a buildup of pressure leading to glaucoma and loss of vision. |
|
|
TRUE EXFOLIATION of lens capsule |
infrared radiation, electric shock or electro-convulsion therapy AKA glass blowers cataract |
|
|
Baby <2 years presenting with squint? |
Rule out RB Check refractive error |
|
|
Steven Johnson Syndrome (SJS)? |
Autoantibodies against basement membrane and hemidesmosomes causing separation of epidermis from dermis (epithelium from basement membrane). This is a type II hypersensitivity reaction (IgA/IgG). |
|
|
Caused of SJS |
Drugs Infection Genetics |
|
|
Causes of catract |
Diabetes posterior subcapsular (snowflakes, white), bilateral (b) Steroids posterior subcapsular (troubled by bright light) (e) Myopes posterior capsular opacity |
|
|
Painless uveitis? |
still’s disease (triad: spiking fever, joint pain (systemic inflammatory disease), salmon- pink rash) |
|
|
flare |
Light scattering seen in anterior uveitis due to proteins that leak from blood vessels. |
|
|
Koeppe’s nodules? (Iris nodules) |
Nodules seen at inner margin of iris in patients with granulomatous anterior uveitis (sarcoidosis, TB). Histologically composed of epithelioid and giant cells surrounded by lymphocytes. |
|
|
Busacca nodules? (Iris nodules) |
Nodules seen on surface of iris away from pupil in granulomatous anterior uveitis, they are nodules of the iris stroma. |
|
|
Rubeosis Iridis? |
Tiny dilated capillary tufts of red spots at pupillary margin; abnormal iris blood vessels obstruct the angle and cause iris to adhere to peripheral corneaàsecondary angle closure glaucoma. |
|
|
Phthisis Bulbi? |
Shrunken, non-functional eye. Softened eyeball with no position or control. - uveitis - hypotony Treatmentàprosthetic eye |
|
|
index myopia? |
Nuclear sclerosis cataract causes myopia as it increases the refractive index of the lens |
|
|
appearance of retina in malignant HTN. |
Hall mark of malignant HTN is swelling of optic nerve (papilledema) Grade 1: diffuse arteriolar narrowing, concealment of vein by arterioles copper wiring, Bonnet sign (banking of veins distal to crossings), Gunn sign (tapering of veins at either side of crossings) Grade 4: silver wiring, papilledema |
|
|
Types of lenses |
Convexàmagnifies, away (converging) Concaveàminimizes, towards (diverging) Cylinder à tilts/distorts |
|
|
Persistent hyaloid artery? |
Part of persistent fetal vasculature syndrome (leukocoria + vitreous hemorrhage) 95% of premature infants lens) |
|
|
Persistent fetal vasculature syndrome (PFVS)?
|
Failure of regression of primary vitreous, stalk of fetal vessels (hyaloid remnants) Anterioràleukocoria, cataract |
|
|
Valsalva Retinopathy? |
Increase in intrathoracic pressure causes increase pressure in orbital veins, causes rupture of prefoveal capillaries pre retinal hemorrhage floaters and loss of vision |
|
|
DDx Corneal opacification |
congenital glaucoma - sclerocornea - mucopolysaccharidosis - endophthalmitis - cataracts - bacterial keratitis - lipid storage diseases like Fabre’s disease |
|
|
Complication of myopia |
(1) Posterior subcapsular cataract (nuclear) |
|
|
ROP STAGES |
(1) Demarcation line (parallel to ora serrata between vascularized posterior and immature peripheral retina (i.e. avascular retina)) (2) Elevated ridge (blood vessels enter the ridge – mesenchymal shunt joining arterioles with venules) Signs after stage 3 (plus disease) engorgement of iris 80% spontaneously regress after stage 3. |
|
|
Tx ROP |
Treatment: - Intravitreal bevacizumab injection (anti-VEGF – angiogenesis inhibitor) - Lens sparing pars plana vitrectomy (stage 4 & 5 – tractional RD) - Cryotherapy |
|
|
Berlin’s edema AKA commotioretinae? |
After blunt injury to eye. Retina appears white in periphery, but vasculature is normal. no edema Decreased visual acuity that is self resovling
|
|
|
Cherry red spots in macula |
Clinical sign seen in context of thickening & loss of transparency of retina at the posterior pole. Sphingolipidosis Sphingolipids deposit on retina, except fovea because of absence of ganglion cells
Hence contrast made |
|
|
Bull’s eye maculopathy? |
vortex keratopathy (drug deposits; swirling grey lines from infraretinal cornea – altered foveal reflex) Chloroquine retinopathy drug binds to melanin in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)à paracentral depigmentation of RPEàparacentral scotomaàspreads over entire fundusàwidespread retinal atrophy & visual loss |
|
|
explain Glaucoma Scotoma (i.e. Seidel's sign or Bjerrum Scotoma) |
arcuate scotoma ISNT
(1) Arcuate fibers (most vulnerable to glaucomatous changes) (3) Nasal fibers (relatively straight course)
sparing of only central island (tunnel vision), sparing of temporal island (nasal fibers) |
|
|
Glaukomflecken |
It is the anterior subcapsular or capsular opacity of lens associated with focal epithelial infarct from past acute angle closure glaucoma |
|
|
Rush disease? |
Aggressive Posterior ROP (AP-ROP). ROP type II ill-defined nature of the retinopathy + plus disease + posterior involvement |
|
|
Optic cup? |
Well-demarcated central non-neural tissue of optic disease |
|
|
Fundus examination? |
Look at far object to prevent accommodation |
|
|
Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy? |
Mitochondrially inherited degeneration of retinal ganglion cells and their axons |
|
|
Different IOP conditions |
Normal tension glaucoma IOP <21 |
|
|
Iridodialysis |
separation/tearing of iris from its attachment to ciliary body |
|
|
Iridodonesis |
vibration of iris with eye movement e.g. due to lens subluxation or aphakia |
|
|
Prevalence of RG blindness |
Male 7% Female is 0.1 to 0.3% |
|
|
Dual supply of retina |
Central RA - peripheral supply Cilioretinal in 30% of pop – macular supply (saved central vision in CRAO) |
|
|
How much is vision reduced in glaucoma and iritis? |
Glaucoma vision is down to counting to fingers Iritis reduced to 6/9 or 6/12 |
|
|
siderosis oculi? |
(progressive pigmentary degeneration of retina pigmentary glaucoma) caused by iron FB |
|
|
Kayser-Fleischer ring? |
bilateral pigmented ring surrounding iris - Ruby red, green, blue, yellow, or brown granular deposits of copper, 1-3mm, located just inside limbus at level of Descemet membrane (sunflower cataract)
Wilsons disease |
|
|
keratoglobus |
Rare, non-inflammatory bilateral corneal ectasia characterized by diffuse protrusion and thinning of cornea. entire cornea is abnormally thin and therefore the eye bulges. (Keratoconus, only centre part is thin)
|
|
|
causes of keratoglobus |
congenital (Ehler-Danlos type IV, Leber Amaurosis, blue sclera syndrome) acquired (end stage keratoconus, vernal keratoconjunctivitis, dysthyroid ophthalmopathy, chronic marginal blepharitis) |
|
|
Tx of keratoglobus |
scleral contact lenses - LAK |
|
|
types of iron accumulation in the eye |
(1) Fleischer’s ring (base of cone in keratoconus) |
|
|
keratoconus |
Sporadic disorder (rarely inherited) in which there is a progressive thinning of the center of the corneaàirregular conical shape of cornea |
|
|
causes of keratoconus |
primary (idiopathic, autosomal dominant (10%)) secondary (ocular, systemic) (a) Ocular: - congenital (aniridia, retinitis pigmentosa) constant eye rubbing - vernal disease/ROP (b) Systemic: - Turners |
|
|
What is corneal topography (aka belin/ambrosia)? |
Corneal mapping in severe allergy when no abnormality is found on slit lamp examination. Very sensitive test to see keratoconus and to monitor its progression (shows irregular astigmatism). |
|
|
keratoconus pathology |
Defective synthesis of mucopolysaccharide and collagen tissueàfragmentation of BM, Bowman’s membrane, degeneration of stromal collagen fibersàthinning & forward bulging of corneaàAXIAL MYOPIA & ASTIGMATISM |
|
|
Signs of keratoconus |
decreased visual acuity (myopia & irregular astigmatism) keratoscopy (irregular rings) pressure |
|
|
Tx keratoconus |
first = counseling for nature of disease, progression, impact on life |
|
|
What is Cupid’s bow in vernal catarrh? |
Cupid’s bow refers to the marginal corneal opacity, resembles arcus senilis (pseudogerontoxon). seen in vernal keratoconjunctivitis |
|
|
Effect of penetrating trauma on the pupil |
-peaked pupil corectopia (movement of iris to patch surrounding sclera) -teardrop pupil (injury to the cornea) |
|
|
Which walls of the orbit are the weakest? |
Inferior wall (maxillary) Medial (lamina papriciya) ethmoid |
|
|
Progression of vision loss in myopes? |
Initially rapidly changing glasses & progression in 2nd decade, slows down at 20-30 years, does not progress after 30 years. |
|
|
Unilateral loss of red reflex? |
corneal opacity (infection, scar) - lenticular lesion - cataract (leukocoria) - RB (leukocoria) - ROP |
|
|
orthophoria |
A normal condition of balance of the ocular muscles of the two eyes in which their lines of vision meet at the object toward which they are directed. |
|
|
Phoria |
Phoria is any tendency of deviation of the eyes from the normal when fusional stimuli are absent or fusion is otherwise prevented. |
|
|
What is the use of rose bengal in the eye? |
It is a stain with increased affinity to dead cells used to stain the devitalized cells of conjunctiva and cornea before they actually degenerate & drop off. Useful in xerophthalmia/keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye syndrome). |
|
|
uses of fluorescein? |
Corneal ulcers/abrasion applanation tonometery FFA fitting of hard lens seidel test (check leakage from eye) |
|
|
Schirmer’s test |
measure amount of tears produced.
filter paper at junction of middle and outer third of lower lid, eyes closed for 5 minutes. Amount of moisture in the paper measured. Normal ≥ 10mm Borderline 5-10mm Xenophthalmia < 5mm |
|
|
keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS)? aka dry eye syndrome |
decreased tear production or increased tear film evaporation; the aqueous tear production is insufficient to maintain normal tear film. |
|
|
causes of KCS |
- Pure keratoconjunctivitis siccaàlacrimal glands involved only - Congenital alacrima |
|
|
Xerophthalmia |
drys eye due to failure of tear production due to vitamin A deficiency |
|
|
Xerosis |
extreme ocular dryness with keratinisation |
|
|
Dx KCS? |
- Tear film break up time; <10s -Rose bengal stain -schrimer's test |
|
|
Tear film layers |
Oil-Aqeous-Mucin Oil:retards evaporation + breaks surface tension Aqueous: anti-bacterial + wash debris + Oxygen to cornea Mucin: makes cornea epithelium hydrophilic |
|
|
Lacrimal glands |
Lacrimal 95% Accessory (a) Krause’s glands: small, mucous glands |
|
|
Tx of KCS |
Artificial tears Isoptoplain (cellulose) – medium viscosity Liquifilm (polyvinyl alcohol) – low viscosity lacrilube eye gel (petroleum mineral oil i.e. paraffin) – high viscosity
Mucolytic agents pilocarpine hydrochloride (plug) retinoids treat blephritis tarsorrhapy |
|
|
Convergence exercises |
Prescribed for convergence insufficiency/disorder. Bring pencil slowly to within 2-3cm of eye just above the nose about 15minutes/day, 5 times a week. |
|
|
Extracapsular cataract surgery? |
- Indicated for hard cataracts |
|
|
bullous keratopathy? |
Bullae form on cornea as the endothelium stops working, fluid accumulates under the epithelium and causes irritation (<1000 cell/mm2) |
|
|
Herberts pits? |
Limbal follicles scar to form Herbert pits. Seen in trachoma. Specific for cicatricial phase of follicles (fibrosis). |
|
|
List the causes of increased IOP post cataract surgery? |
viscoelastic not removed, it solidifies and blocks aqueous outflow (2) uveitis (if iris is irritated) |
|
|
Recurrent episodes of chalazion? |
Meibomian cell carcinoma |
|
|
frontalis sling surgery? |
Done for congenital ptosis – eyelid coupled to frontalis relieves dysfunctional levator from contributing to eyelid elevation. (Use fascia lata for the surgery) |
|
|
Uses of prisms |
(1) Treatment for paralytic strabismus |
|
|
ophthalmoplegic migraine? |
Recurrent attacks of migraine associated with paresis of one of more ocular nerves (commonly CN III) in the absence of demonstrable intra-cranial lesion other than within the affected nerve. It is a rare disorder that usually occurs in children <10 yrs |
|
|
Fuchs endothelial dystropy |
Due to mutated gene for collagen VIII α2 Central wart deposits on Descemet membrane, defect in endothelial cells function and anatomy resulting in corneal edema Tx first relieve corneal edema (hypertonic agents, treatment of ocular HTN, contact lenses), then PKP or DSAEK surgery (for visual rehab) |
|
|
Hertel's Exophthalmometer? |
Abnormal protrusion of the eye in: - edema - inflammation >3mm difference exophthalmos/proptosis |
|
|
What are secondary causes of glaucoma? |
Pre-Trabecular neovascular glaucoma iridiocorneal syndrome (endothelial) – abnormal endothelial growth over angle – closed angle ingrowth – epithelial down growth through wound over angle – closed angle |
|
|
What are secondary causes of glaucoma? Trabecular |
(a) pigmentary glaucoma – pigment in AC, cornea, trabecular, iris - open angle (c) ghost cell glaucoma – bleached erythrocytes in AC – open angle – also hyphema (e) acute anterior uveitis glaucoma – angle zipped shut by peripheral anterior synechiae (closed angle) OR inflammation (acute open angle) (f) pseudoexfoliation glaucoma – deposited pseudoexfoliative material and pigment in trabecular meshwork – open angle |
|
|
What are secondary caused of glaucoma? Post Trabecular |
increased Pe (episcleral venous pressure) Cartotidocavernous fistula ii. sturge-weber syndromeàembryonic developmental anomaly resulting from errors in mesodermal and ectodermal development SVC Obstruction |
|
|
What are two characteristic signs of pigmentary glaucoma? |
1) Pigmentary loss and increased red reflex 2)Krukenberg syndrome Generally affectedàmyopes, males>females, 25-40 years |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of rubeotic glaucoma (90 days glaucoma)? |
Ischemia>VEGF>neovasculaization at angle of anterior chamber>Impairs aqueous outflow > Open angle
Neovascularization>Fibrosis>blocks trabeculum>contracture of iris to block trabeculum>close angle glaucoma risk factors - ischemic CRVO, diabetic retinopathy) |
|
|
What is iridiocorneal endothelial syndrome? |
- abnormal corneal endothelium migrates across angle, trabecular meshwork, and anterior iris. - corneal edema + iris atrophy + secondary open/closed angle glaucoma HSV
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of sympathetic ophthalmia? |
- Rare, devastating, bilateral, granulomatous uveitis that comes 10 days to many years (90% within a year) following a perforating eye injury (involves injured + healthy eye) Immune response to retina antigens - Treatment: |
|
|
What is Amaurosis Fugax (CRAO)? |
- Transient retinal ischemia Emboli Cholesterol - Carotid artery Calcific - Heart valves Fibrin -diseased carotid artery
Tx Cardiac workup Dec. IOP CO2 breath anterior chamber parencenteis s |
|
|
Ischemic retinal disease |
- Pale edematous retina, cherry red spot, atrophic disc, cattle trucking, emboli |
|
|
Loss of peripheral field vision? |
Absolute>branch retinal artery occlusion (cilioretinal supplies center) Relative>retinal detachment (large, bright still seen) Disease>retinitis pigmentosa (tunnel vision) |
|
|
Macular holes seen in? |
Idiopathic or blunt trauma (associated with vitreous detachment – vitreous traction, edema causes lamellar macula hole)
- Peripheral retinal holes>retinal detachment - CMO - Laser injury - DR - RD (rheg) - HTN - ERM/vitreomacular traction syndrome |
|
|
List the complications of blepharitis |
Trichasis. madarosis. stye. poliosis. ptosis Conjunctivitis Keratitis, tear film disruption, |
|
|
Treatment for corneal ulcer |
Control infection pain relief prevent perforation - anti-glaucoma drugs, pressure bandage, conjunctival flap, contact lens, corneal graft, paracentesis, avoid straining factors, NO eye pad as it gives too good a condition for bacteria to grow
|
|
|
Corneal ulcer complications |
perforation, uveitis, endophthalmitis, anterior synechiae, open angle glaucoma, scar, corneal fistula |
|
|
What is RAPD (Marcus-Gunn pupil)? |
You know this :P The most common cause of Marcus Gunn pupil is a lesion of the optic nerve (between the retina and the optic chiasm) or severe retinal disease. |
|
|
RAPD +ve conditions? |
Optic neuritis RD Optic nerve atropy neuropathy cellulitis sever glaucoma |
|
|
RAPD -ve? |
- Dense cataract |
|
|
What is absolute APD (absolute afferent pupillary defect)? |
No response to light stimulation of a completely blind/amaurotic eye. Consensual reflex is intact in affected eye. |
|
|
Pupillary light-near disassociation? |
Normal near response > eyes focus on near object, they converge and pupils constrict. Due to APD, there is decreased response to light (i.e. miosis test) but normal near reflex
- tonic/Adie’s pupil (due to ciliary ganglionitis)àthere is anisocoria - midbrain tumor (parinaud’s syndrome)
- diabetes - not seen with opacities of corneal lens - chronic alcoholism |
|
|
papilledema |
Optic disc swelling caused by increased ICP (intracranial pressure)
blurring of margins of optic disc (earliest sign) venous engorgement & hyperemia of optic disc (early) hemorrhages (hemorrhagic disc swelling) with cotton wool spots elevation of optic disc – filling of the cup
ICP (Headache, tinnitus) |
|
|
Fundoscopic findings in ION (ischemic optic neuropathy) |
Peripapillar hemorrhages on disc and disc margins - Cotton wool spots around disc |
|
|
What are the types of age related macular degeneration (ARMD)? |
Atropic - nonexudative, more common, less severe, slow progress, dry. Lipofuschin deposits b/w bruch's membrane and RPE (DRUSEN) Exudative less common, rapid loss of vision, severe, wet (neovascularization), RPE detached. VEGF. neovascularisation. subretinal leaks
Tx Argon laser Photodynamic therapy |
|
|
Hermansky-Pudlak? |
abnormalities in synthesis of melanin resulting in pigment deficiencies. Associated systemic disease with albinism Features – decreased visual acuity, photophobia, nystagmus, strabismus, ametropia, iris hypopigmentation
|
|
|
Fat, young guy presenting with blurred vision in one eye? |
MS Optic neuritis Signsàdecreased visual acuity àdecreased color vision - Diagnosed by CT, MRI, perimetry (field testing) |
|
|
stargardt’s dystrophy? |
- Variant of fundus flavimaculatus is an inherited form of juvenile macular degeneration (affects both the RPE and, secondarily, the photoreceptors)àprogressive vision lossà blindness [rapid decrease of visual acuity (6/18 – 6/60)]
Fundus flavimaculatusàvision more preserved, widespread pisciform yellow flecks Shiny – ‘16 37 throughout the fundus (more in adulthood) |
|
|
Describe basal cell carcinoma (BCC)? |
most common slow growing local invasion non metastasis painless lesion (ulcerative, sclerosing, nodular) ectropion or entropion + loss of eye lashes (madarosis)
Tx Excision. clear margins. cryo. radio.
|
|
|
Describe squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)? |
Less common malignant neck nodes scaly patch, hard nodule Tx excision
*- SC papillomaàfrond like lid lesion (fibrovascular core + thickened squamous epithelium) - asymptomatic |
|
|
Iris bombe |
Iris bombe is a condition in which there is apposition of the iris to the lens or anterior vitreous, preventing aqueous from flowing from the posterior to anterior chamber. This causes increased pressure in posterior chamberàanterior bowing of peripheral irisà obstruction of trabecular meshworkàacute attack of ACG (angle closure glaucoma) IOP at presentation is usually ≥ 60 |
|
|
Risk factors iris bombe
#39 |
àage > 60 years àfemales > males (4:1) Shiny – ‘16 38 àshallow anterior chamber/small corneal diameter ànarrow entrance to chamber angle àhypermetropes (short axial length) |
|
|
Tx of acute close angle glaucoma |
àprophylactic peripheral laser iridotomy (YAG laser) or iridectomy àintermittent angle closure (increased by physiologic mydriasis, prone and semi-prone) |
|
|
chronic open angle glaucoma risk factors |
àage > 65 àrace (blacks) |
|
|
pathophysio of chronic open angle glaucoma |
(1) thickening of trabecular lamellae (decreased pore size) |
|
|
Chronic open angle glaucoma SX |
- Symptoms: |
|
|
TX chronic open angle glucoma |
β-blockers Prostaglandin analogues àα2 agonists adrenergic drugs |
|
|
DX chronic open angle glaucoma |
- For diagnosis: à pachymetry |
|
|
Drugs for Glaucoma |
B-Blockers (Timilol) - reduce aqueous production increases asthma and CVD, decreases BP and HR
Prostaglandin analogue (Latanoprost)-increases uveoscleral outflow iris pigmentation, darkening of eyelashes, conjunctival hyperemia, macular edema, uveitis
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Dorzolamide) tinging, headache, unpleasant taste (local), SJS
α2 agonists (Brimolidine) red eye, fatigue, drowsiness
Parasympatheticomimetic (Pilocarpine) increases outflow by pulling at longitudinal fibers of ciliary body
Sympatheticomimetic (Adrenaline)
|
|
|
laser for glaucoma |
Laser trabeculoplasty (diode or argon) Laser ciliary ablation (diode)
laser only reduces IOP by 30%, so for IOP > 28 laser is not effective |
|
|
Surgery for glaucoma |
TRABECULECTOMY- fistula b/w AC and subconjuctival space
Dec IOP Infection Shallow AC cataract
no sympthamimetics (cause scarring) 5-FU to prevent scarring |
|
|
function and mechanism of action of photodynamic therapy? |
- Treatment for age related macular degeneration (ARMD) - Subfoveal vascular membranes cannot be treated by argon laser since energy is sufficient to damage photoreceptors (indocyanine greenàporphyrin like dye) |
|
|
Anti-VEGF? |
Lucentis (Ranibizumab) – 94% vision stabilization (2) Avastin (Bevacizumab) |
|
|
LASER |
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emitted Radiation, single wave length
Photocoagulation green Argon, red Kyrpton, diode Photoevaporative Photodecomposition
|
|
|
Photocoagulative Laser |
àthermal laser, tissue pigments absorb light and convert it into heat, thus raising target tissue temperature high enough to coagulate and denature cellular component green argon laser krypton red laser |
|
|
Photo disruptive laser |
Yag Laser Capsulotomy, iridotomy, anterior capsular contraction, posterior capsule opacification,
release of giant pulse of energy, when pulse is focused on a spot, light exceeds a critical level of energy density, optical breakdown occurs in which temperature rises so high that electrons are stripped from atoms resulting in a physical state called plasma. Plasma expands with increasing pressures cutting ocular tissues |
|
|
photoevaporative laser |
absorbed by water, does not enter Vitrous cavity CO2+erbium+horilium surface lesions, lid lesions, blood less incisions, |
|
|
photodecomposition |
Argon+fluorine breaks bonds and converts polymers to smaller tissue PRK, LASIK, LASEK, superfical corneal opacity |
|
|
Argon laser for Diabetic retinpathy |
- The laser is used around the retina - Diabetic maculopathy>focal or grid pattern laser photocoagulation àtreating entire retina except temporal arcade (macula + optic nerve) |
|
|
Jones Test I and II |
Test 1 to see if lacrimal system working as a whole Test 2 to see where the obstruction is
Partial obstruction Total Obstruction Pump failure |
|
|
Posterior polar cataract? |
Very dangerous because capsule is degenerated. Never do hydrodissectionàopens up weak areaàdamage to posterior capsule |
|
|
Cherry red spots in ischemia? |
- Fovea has decreased layers, it is the thinnest part of the retina, so dual supply of chorioretinal artery shows as cherry red spot (choroid reflection) |
|
|
Hippus AKA pupillary athetosis (unstable pupil)? |
Irregular dilation and constriction of pupil Continuous sympathetic flow. Aconite poison. Cirrhosis. |
|
|
iridodonesis |
Tremorous or agitated iris with eye movement caused by lens subluxation or aphakia or ectopia lentis. |
|
|
Disadvantage of LASIK? |
Thin cornea Diffus lamillar keratitis flap complications (don't lose the flap) |
|
|
Use of pachymetry |
Measure corneal thicknessàif IOP readings very high on tonometry, you can measure corneal thickness to rule out any possible over estimation. |
|
|
What is solar keratopathy? |
UVA keratitis Pinguecula.(fibrofatty) Ptergium. (fibrovascular) |
|
|
FFA stages |
1) choroidal phase>mosaic pattern, lack of dark areas 4) venous phase>veins filled |
|
|
steroid keratopathy? |
band calcific keratopathy |
|
|
Red tears |
Rifampicin; endometriosis of conjunctiva |
|
|
Cosopt |
Timolol (β-blocker) + Dorzolamide (carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) |
|
|
What is plica semilunaris? |
remnant of nictitating membrane (third eyelid) |
|
|
What are Purkinje-Sanson images? |
They are reflections of objects in slit lamp examination from the structure of the eye. P1àouter cornea P3àanterior lens
|
|
|
Piggy bank lens? |
Smaller lens on bigger lens (soft lens floats on cornea for comfort, hard lens on soft lens for vision correctionàused in keratoconus, astigmatism |
|
|
Trauma - |
Trauma to cornea > astigmatism |
|
|
Corneal Incision healing time |
3 months; avascular |
|
|
Orbital bones in order of increasing weakness? |
Lacrimal |
|
|
Cataract with yellowish hinge? |
Post subcapsular |
|
|
Indications for FFA? |
DM/HTN ARMD Planing retinal laser |
|
|
Indocyanine green use? |
Used for choroidal vessels; binds to protein and does not leak. choroidal neovascular membrane. |
|
|
Natural location of CA I (acetazolamide)? |
- Kidney - RBCs - Eye - GI - CNS |
|
|
Drugs for allergic eye disease? |
Mast cell stabilizers, anti-allergies, weak steroids, Xepat (Olopatadine) |
|
|
What are shield ulcers? |
Central, corneal ulcers covered by exudate i.e. vernal ulcers with adherent mucus plaque (seen in vernal KC) |
|
|
Complications of Chronic blepharitis? |
- Inflammation of the eyelid - Chalazion - Poliosisà |
|
|
Inherited cataract occurs at which age |
30-40 |
|
|
Complication of Avastin (Bevacizumab)? |
Corneal ulcer/abscess |
|
|
Traumatic cataract? |
Rossete shape |
|
|
Placido’s disc? |
Instrument for examining the front surface of the cornea seen through a convex lens mounted in an aperture at the center of the pattern. Such an instrument gives a qualitative evaluation of large corneal astigmatism, and is useful in cases of irregular astigmatism as in keratoconus.
|
|
|
Scotomas? |
Centrocecal > macula + blind spot (retinal ganglion cells)
Altitudinal > either upper or lower half of visual field affected (retinal vascular disease, glaucoma, etc.) |
|
|
Pulsation of CRA? |
This is abnormal and indicates occlusion |
|
|
Factors predisposing to HSV keratitis? |
- Sunlight |
|
|
Marginal naevus? |
In a nevus there is a marginal growth of vessels. |
|
|
Subconjunctival hemorrhage |
Trauma Bleeding disorder HTN Anticoagulant Inc. pressure atheroscelrosis
|
|
|
What is HUG syndrome? |
Hyphema, uveitis, glaucoma
Late post-op period after cataract surgeryàendothelial cell damageàstromal edema - àbullous keratopathy |
|
|
Apraclonidine |
Short acting β-blocker given after YAG laser treatment (e.g. capsulotomy) to prevent rise in IOP |
|
|
How does adrenaline cause pigmentation? |
Disrupts melanin metabolismàpigmentation on underside of eyelid |
|
|
Indications for vitrectomy? |
- RD (rheg or tractional) - Posterior lens displacement |
|
|
Differentials for Rubeotic Iridis? |
- Diabetic retinopathy - malignant melanoma - RB - Sickle cell retinopathy - Leukemia/lymphoma - CMV retinitis - Coat’s disease |
|
|
Clinically significant cataract? |
central location |
|
|
Hydrodissection |
Is performed to separate nucleus and cortex from lens capsule so that nucleus can be more easily and safely rotated |
|
|
Lens development? |
From surface ectoderm. Hence people with skin problems are likely to develop cataract |
|
|
How to remove lens? |
Phaco - Hard part Aspiration and irrigation - soft part |
|
|
Modes of anesthesia? |
Retrobulbar > ciliary ganglion block – 25G long needle Peribulbar> short needle Subtenon> under conjunctiva Topical > drops, gel General Anesthesia (GA) |
|
|
Treatment for congenital cataract? |
Under GA |
|
|
Types of cataract? |
Shiny – ‘16 51 - Posterior subscapular - Polar |
|
|
Giant papillae seen in? |
allergies contact lens users |
|
|
Transient blurring of vision in DM? |
- TIA - Sorbitol> swelling of lens |
|
|
Gonioscopy |
Used to see angle of anterior chamber - edge of cornea (schwalbe's line) - ciliary body (anterior part) – deep angle>increased in myopes & aphakia |
|
|
What are corneal verticillata? |
Sub-epithelial corneal deposits; fine, gold-brown, bilateral AKA vortex keratopathy (branch out from central whorl) |
|
|
What is Asteroid hyalosis? |
Degenerative condition of the eye involving small white opacities in the vitreous humor – calcium degeneration in vitreous, commonly seen in DM, HTN, hypercholesterolemia (cause unknown) |
|
|
Drugs after trabeculectomy? |
Abx steroids +5FU |
|
|
Most common cause of distorted pupil? |
post-catract |
|
|
Radial keratotomy? |
Refractive surgical procedure to correct myopia |
|
|
Choroidal sclerosis? |
Atrophy of choroidal blood vessels > RPE/photoreceptor atrophy |
|
|
Sight threatening features of Paget’s disease? |
Paget’s diseaseàchronic enlarged and misshapen bones because disorganized bone remodeling |
|
|
Angioid streaks in? |
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum - Ehler-Danlos syndrome - Acromegaly - Idiopathic Can decrease vision if: |
|
|
Cataract post-op complications? |
- Folds in descemet membrane (if IOP decreases) |
|
|
Capsular tension ring |
Used in pseudoexfoliation syndrome (AKA exfoliation glaucoma)>weak zonules |
|
|
Iris hooks |
Used if synechiae are present or if pupil does not dilate during surgery |
|
|
Watery eyes due to stenosed punctum? |
3 snip surgery to obliterate any punctum blockage |
|
|
Posterior capsular opacification? |
Residual cells migrate across its surface leading to opaque scar |
|
|
Injectable lens |
Optic Haptic |
|
|
Phaco machine (pumps) |
- Peristaltic (vacuum only when port is blocked) - Venturi (always vacuum, more aggressive) |
|
|
Viscoelastic |
- maintains chamber |
|
|
Peri-operative complications |
- prolonged phaco> stitches needed, corneal edema, uveitis - posterior capsular rupture - suprachoroidal hemorrhage |
|
|
Phaco probe – double tube |
- vacuumàsucks out lens |
|
|
Adenoviral conjunctivitis |
Immuune complex deposits on cornea |
|
|
Treatment of Retrobulbar optic neuritis (isolated) |
IV steroids (3 days), then oral – giving oral first will lead to increased severity of later events |
|
|
Signs in allergies |
Acute (<6wk) Chronic/Vernal (>6wk)
Sign Papillae Shield ulcer Trantas spots (gelatinous white clumps, upper limbus) lid edema conjunctival injection cupid bow
|
|
|
Axial Length of eyeball |
Normal 22-24mm Myopes >24mm Hypermetropia <22mm |
|
|
Back vertex distance BVD? |
Distance b/w surface of contact lens and cornea. Ideal 14mm
|
|
|
Steroids for glaucoma/cataract |
Systemic Cataract>Glaucoma Topical Glaucoma/Cataract |
|
|
Post op Endophthalmitis |
Syx Red eye pain Dec VA Hypophon
TX Steroids ABx (Intravitreal) |
|
|
Corneal transparency is maintained by? |
Avascularity Lattice framework tight epithelial junctions endothelial pump function tear film equal refractive power of all layers
|
|
|
Complex lid injury? |
Medical 1/3 canthus of eye orbital fat visible eyelid margin tear Greater than 25% skin lost |
|
|
Tx Retrobulbar hemorrhage |
Epicanthotomy
Do not do in globe rupture |
|
|
Open globe |
Pentrating injury through cornea sclera or both. Eye margin is sclera and ant. cornea |
|
|
Tenon capsule |
Connective tissue layer between conjunctiva and sclera. Makes sheath around rectus muscle |
|
|
Choroidal folds seen in |
Dusthyroid eye orbital tumors |
|
|
Delien Effect |
Post-trabeculectomy bleb at limbus causes cornea to become thin and dry
Bleb prevents tear film distribition
Tx Lubricant or bandage lens |
|
|
Minimum vision for driving |
20/40 or 6/12
Visual field
120 left and right 20 up and down |
|
|
Chronic lens wear lead to? |
Giant papillae Muller muscle damage ptosis |
|
|
Normal endothelial cell count |
3000 cornea is longer horizontally <1000 bullous keratopathy |
|
|
Define orbital blow-out fracture |
# of one of the walls of the orbit, but orbital rim remains intact
Sx Enopthalmosis emphysema diplopia infraorbital anesthesia |
|
|
gonitomy done is what conditions |
Buphthalmos Haab striae Gonidodysgeneis |
|
|
naevus of ota |
Congenital melanosis bulbi. Entrapped melancoytes in upper 1/3 of dermis
Heterochromia inc risk of melanoma |
|
|
Cause of heterochromia |
Congenital horners Physiological (inherited) hemmorhage FB glaucoma medicines (latanoprost) melanoma pigment deposition syndrome Fuchs uvieits ICE syndrome
|
|
|
Blunt trauma to the eye consequences |
Lid: Edema > ptosis Lacrimal puncta > epiphora Cornea >abrasion, edema Conjunctiva > hemorrhage, chemosis Scelra> rupture Iris > iridodialysis, iridonesis Lens > subluxation, cataract Angle > recession
Mydriasis, uveitis, Retinal dialysis, Vit hemorrhage, blowout fracture, phthisis bulbi, commotio retina, choroidal tear, optic neuropathy |
|
|
How to measure IOP? |
Goldman applanation Non contact/air puff Tono pen Rebound Palpation Pneumo Electronic indentation Schiotz |
|
|
Aniridia |
Absence of iris, usually B/L WAGr syndrome |
|
|
Role of NaCl in corneal edema |
Hypertonic saline > hypertonic tearfilm > draws water out of cornea |
|
|
Morgagnian cataract |
Hypermature cataract > liquefication |
|
|
Altitude retinopathy |
Ophthalmoscope will show flame shaped hemorrhages, dis edema, tortuous veins. Blurring of vision. |
|
|
Chemical injury |
Acid > causes coagulation of proteins to make barrier. prevents further damage. Eye is red Alkali > keeps penetrating. eye is white |
|
|
Berlin/ambriosa |
Corneal topography |
|
|
Difinition and classification of amlyopia |
Dec in visual acuity of one eye w/o organic disease
-Strabismus -Deprivation of light -Anisometropia -Meridoneal (astigmatism) -Isometropia (Hypermetropia) |
|
|
Manual small incision cataract surgery |
Entire lens exposed thru self-healing tunnel. Wound > phaco |
|
|
Intracapsular cataract extraction |
Removal of lens and lens capsule in one piece |
|
|
IOP in normal tension glacoma |
<21mmHG |
|
|
In squint exam corneal image can calculate degree of squint b/w? |
15 to 40 |
|
|
Fundoscopy, it is necessary to give patient a target to prevent? |
Accommodation |
|
|
Intrapalpebral staining or cornea + conjunctiva leads to |
Aqueous tear deficiency |
|
|
Different stains |
Sup Conjunctival stain > superior limbus, KC Inferior cornea + conjunctiva > blephritis + exposure |
|
|
Normal corneal thickness
|
540 micrometer
|
|
|
Chronic allergy |
CUpid bow/ shield ulcer |
|
|
Corneal graft success |
Visual improvement (2 snellen chart lines) Clarity of cornea no infection cosmetic |
|
|
Dense cataract complications |
Phacolytic glaucoma Phacomorphic glaucoma Phacoananaphylactic uveitis |
|
|
How to check color vision aside from ishiara chart |
100 hue test |
|
|
Tx chronic blephritis |
botox |
|
|
use of epicentral fold |
no function skin fold of upper eyelid, covering medial canthus |
|
|
OD and OS stand for |
Oculus dexter (right) Oculus sinister (left eye) |
|
|
Mylination of optic nerve fibre is called |
pseudo-papiledema |
|
|
Peter's anomaly |
Developmental disorder of anterior segment
incomplete separation of cornea from iris or lens |
|
|
Distichiasis |
Abnormal growth of lashed from meibomian gland orfices |
|
|
Maxiden is |
dexamethsone |
|
|
trilateral RB |
pinealoma and B/L RB |
|
|
For glaucoma is Oct or perimetery better? |
OCT |
|
|
Lisch iris nodule |
Seen in NF1 Pigmented nodular aggregate of dendritic melanocyte affecting iris |
|
|
Differenciate b/w Fuchs uveitis and simple uveitis |
Heterochromia KP in stellar arrangment (diffuse) Absence of synechia |
|
|
Blepharophimosis |
B/L ptosis, reduced lid size, vertical and horizontal |
|
|
Pellucid marginal degeneration |
** |
|
|
Ankyloblepharon |
Adhesion of the ciliary edges of the eyelids to each other |
|
|
Corneal scarring stages |
Nebula Macula Leucoma Adherent Leucoma |
|
|
Symblepharon |
Adhesion of the globe to the eyelid (conjunctiva)
Due to disease or trauma |
|
|
Pavingstone degeneration |
peripheral small areas of retinopathy in the outer retinad |
|
|
difference between PRK and LASIK |
PRK - laser applied to corneal surface after removing epithelium
LASIK partial thickness flap created, laser applied, flap restored |
|
|
Which disease had long arms |
Marfan syndrome Ectopic lentis, RD, myopia, Keratoconus |
|
|
Which corneal dystropies are autosomal recessive? (AD) |
Macular. Gelatinous. Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy II |
|
|
Staphlyoma |
Abnormal profusion of uveal tissue thru weak point in eyeball. |
|
|
jack in the box phenomenon |
Aphakic eye with glasses. Central field magnified, and peripheral field is blurred. So when something moves into centre its pops out. |
|
|
Phlyctenule |
Subepithelial inflammatory nodule resulting from cell mediated Ag-Ab reatcion. |
|
|
Uthoff's syndrome |
Worsening of neurological symptoms in MS when body is heated. Heat slows doen nerve impulses |
|
|
Epiblepharon |
Congential horizontal fold of skin near upper margin of eyelid caused by abnormal insertion of muscles |
|
|
River blindness |
Onchocerciasis, parasitic worm |
|
|
Visual blue in white cataract |
Visualize capsuleT |
|
|
tobaco dust particles |
Pigmented cells in the citrous and occasionally AC in rheg RD |
|
|
With the rule atsigmatism |
Vertical meridian steepest, -ve cylinder is used for correction
normal in nature |
|
|
Against the rule astigmatism |
Horizontal meridian is steepest. +ve cylinder is used for correction |
|
|
Colobma |
Incomplete fusion of choroidal tissue leading to hole in the iris, retina or choroid. Most affect the iris |
|
|
Small perforation of cornea Tx |
Cyanoacrylate glue + bandage contact lens |
|
|
Hutchinson sign |
vesicle at tip of nose, HZV ophthalmicus. |
|
|
Hutchinson triad |
Interstitial keratitis Deafness notched central incisors
(syphillis ^ + saddle nose) |
|
|
Hutchinson pupil |
dilated pupil, poorly reactive to light, supratentorial mass Inc ICP, coma patiEents |
|
|
Embryotoxon |
Congenital opacity at margin of cornea |

