![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
364 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is meant by "Subject Contrast"?
|
The contrast encoded in a signal (such as x-ray beam) as a result of interaction with the patient and anything in the patient BEFORE being measured.
|
|
|
What is an eV?
|
A measure of energy. 1 eV is the amount of kinetic energy gained by an electron accelerated by one volt of electrical potential.
|
|
|
X-rays are (transverse/longitudinal) waves?
|
Transverse. Ultrasound is longitudinal.
|
|
|
For electromagnetic waves, the product of wavelength and frequence equal what?
|
The speed of light (c).
|
|
|
X-rays used in radiology typically have wavelengths measuring between ___ and ____ in angstroms?
|
0.08 and 1.24 angstroms.
|
|
|
1 angstrom equals ____ cm.
|
1 x 10^-8 cm.
|
|
|
What is the term given to a single x-ray, the smallest unit of electromagnetic radiation?
|
Photon.
|
|
|
What is Planck's law?
|
E = h x v (v = frequency). The higher the frequency, the higher the energy of the x-ray.
|
|
|
What is 1 keV?
|
The amount of energy given to an electron when accelerated by an electrical potential of 1000 volts.
|
|
|
X-rays with high energy, short wavelengths, and high frequency cause what change in patient dose?
|
Decrease, because fewer overall x-rays can be used to produce the image.
|
|
|
What is the value of nano-? mill-? kilo-? mega-?
|
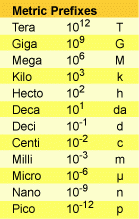
|
|
|
The positively charged portion of the x-ray tube (the target) is called what?
|
The anode.
|
|
|
What is the name of the process of "boiling off" electrons from a hot wire?
|
Thermionic emission.
|
|
|
What are the respective charges of the cathode and anode?
|
Cathode- negative to repel electrons.
Anode- positive to attract electrons. |
|
|
What percentage of the energy of the electrons that bombard the target of an x-ray tube are converted to heat?
|
99%
|
|
|
What are units of tube current and what does it measure?
|
mA. Measures the flow of electrons from cathode to anode.
|
|
|
What is the typical mA range for fluoroscopy? For CT? For angiography?
|
Fluoro- 1-50 mA
CT- 50-400 mA Angiography- 400-1000 mA |
|
|
What is the unit for TOTAL number of electrons hitting the anode during image acquisition?
|
mAs, which incorporates the amount of time the tube was on.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between the number of x-rays produced and the tube current?
|
Directly proportional (i.e. Doubling mAs doubles the number of electrons produced)
|
|
|
What is the 15% rule regarding kVp and image exposure?
|
An increase in kVp by 15% must be accompanied by a reduction in mAs by 50% in order to maintain radiographic density. Inversely, a reduction of 15% in kVp must be accompanied by an increase in mAs by a factor of 2 (Doubling).
|
|
|
What is the effect of kVp on the number of x-rays produced?
|
X-ray intensity (number of x-rays) increases as the kVp squared. So if applied voltage is doubled, the number of x-rays is quadrupled.
|
|
|
Why is the typical kVp for mammography 25-30 kVp while the typical kVp for chest radiography is 110-130 kVp?
|
Lower kVp produces more tissue contrast. This is not needed in the chest which has high inherent contrast between structures. Contrast must be "created" in the breast.
|
|
|
Effect of smaller focal spot on spatial resolution?
|
Increased
|
|
|
Why can't small focal spots always be used?
|
Denser (or fatter) body parts require a higher mAs, which necessitates a longer filament wire which won't work with a small focal spot. Also tube heating becomes an issue.
|
|
|
What is the line focus principle?
|
Taking advantage of the beveled edge of the rotating anode target to produce a smaller "effective focal spot".
|
|
|
What is the anode angle?
|
The angle between the surface of the anode target and a perpendicular line drawn from the anode to the image receptor. Most commonly 12.5 degrees.
|
|
|
For a given effective focal spot size, what is the effect on heat dissipation of a smaller anode angle?
|
Dissipates heat better.
|
|
|
For a given effective focal spot size, does a smaller anode angle have more or less heel effect?
|
More heel affect.
|
|
|
What is the heel effect?
|
A reduction in the amount of x-rays on the anode side in comparison with the cathode side. Want denser body parts (i.e. chest wall in mammongraphy) to be on the cathode side. (My Cat is Dense).
|
|
|
What causes the heel effect?
|
Greater attenuation of x-rays on the anode side as they have a longer path length through the target.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the x-ray tube focusing cup?
|
Keeps the electron beam from spreading and increasing the focal spot size.
|
|
|
Why does a high kVp produce a smaller effective focal spot size than a lower kVp?
|
Because electrons tend to spread out, but higher energy electrons go faster and have less time to spread out.
|
|
|
What is "leakage radiation"? What is the allowed limit?
|
Small amount of radiation that passes through the lead lining of the x-ray tube. Limit is less than 100 mR/hr at max kVp and max continuous mA at a distance of 1 m from the tube.
|
|
|
What is included in "secondary radiation"?
|
Scattered radiation plus the leakage radiation.
|
|
|
What is meant by "primary radiation"?
|
The main x-ray beam that has been neither attenuated nor deflected.
|
|
|
How closely aligned must the light indicator and actual x-ray beam be for a collimator?
|
Within 2% of the SID distance in each orthogonal direction.
|
|
|
What is the name of the system that automatically adjusts the x-ray field size to the detector/cassette size?
|
Positive Beam Limitation
|
|
|
The percentage of x-rays produced is generally 1% but increases with what two parameters?
|
Increasing energy of the bombarding electrons and increasing Z number of the target material.
|
|
|
What are the most commonly used target materials and their atomic numbers for general radiography (1) and mammography (2)?
|
General- Tungsten, Z = 74
Mammography- Molybdenum, Z = 42 and Rhodium, Z = 43 |
|
|
What are the two main types of xrays produced at the anode?
|
Bremsstrahlung (85-100%) and Characteristic (0-15%)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism for production of Bremsstrahlung x-rays?
|
"Braking radiation". X-rays released as the approaching electrons electrostatically interact with the postively charged nuclei of the target, slowing down as they do.
|
|
|
What determines the highest energy x-ray produced at the target anode?
|
It is limited by the energy (keV) of the bombarding electron.
|
|
|
What happens to the lowest energy Bremmsstrahlung x-rays that are produced?
|
They are absorbed by the glass envelope of the x-ray tube and the filtration in the collimator assembly.
|
|
|
How are characteristic x-rays produced?
|
A bombarding electron collides with the orbital electrons rotating around the nucleus of the target atoms. If the bombarding electron has enough energy to overcome the binding energy of the orbital electron, it is displaced. Outer shell electrons then fall to fill the void, releasing a specific quanta of x-ray energy.
|
|
|
What is binding energy proportional to?
|
[Z/n]^2. So higher for higher atomic number and higher for inner shells (highest for K shell).
|
|
|
What are the K-shell binding energies for Tungsten, Molybdenum, and Rhodium?
|
Tungsten- 69.5 keV
Molybdenum- 20 keV Rhodium- 23 keV |
|
|
What is the average energy of an x-ray spectrum?
|
1/3 to 1/2 of the maximum kVp in keV.
|
|
|
What is the effect on characteristic x-rays as kVp increases (assuming already above the K binding energy)?
|
More characteristic x-rays... but the energies stay the same.
|
|
|
What is the effect of filtration on average energy? Maximum energy?
|
More filtration = higher average but does not affect the max.
|
|
|
How is x-ray beam quantity (exposure) measured?
|
In roentgens (R) which is equal to 2.08 x 10^9 ion pairs produced per cubic centimeter of air at standard temp and pressure. In SI units, exposure is measured in coulombs/kg of air.
Quantity is simply the number of x-rays produced. |
|
|
What is the quality of the x-ray beam? How is it measured? What material is used to calculate HVL in diagnostic radiology?
|
Quality is the penetration of the x-ray beam through matter. Measured in units of half-value layer (HVL). In diagnostic radiology HVL is measured in mm of aluminum.
|
|
|
What two things increase the quality of an x-ray beam?
|
Higher kVp and increased filtration (which increases the average energy of the beam).
|
|
|
What is the relationship between quality of the x-ray beam and patient dose?
|
Higher quality means more penetration and that fewer x-rays can be used, decreasing patient dose.
|
|
|
What is the effect of increasing Z of the target material on the quantity of the x-ray beam?
|
Quantity increases linearly with increasing Z.
|
|
|
What is the effect of higher kVp (or increased filtration) on image contrast and the relative amount of scattered radiation?
|
Image contrast is degraded. Relative amount of scattered radiation is increased.
|
|
|
What four metrics should be monitored during fluoroscopy procedures?
|
1. Fluoroscopy time
2. Peak skin dose 3. Reference dose 4. Kerma-area product |
|
|
What three parameters determine the percentage of x-rays transmitted through matter?
|
The mass attenuation coefficient, the density, and the thickness of the material.
|
|
|
What is the equation for transmitted x-rays through matter?
|
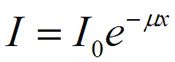
The nuclear decay constant is very similar.
|
|
|
What is the name given to the product of the mass attenuation coefficient and the density?
|
Linear attenuation coefficient, u.
|
|
|
What equation relates linear attenuation coefficient to half-value layer?
|
HVL= 0.693/u
|
|
|
What three types of x-ray interactions in matter predominate in the diagnostic energy range?
|
Coherent scatter, Photoelectric effect, and Compton scatter.
|
|
|
What is coherent scatter (Rayleigh scatter)? What percentage of interactions does this contribute in the diagnostic range?
|
Incoming x-ray excites an outer shell electron, which remains excited for a short time before releasing a photon of the same initial energy in a random direction. 2-12% of all interactions.
|
|
|
What type of x-ray interaction produces the best tissue contrast?
|
Photoelectric effect
|
|
|
What is the photoelectric effect?
|
Incoming x-ray displaces an inner shell electron within the body, which is ejected as a photoelectron. Outer shells rearrange with the subsequent ejection of either a characteristic x-ray or Auger electron.
|
|
|
What determines whether the photoelectric effect will have a substantial contribution to the percentage of x-ray interactions? (2)
|
Both the Z of the matter and the keV of the incoming electrons. At low Z (tissue, bone...) photoelectric effect only matters for low energy x-rays. At high Z (iodine, barium), photoelectric interactions dominate at all diagnostic ranges.
|
|
|
What two things cause a decrease in the ratio of photoelectric interactions?
|
Decreasing Z of the matter and increasing keV.
|
|
|
Does the photoelectric effect contribute significantly to patient dose?
|
Yes... all energy for photoelectric interactions is deposited locally.
|
|
|
What is Compton scatter?
|
Billiard ball effect of the incoming x-ray on an outer shell electron. The electron is displaced and the original x-ray continues on with lower energy.
|
|
|
What is "Crossover energy"?
|
The energy of x-ray at which the probability of photoelectric interactions and Compton scatter are the same. Below the crossover energy, Photoelectric interactions dominate. Above the crossover energy, Compton scatter dominates.
|
|
|
The energy of a scattered photon in a Compton scatter interaction depends on what two parameters?
|
The initial energy and the scatter angle. More energy lost at 180 degree scatter, nearly all energy retained for a 0 degree scatter.
|
|
|
What is pair production? Is it important in the diagnostic energy range?
|
Transformation of a high energy x-ray to a positron and electron as it approaches the nucleus. Each requires 511 keV to be produced. Not important in the diagnostic range.
|
|
|
What is photonuclear disintegration? Is it important in the diagnostic energy range?
|
High energy photo penetrates the nucleus and deposits energy, resulting in particle ejection from the nucleus (usually a neutron). Not important in the diagnostic range.
|
|
|
What are some examples of inherent filters? (3)
|
Glass wall of x-ray tube, oil inside the x-ray tube housing, mirror in the collimator.
|
|
|
What is the effect of added filtration on exposure time?
|
Increased exposure time. Filtration reduces the quantity of the x-ray beam, and more mAs may be required for the same exposure (thus longer exposure time). Keep in the mind that overall dose to the patient is still decreased in this setting.
|
|
|
What is the effect of added filtration on the subject contrast?
|
Decreased contrast because lower energy x-rays (which would have interacted via the photoelectric effect) are removed.
|
|
|
What are typical values of HVL in the diagnostic range? What is the effect of added filtration?
|
2.5 to 8.0 mm of aluminum. Added filtration increases the HVL.
|
|
|
What are the federal requirements for HVL in mammography? In other diagnostic imaging?
|
Mammo-
HVL > (kVp/100) + 0.03 in mm Al eq HVL > (kVp/100) + C in mm Al eq (C= 0.12 for Mo/Mo, 0.19 for Mo/Rh, and 0.21 for Rh/Rh) Diagnostic- HVL > 2.2 (kVp/100) + 0.56 in mm Al eq |
|
|
In compressed breast tissue at mammo energy ranges, what is the typical HVL of tissue? In the diagnostic range?
|
Mammo- HVL = 1 cm of compressed tissue.
Diagnostic- HVL = 3 to 5 cm. (So for a 24 cm thick patient, only 1 to 5% of x-rays actually pass through the patient. |
|
|
What is the overall effect of using too little filtration? Too much?
|
Too little filtration leads to increased patient dose at the lower energy x-rays can't penetrate the patient.
Too much filtration degrades image quality as the lower kVp x-rays would have produced more photoelectric interactions and thus more subject contrast. |
|
|
What are the three major functions of collimators?
|
1. Prevent irradiation of unnecessary parts of patient.
2. Decrease FOV, thus decreasing scatter radiation. 3. Improve image contrast because of less scatter. |
|
|
Where are fixed aperture collimators used?
|
Mammography and linear tomography units.
|
|
|
What type of collimator is the most commonly used?
|
Variable aperture, which have two sets of orthogonal lead blades that can be adjusted to provide variable-size rectangular FOVs.
|
|
|
What is the effect on S/P (scatter to primary) ratio for the following:
1) Increasing patient thickness 2) Increasing FOV 3) Increasing kVp 4) Increasing filtration |
1) Increase S/P ratio
2) Increase S/P ratio (leveling out around 1000 cm2) 3) Increase S/P ratio because of more Compton scattering at higher kVp 4) Increase S/P ratio (same reason as 3) |
|
|
What's good about grids? What's bad about grids?
|
Grids prevent scattered x-rays from reaching the detector/film, thus decreasing S/P ratio and improving image contrast. However, they also increase patient dose as higher exposure is needed.
|
|
|
What is the "grid ratio"?
|
The ratio of the height of the lead strips to the width between strips. Grid ratios range between 6:1 and 17:1
|
|
|
What are the four types of grids characterized by shape?
|
Focused, Parallel, Crossed, Cellular
|
|
|
What are Bucky grids? Does their use lead to increased or decreased radiation dose?
|
Moving grids. Less visibility of grid lines. However, their use does lead to increased dose and exposure times.
|
|
|
Where are stationary grids used and why?
|
Chest x-rays because short exposure times do not allow for adequate grid movement. Also used on some portable units.
|
|
|
What is the Bucky factor? As Bucky factor increases, what happens to patient dose?
|
Patient's dose with grid/Patient's dose without grid. As Bucky factor increases, patient's radiation dose increases.
|
|
|
What is grid selectivity?
|
Ratio of the primary radiation transmitted through the grid over the scattered radiation transmitted through the grid. As selectivity increases, contrast improves.
|
|
|
What is "grid cutoff" and what is the equation?
|
At a distance from the center of the grid, both primary and scatter radiation is attenuated and the image is darker.
Grid cutoff = [SID/r} where r = grid ratio |
|
|
What grid misplacement results in central darkness?
|
Grid placed upside down.
|
|
|
What grid misplacement results in density gradually decreasing on both sides of center of image?
|
"Distance decentering"- Can be seen when wrong focus grid used.
|
|
|
What is the effect of "lateral decentering" of a grid on the image?
|
Uniform decrease in density or higher radiation requirement for similar exposure.
|
|
|
What grid errors result in an image being dark on one side and light on the other?
|
Combination of distance decentering and lateral decentering.
|
|
|
How large must an air gap be to effectively reduce scatter? At what kVps are air gaps most effective?
|
Air gap must be at least equal to the patient's thickness. They are most effective at lower kVp values (thus used more in mammo)
|
|
|
What is the main function of intensifying screens?
|
Capture a large percentage of x-rays and convert them to light which is directed onto film. Results in less radiation to the patient.
|
|
|
What is the "intensification factor"?
|
Radiation required for direct film exposure/Radiation required for film-screen combination. Usually in the 40-50 range, meaning that 50 times less radiation is used.
|
|
|
What are the two big disadvantages of using intensifying screens?
|
Reduced spatial resolution as light disperses from the x-ray incidence point source. More noise as less radiation is used.
|
|
|
Compare thicker intensifying screens to thin ones.
|
Thicker screens stop more x-rays (leading to decreased dose) but degrade spatial resolution more as light diverges more in the screen.
|
|
|
What are the two types of efficiency associated with intensifying screens that produce the overall screen efficiency?
|
Absorption efficiency and Conversion efficiency.
Absorption efficiency = the fraction of x-rays interacting with the screen. Conversion efficiency = the fraction of energy deposited in the intensifying screen that is converted to light. |
|
|
As the speed of the film-screen combination increases, the patient's dose _____.
|
Decreases.
|
|
|
What are the four layers of an intensifying screen?
|
1. Base material (structural support)
2. Reflective layer (reflects light back to film) 3. Phosphor layer (converts x-rays to light) 4. Protective coating. |
|
|
What is the net effect from using the reflective layer in an intensifying screen?
|
Higher efficiency (allows greater light capture) but decreased spatial resolution as light travels longer and thus disperses more.
|
|
|
What is screen mottle secondary to?
|
Variation in the thickness and density of the screen from point to point.
|
|
|
What is film (or grain) mottle secondary to?
|
Variations in the silver grains from point to point on the film surface.
|
|
|
What is quantum mottle secondary to?
|
Statistical variations in the number of x-rays per mm2 of the image surface.
|
|
|
Which type of mottle is the most important for film-screen combinations?
|
Quantum mottle, by far.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between quantum mottle and film speed?
|
Quantum mottle is higher for faster film speed. (Analogous to higher ISO in digital photography, where more noise is seen).
|
|
|
What is the importance of maintaining good film-screen contact?
|
Important for uniformity and spatial resolution. Can be reduced by dirt or nonuniform pressure. Screens must be cleaned weekly for mammo or at least quarterly for radiography.
|
|
|
What are the four components of film?
|
1. Base material of clear plastic to support emulsion.
2. Adhesive layer to hold emulsion. 3. Emulsion- mixture of gelatin plus silver halide grains. 4. Supercoat- protects the emulsion. |
|
|
What creates the black appearance of film hanged at the viewbox?
|
Oxidized silver atoms, which gather around "sensitivity specks" creates by the interaction of light and/or x-ray photons.
|
|
|
In what setting is "latent image fading" encountered?
|
Long delay between x-ray exposure and film processing causes loss of sensitivity specks and a lighter overall image.
|
|
|
For each 50% reduction in transmitted incident light from the viewbox through the film, the optical density increases by? For each reduction by a factor of 10?
|
0.3 for each 50% reduction.
1.0 for each factor of 10 reduction. |
|
|
What is the difference between the H&D curve for film-screen vs. digital detectors?
|
Film-screen curves have a "toe" and "shoulder" region. Digital detectors have a linear curve resulting from more uniform reaction to incident x-rays.
|
|
|
Average contrast gradient values < 2.5 are seen with ____ film. Values > 3.0 are seen with ____ film.
|
< 2.5 = Latitude film
> 3.0 = Contrast film |
|
|
What is "base + fog" and what should their levels be for radiographic and mammographic film?
|
Base + fog is the density of the film in the toe region of the characteristic curve and results from the tint of the film + background exposure (not imaging x-rays).
Should be < 0.25 OD for radiographic film, < 0.20 OD for mammographic film. |
|
|
What is the trade-off for film speed?
|
Higher speed film is darkened by less radiation, so means less dose to the patient. However, higher speed film also has more quantum mottle (noise).
|
|
|
What is the limiting factor for spatial resolution in a film/screen combo? Limiting factor for overall speed?
|
Both are limited by the screen.
|
|
|
What are the four stages of film processing?
|
1. Development- softens the supercoat, wets the film, and oxidizes the silver grains that have been exposed to light or x-rays.
2. Fixation- washes off the unaltered or oxidized silver grains and stops development. 3. Washing- removes remaining chemicals. 4. Drying. |
|
|
Problems with the developing step can affect what three parameters?
|
1. Film speed.
2. Contrast gradient. 3. Base + Fog |
|
|
Problems with the fixation step can affect what?
|
Archival storage, as incomplete fixation will lead to darkening of films over time.
|
|
|
Problems with washing in film processing can cause what?
|
Spots on the film.
|
|
|
What are the plates in computed radiography made from?
|
Barium fluorohalides
|
|
|
What is the "fast direction" vs. "slow direction" for a CR reader?
|
Fast direction- laser scans the image one line at a time
Slow direction- plate physically moved on conveyor belt so that next line can be read. |
|
|
What is the process of "photostimulated phosphor emission (PSP)"?
|
Laser light adds energy to already excited electrons in a CR plate. The electrons eventually give up in the energy in the form of light (which is of a higher frequency than the laser).
|
|
|
Advantages of CR over film-screen: (6)
|
1. Larger dynamic range (12 bits vs. 8 bits)= more shades of gray.
2. Ability to record radiation levels from 0.01 to 100 mR incident on cassette. 3. Post-processing ability 4. Easier distribution of images. 5. Better storage and retrieval. 6. Better low-contrast image quality and discrimination. |
|
|
Disadvantages of CR relative to film-screen: (6)
|
1. More radiation.
2. Lower spatial resolution (CR limit of 3.0 to 3.5 LP/mm, film-screen limit of 6.0 to 10.0 LP/mm) 3. Expensive components which require frequent upgrades. 4. Necessitates highly skilled support staff. 5. Additional network costs. 6. Latent image fades during the first 10 to 20 minutes. |
|
|
What is the spatial resolution limit for CR systems?
|
# of pixels in image/[2 x FoV]
|
|
|
How to calculate data size of digital images?
|
matrix width x matrix length x depth in bytes
|
|
|
How many bits in a byte?
|
8
|
|
|
Of all the digital modalities, which single digital image has the largest file size?
|
Mammography (~21.8 Mb)
|
|
|
Direct DR vs. Indirect DR?
|
Direct is composed of an array of amorphous selenium detectors that capture the ionizations created in the detectors and measure the deposited charge directly.
Indirect has a scintillator (such as CsI) coated over an array of light-sensing solid-state devices (such as CCD or TTL chips). |
|
|
What term describes the length of a side of a DR array? What is the "area of a detector"?
|
Pitch
Pitch x Pitch |
|
|
What is "fill factor" in DR imaging?
|
The usable surface of each detector (excluding PC connections and switches). The higher the fill factor percentage, the lower the patient dose.
|
|
|
What is the term given to the overall efficiency of a DR system to use the incident x-ray energy?
|
DQE- detected quantum efficiency
|
|
|
Are mammography DR detectors (pixels) smaller or larger than radiography?
|
Smaller... this allows for greater spatial resolution
|
|
|
Main advantage of DR over CR? Main disadvantage?
|
Advantage- Much faster image processing, increasing patient throughput.
Disadvantage- High cost. |
|
|
What does DICOM stand for?
|
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine.
|
|
|
What is the SMPTE?
|
Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. Pattern used to check imaging monitors for consistent gray scale, low-contrast visibility, high-contrast resolution, and distortion.
|
|
|
How much light intensity is generally required for imaging?
|
200 to 400 Cd/m2
|
|
|
What are the six basic descriptors of image quality?
|
Density, Spatial resolution, Contrast, Latitude, Unsharpness, Noise.
|
|
|
What is meant by image "latitude"?
|
The ability to display many different gray scales in density for the various portions of the imaged anatomy.
|
|
|
If contrast increases, latitude must _____.
|
Decrease. Contrast and latitude are opposites.
|
|
|
What makes up the image contrast?
|
Both the subject contrast and image receptor contrast.
|
|
|
How does the intensifying screen affect contrast?
|
It doesn't. Image receptor contrast is solely determined by the film. Screen does affect spatial resolution.
|
|
|
What three things determine image receptor contrast in a DR/CR system?
|
1. Window and level settings for the display.
2. Software processing of the data, such as smoothing and edge enhancement. 3. Display monitor contrast gradient. |
|
|
How is geometric magnification calculated?
|
SID/SOD
SID- source to image receptor distance SOD- source to anatomy distance |
|
|
How is the penumbra of an image caculated?
|
(M-1) x F
M= magnification F= focal spot diameter |
|
|
What is the relationship between spatial resolution and unsharpness?
|
Inversely proportional. As unsharpness increases, spatial resolution decreases.
|
|
|
How is spatial resolution measured?
|
LP/mm or MTF (modulation transfer function)
|
|
|
What does an MTF value of 1 imply?
|
No loss of contrast for that particular spatial frequency (on x axis)
|
|
|
How to identify the "best" imaging system on an MTF curve?
|
The highest line is the best.
|
|
|
To reduce quantum mottle by half, the amount of radiation used to form the image must be ____ times greater.
|
Four.
|
|
|
Discuss different mechanisms of dose measurement.
|

|
|
|
What are the quality factors for the following:
1. X-rays 2. Gamma rays 3. Slow neutrons 4. Fast neutrons 5. Alpha particles |
1. 1.0
2. 0.9 3. 10 4. 20 5. 20 |
|
|
What is air kerma?
|
The amount of energy released into a material by the radiation beam. Measurement similar to absorbed dose.
|
|
|
What is surface integral area dose?
|
Attempts to relate the radiation dose to its potential biologic impact more accurately by incorporating the amount of tissue that was irradiated. Is the DAP (Dose Area Product) on newer fluoroscopy machines.
|
|
|
Triple 100 dose estimation:
For 100 kVp and 100 mAs at 100 cm from the focal spot, the entrance skin exposure (ESE) is ____ mR |
1000
|
|
|
What is the approximate entrance skin dose of a PA chest x-ray? An extremity x-ray? 1 minute of GI fluoro? Head CT? Body CT?
|
Chest x-ray- 0.40 mSV
Extremity x-ray- 1-2 mSv 1 min GI fluoro- 20-40 mSv Head CT- 40-60 mSv Body CT- 20-40 mSv |
|
|
What is the largest source of natural background radiation?
|
Radon
|
|
|
Standard lead aprons with 0.50 lead equivalent thickness attenuate what percentage of scattered x-rays for kVp less than 100?
|
94-96%
|
|
|
How much scattered radiation is present 1 meter from the patient?
|
0.1% of the entrance exposure
|
|
|
What is Dq for an LET curve?
|
The radiation dose necessary to go from zero radiation to the extrapolated straight line curve (across the shoulder). A large Dq represents an extended period over which some repairs can occur.
|
|
|
What is the LET?
|
Linear energy transfer- a measure of the rate at which ionizing radiation transfers energy to soft tissues.
|
|
|
Which type of radiation has the highest LET?
|
Alpha particles. They are highly damaging but travel a short distance.
|
|
|
Describe a stochastic effect.
|
Increased radiation increases the chances that the effect will occur, but there is not threshold above which it WILL occur. The chances of developing the effect increase with higher dose, but the severity of the effect itself does not change. Ex- cancer.
|
|
|
Describe a deterministic effect.
|
Higher radiation increases the severity of the effect. There is a threshold above which the effect will occur.
|
|
|
Why is the "linear no-threshold hypothesis" regarding radiation effects used at low dose levels?
|
Because it is the most conservative estimate.
|
|
|
What is the "genetic doubling dose"?
|
The amount of radiation that would have to be delivered to the gonads of everyone of childbearing age in the US in order to double the number of birth defects. Estimated to be 0.5 to 1.0 Sv delivered to the gonads.
|
|
|
At what radiation levels does epilation (loss of hair) occur?
|
5 to 6 Sv
|
|
|
What is LD 50/30 and what is the LD 50/30 for humans?
|
LD 50/30 is the radiation dose that will kill 50% of the population within 30 days of receiving acute, whole body radiation. It is 4.0 to 4.5 Sv in humans.
|
|
|
Compare fluoroscopic flat panel displays to older image intensifiers.
|
Flat panel displays have lower spatial resolution but have a greater dynamic range.
|
|
|
What is the function of the aperture in fluoroscopic systems?
|
Restricts light to increase radiation dose so that quantum mottle is at acceptable level and distortion at the edge of the lens is limited.
|
|
|
Describe the components and function of the image intensifier.
|
-X-rays enter through the window of the image intensifier
-X-rays are converted to light at the input phosphor. -Light is captured in the photocathode and converted to electrons. -High voltage accelerates the electrons across the vacuum, giving them energy (flux gain) -Focusing electrodes in the gap focus and invert the image onto the output phosphor -Output phosphor converts a portion of the electrons to light, which then goes to the tv. |
|
|
What is minification gain? How is it calcuated?
|
Increase in light from the output phosphor because of the area decrease from the large photocathode. It is the Input FOV/Area of the output phosphor.
|
|
|
Why does magnification on traditional Image Intensifiers lead to increased dose?
|
Because of a loss of minification gain (smaller FOV/area of the output phosphor).
|
|
|
What is brightness gain of an II?
|
Brightness gain = Flux gain x minification gain.
|
|
|
What is the maximum entrance skin exposure rate (ESER) of the following fluoroscopy systems:
1) Manually controlled system 2) ABC systems with one operational level 3) ABC systems with two operational levels. |
1) 5.0 R
2) 10.0 R 3) 10. R for first level, 20.0 R for second level |
|
|
What is the F# of a lens? Describe light gathering capabilities at different F#.
|
The ratio of the focal length of the lens divided by the lens diameter.
Higher F#s gather less light than small F#s. |
|
|
What is pincushion distortion in fluoroscopy?
|
Straight lines curved in large FOV.
|
|
|
What is vignetting in fluoroscopy?
|
Image brighter in center than at edge
|
|
|
What is retrograde light flow in fluoroscopy?
|
Light from the output phosphor illuminates the photocathode.
|
|
|
What are burn spots in fluoroscopy?
|
Excessive radiation continually at one spot destroys phosphor.
|
|
|
What is lag in fluorscopy?
|
Persistence of fluoroscopic image because of slow phosphorescent decay.
|
|
|
What is unsharpness in flouroscopy?
|
Focal spot blur and lens/electrodes not focused
|
|
|
What is flare (glare) in fluoroscopy?
|
High brightness at edge of anatomy or in lung field.
|
|
|
What component limits the spatial resolution in a traditional fluoroscopy system?
|
The television.
|
|
|
Does the FOV affect overall spatial resolution in a flat panel fluoroscopy system?
|
No, because the size of the detector is fixed. In a traditional system, smaller FOV would yield higher spatial resolution.
|
|
|
Keeping the image intensifier close to the patient does what to dose?
|
Keeps it low.
|
|
|
In fluoroscopy, is the scattered radiation to personnel higher on the x-ray tube side or image intensifier side?
|
X-ray tube side.
|
|
|
Mammographic film-screen systems have how many screens? How many emulsions?
|
One of each. High resultant spatial resolution.
|
|
|
What is the spatial resolution of mammogaphic film-screen systems? Mammographic DR systems?
|
15-20 LP/mm for film
5-10 LP/mm for DR |
|
|
Compare focal spot size in mammography vs. radiography.
|
Smaller focal spot for mammo (everything for higher resolution)
|
|
|
Why do the lower keV x-rays used in mammography better accentuate calcium and tissue contrast?
|
Because they emphasize the photoelectric effect.
|
|
|
What is the "baseline" target for mammo? With what filters can it be used?
|
Molybdenum. Can be used with both Moly and Rhodium filters.
|
|
|
Why use Rhodium target or filter? Can a molybdenum filter be used with a rhodium target?
|
Use a rhodium target or filter when higher kVp is needed (i.e. dense or thicker breasts).
No, a molybdenum filter may not be used with a rhodium target (that would filter higher kVp x-rays, which defeats the purpose of using rhodium in the first place). |
|
|
What is the K-edge for Mo? For Rh?
|
Mo- 20 keV
Rh- 23 keV |
|
|
What is the theory behind using Moly or Rh filters in mammo?
|
They attenuate low energy Bremsstrahlung x-rays which contribute to patient dose and also high energy Bremsstrahlung x-rays above the K-edge which degrade contrast.
|
|
|
What four parameters might newer AEC mammo units control automatically?
|
Target, filter, kVp, mAs
|
|
|
What is average glandular dose (Dg) in mammo? How much is allowed for a 4.2 cm compressed breast?
|
Dg is an average of the radiation dose throughout most of the breast tissue, excluding the 3 to 5 mm at the skin surface. 3.0 mGy allowed for MQSA.
|
|
|
What three mammo QC issues must be addressed daily?
|
Sensitometry, viewing conditions, darkroom cleanliness.
|
|
|
What mammo QC issue must be addressed weekly?
|
Phantom evaluation.
|
|
|
What mammo QC issues must be addressed quarterly? (2)
|
Fixer retention and repeat rate.
|
|
|
What three mammo QC issues must be addressed semi-annually?
|
Darkroom light leakage, film-screen contact, compression.
|
|
|
How often must physics QC (HVL, kV, collimation, AEC evaluation, focal spot size, and dose) be performed in mammo?
|
Yearly.
|
|
|
What is considered a passing score on the ACR mammo phantom?
|
Visibility of 4 fibrils, 3 calcium speck groups, and 3 masses.
|
|
|
What is the risk of cancer from mammography?
|
30 cases per million persons examined.
(7.5 cases/mGy) per 1 million women. |
|
|
For what thresholds does the Society of Interventional Radiology recommend followup of the following:
1) Minutes of total fluorscopy time 2) kerma-area product 3) reference point air kerma 4) peak skin dose |
1) 60 minutes
2) 500 cGy m^2 kerma-area product 3) 5000 mGy^3 reference point air kerma 4) 3000 mGy peak skin dose |
|
|
Most CT scanners today are of what generation?
|
3rd generation. The tube and detectors rotate together.
|
|
|
What determines the maximum number of slices that can be simultaneously acquired by a CT scanner?
|
The number of detectors along the z axis (i.e. the number of detector rows). Keep in mind that detectors can be "grouped" to create fewer, and thicker, slices.
|
|
|
What are the two biggest advantages of using dual energy CT?
|
Shorter scan times.
Simultaneous dual energy scanning allows for "recombinant" images that select (selectively drop) a given tissue according to its linear attenuation coefficient values. |
|
|
What best describes modern CT scanner x-ray beams, fan-shaped or cone-shaped?
|
Cone shaped.
|
|
|
What is effective mAs in CT scanning?
|
The tube current (mA) multiplied by the time that a given point within the patient experiences the x-ray beam.
|
|
|
How is "pitch" defined?
|
Pitch = Table movement per tube revolution/Beam width
|
|
|
A pitch of less than 1 implies what? A pitch of greater than 1?
|
Less than 1 = Overlap in slices
Greater than 1 = Gaps in slices |
|
|
Hounsfield units represent the linear attenuation coefficients of various tissues normalized to ____.
|
Water and Air
|
|
|
Filtered backprojection is an example of an _____ reconstruction method.
|
Analytical
|
|
|
What is first generation CT?
|
Translate/Rotate mechanism using a pencil beam and only two detectors.
|
|
|
What is second generation CT?
|
Translate/Rotate mechanism using a fan beam and many detectors. Larger matrix (up to 512 x 512) than first generation CT.
|
|
|
What is third generation CT?
|
Rotate/rotate mechanism (i.e. the tube and detectors rotate simultaneously). Can obtain multiple slices per image with a cone beam.
|
|
|
What is fourth generation CT?
|
X-ray tubes rotate, detectors are stationary.
|
|
|
What is fifth generation CT?
|
Also called electron beam computer tomography. No motion, electron beam is scanned across numerous stationary x-ray targets. Very fast.
|
|
|
What is the effect on radiation dose and image noise of using a flat filter in CT?
|
More radiation and less noise at the periphery.
Less radiation and more noise at the center. |
|
|
What is the effect of using a bowtie filter in CT?
|
Produces a relatively uniform radiation dose and CT noise. It attenuates peripheral beams more to match the thinner peripheral anatomy.
|
|
|
How to determine the width and thickness of a CT voxel?
|
Thickness of the voxel matches the slice thickness.
Width = Diameter of the field of view/Matrix size |
|
|
Upon what four factors are effective linear attenuation coefficients dependent?
|
1. Density of the material within a voxel.
2. Atomic number of the material within a voxel. 3. Electron density of material within a voxel. 4. Effective energy of the x-ray beam (kVp, filtration, patient attenuation) |
|
|
What is the effect of voxel size (both thickness and width) on CT noise?
|
Smaller voxel size (either decreased thickness, width, or both) means more noise.
If the scanned slice thickness were reduced from 10 to 1 mm, the radiation would require an increase of 10 times to produce the same CT noise. A decrease in voxel width from 1.0 to 0.5 mm would require an increase in radiation dose by a factor of 8 to maintain same CT noise (Width is cubed in the CT noise equation). |
|
|
If the radiation dose to the patient is increased by four, the CT noise decreases by?
|
One divided by the square root of four.
Remember that the relationship between dose and noise is not linear in CT. |
|
|
What is window level and width on CT?
|
Affects what gray-scale values are assigned to a given HU. Level is the center CT#. Window is the range above and below this central value. Small window=higher contrast.
|
|
|
How does spatial resolution of CT scanners compare to film-screen or DR/CR systems?
|
Much worse. But CT wins for having significantly better low contrast performance (think KUB vs. Abdominal CT).
|
|
|
For large FOV CT scans (i.e. abdominal), what limits the spatial resolution?
|
Only the pixel size.
|
|
|
What is CTDI?
|
Computed tomography dose index. The radiation dose to the center slice of 15 adjacent, sequential slices without overlap.
|
|
|
Can CTDI be used for overlapping slices? What can?
|
No it cannot. For this, use CTDI(volume).
|
|
|
What is CTDI(w)?
|
Averages the radiation dose with depth. Assigns 1/3 value to center measurements and 2/3 value to surface measurements.
|
|
|
How is CTDI(volume) calculated?
|
CTDI(w)/Pitch
|
|
|
What is dose-length produce (DLP)?
|
CTDI(w) x physical length of the scan in cm.
|
|
|
How does the ACR accreditation program estimate effective dose for head scans and body scans?
|
0.0023 x DLP for head scans
0.015 x DLP for body scans |
|
|
How does CT radiation dose vary with mAs?
|
Directly (i.e. double mAs = double radiation dose)
|
|
|
How does CT radiation dose vary with kVp?
|
Varies with the kVp squared (i.e. increase kVp by 20, get 40% to 70% increase in dose)
|
|
|
What two factors affect the speed of sound in a given material? How are the factors related to speed?
|
Compressibility and Density
More compressibility- slower sound More density- slower sound |
|
|
What is the average speed of sound in body tissues?
|
1540 m/sec
|
|
|
What is the purpose of transducer backing material?
|
To stop vibrations as quickly as possible.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between the thickness of the piezoelectric crystal and the wavelength of the sound wave?
|
Wavelength = 2 x thickness of the crystal
|
|
|
What is meant by "high Q"?
|
High Q transducers have a narrow range of frequencies and take a long time to ring down. Used in continuous doppler.
|
|
|
Which has better axial resolution, high Q or low Q transducers?
|
Low Q, because they ring down faster, allowing higher pulse repetition frequencies.
|
|
|
What percentage of time is an ultrasound transducer listening for return echoes?
|
99%
|
|
|
What is acoustic impendance?
|
Characteristic of each tissue. Represents the speed of sound in that tissue x density.
|
|
|
What determines the % reflection at a tissue interface?
|
the difference in acoustic impendance between the adjacent tissues. %reflected=100%(Z1-Z2)^2/(Z1+Z2)^2.
|
|
|
Regarding decibels, for each factor of 2 reduction in the echo, add _____ dB. For each factor 10 reduction, add _____dB.
|
Factor of 2 (i.e. 100%->50%)- -3dB
Factor of 10 (i.e. 100%->10%)- -10dB |
|
|
To what is ultrasound attenuation related? (3)
|
Attenuation coefficient, frequency of the transducer, and total distance traveled.
|
|
|
What is the assumed attenuation coefficient for most tissues?
|
1.0(dB/Mhz-cm)
|
|
|
Why are high frequency transducers less penetrating?
|
Because higher frequencies are attenuated more rapidly.
|
|
|
What is specular reflection?
|
Bouncing ultrasound signal from a smooth surface.
|
|
|
What is diffuse (non-specular reflection)?
|
Bouncing of the ultrasound wave from a rough surface in many different directions.
|
|
|
When does Rayleigh scatter (US) occur?
|
When the scattering objects are much smaller than the ultrasound wavelength.
|
|
|
What determines the angle of refraction at an interface?
|
Snell's law
Sin(angle of incidence) Speed incidence media __________________________ X ___________________________ Sin(angle of refraction) Speed refraction media |
|
|
What is Fresnel zone of an ultrasound transducer?
|
The depth in which the lateral width of the sound wave does not expand. Also the depth over which the sound wave can provide useful images without loss of lateral resolution.
Most modern transducers have focusing elements to provide maximum lateral resolution at a given depth. |
|
|
What is the Fraunhofer zone of an ultrasound transducer?
|
The region in which the ultrasound beam continues to expand in width, degrading lateral resolution.
|
|
|
What is ultrasound frame rate? How does it relate to temporal resolution?
|
Frame rate is the number of images than can be shown per second. It directly determines temporal resolution.
|
|
|
What is axial spatial resolution in ultrasound?
|
The ability to see small objects in the direction of the ultrasound beam.
|
|
|
What two parameters affect axial resolution?
|
The frequency of the transducer (higher frequency = better axial resolution.
The number of cycles in a pulse (fewer pulses = better axial resolution) |
|
|
What is lateral spatial resolution in ultrasound?
|
The ability to see small objects perpendicular to the direction of travel of the ultrasound beam.
|
|
|
What determines the lateral resolution in ultrasound?
|
The width of the ultrasound beam and width of the transducer. Is enhanced by focusing elements to narrow the beam.
|
|
|
What is ultrasound thermal index?
|
The ratio of the actual transmit power over the power required to cause tissue heating to a temperature increase of 1 degree C.
|
|
|
What thermal index is considered safe?
|
1.0 to 2.0
|
|
|
What is the mechanical index of ultrasound? What level is considered safe?
|
Compares the pressure in the ultrasound wave with pressure that could cause mechanical damage. Pressure less than 0.3 MPa is considered safe.
|
|
|
Why is Doppler imaging not considered safe in pregnancy?
|
Because it exceeds the maximum allowable Spatial Peak Temporal Average (SPTA), which is <100 mwatts/cm^2 for Ob/Gyn.
|
|
|
Which nuclei have the largest magnetic moment?
|
Those with odd numbers of protons.
|
|
|
What is the term applied to the rate of precession of proton about the external magnetic field?
|
Larmor frequency
|
|
|
What is Larmor's equation?
|
Precessional frequency = gyromagnetic ratio x applied external magnetic field strength.
|
|
|
To provide energy to change the configuration of a processing nucleus, how must the RF pulse relate to the processional frequency?
|
It must be identical
|
|
|
What is T1?
|
The longitudinal relaxation time. The time required after a 90 degree tip for 63% of the magnetic moments to realign with the applied magnetic field.
|
|
|
What is T2?
|
The time for the amplitude of the echo to decay to 37% of the initial free induction decay amplitude.
|
|
|
What two processes are responsible for the T2* decay rate?
|
1) Nonrecoverable dephasing caused by random spin-spin exchanges with adjacent atoms and molecules.
2) Recoverable dephasing caused by local nonuniformities in the main magnetic field. |
|
|
T1 increases with applied external magnetic field strength. What is the effect of higher applied magnetic field to T2?
|
No significant change. T2 is affect mainly by the local environment of the proton (i.e. what the proton is bound to and how it interacts with other molecules in the neighborhood)
|
|
|
Signal can only be detected in the _____ plane on MRI and then only if the magnetic moments are _____.
|
Tranverse plane.
In phase. |
|
|
What is "quenching" of a superconducting magnet?
|
Heating of the liquid helium, causing a rapid "boiling off". A large pipe is require to vent the gas to the outside.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of shim coils?
|
To correct for minor nonuniformities in the main magnetic field.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the gradient coils? What are the main three?
|
Gradient coils are used for localization. Slice select, frequency, phase encoding.
|
|
|
Higher gradient strengths produce _____ slices.
|
Thinner.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of RF quadrature coils?
|
They are used to send the Larmor excitation pulse and to receive the signal from the tipped hydrogen nuclei.
|
|
|
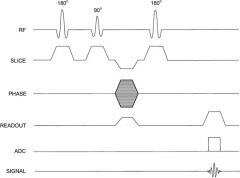
What occurs in a spin echo sequence?
|
A 90 degree RF pulse is followed by a 180 degree RF pulse followed by readout.
|
|
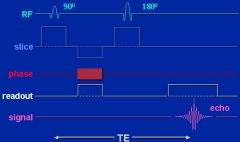
|
Spin echo
|
|
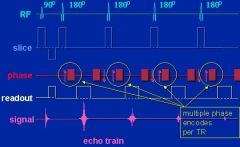
|
Fast spin echo
|
|
|
Inversion recovery
|
|
|
What is echo time (TE)?
|
Double the time between 90 and 180 excitation pulses. It is the time that the echo shows up after the 180 degree pulse.
|
|
|
What is repetition time (TR)?
|
The delay before the 90- and 180- degree RF pulses are repeated.
|
|
|
TE and TR for T1 weighting?
|
TE- short
TR- short |
|
|
TE and TR for T2 weighting?
|
TE- long
TR- long |
|
|
TE and TR for proton density weighting?
|
TE- short
TR- long |
|
|
What is gradient echo?
|
Uses an initial RF pulse less than 90 degrees. Gradient fields are used to dephase net magnetization and then are reversed to produce an echo. No 180 degree pulse is used.
|
|
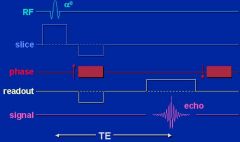
|
Gradient echo
|
|
|
What are the benefits of gradient echo sequences?
|
Fast imaging, deposits less energy, allows 3D imaging, sensitive for flow
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the spoiler pulse/gradient in spoiled gradient echo imaging?
|
To wipe out the transverse magnetization component, allowing for more t1 weighting (example: the 3D SPGR neuro images from the VA)
|
|
|
What sequence uses an initial 180 degree pulse and variable time to initiate spin echo sequence to suppress specific tissues?
|
Inversion Recovery (including FLAIR, STIR)
|
|
|
What is inversion time (TI)?
|
The time between the first 180-degree RF pulse and the following 90-degree RF pulse.
|
|
|
What sequence utilizes a 90 degree pulse followed by a series of 180-degree pulses?
|
Fast spin echo
|
|
|
The image acquisition time in FSE is shortened by a factor equal to what?
|
The number of echoes formed per TR. This is called the echo train length.
|
|
|
This sequence employs a continuously oscillating gradient field to gather a significant amount of the total image in a very short period of time.
|
Echo planar imaging (EPI)
|
|
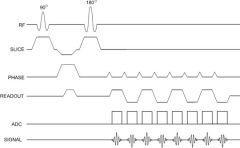
|
Echo planar imaging
|
|
|
Upon what does spatial resolution in MRI depend? How is it calculated?
|
Voxel size.
Voxel size = FoV/matrix size. Larger matrix- better spatial resolution. |
|
|
Large voxels (larger FoV) do what to MRI SNR?
|
Large voxels- more protons- more signal- better SNR
|
|
|
Thicker MRI slice does what to SNR?
|
Increases
|
|
|
Smaller matrix does what to MRI SNR?
|
Increases
|
|
|
Summation of multiple images, for a larger number of excitations (NEX), does what to MRI SNR?
|
Increases
|
|
|
Narrow bandwith _____ SNR but at the expense of _____.
|
Improves.
Greater chemical shift artifact. |
|
|
What is the equation for scan time in a spin echo sequence?
|
Scan time = NEX x (# of phase encodes) x TR
|
|
|
The FDA specifies that acoustic levels must be below what number in mri?
|
140 dB
|
|
|
What is the appropriate step in management of a patient suffering an emergency in the MR scan room?
|
Remove them from the room
|
|
|
What is proton density?
|
The number of MOBILE protons that can contribute to signal
|
|
|
Long TE enhances _____.
Short TR enhances _____. |
Long TE enhances T2
Short TR enhances T1 |
|
|
The center of K space represents ______.
The periphery of K space represents ______. |
Center- Contrast information
Peripheral- Fine detail |
|
|
Two mechanisms to make selected MR slices narrower?
|
Stronger (steeper) slice select gradient and narrow bandwidth.
|
|
|
To reformat 3D MRI acquisitions into additional planes, the obtained voxels must be _____.
|
Isotropic.
|
|
|
Broad readout bandwidth in MRI leads to shorter scan times but at the expensive of decreased ____?
|
Signal to noise ratio
|
|
|
What is the relationship between matrix size and acquisition time?
|
Largest matrix, longer acquisition time. Takes longer to collect more data points for the larger matrix.
|
|
|
What determines the plane of MRI acquisition?
|
The direction of the slice select gradient (Z- axial, Y-coronal, X- sagittal. )
|
|
|
General statements about 3D MRI vs. 2D MRI
|
3D allows thinner slices and has better SNR. However, 3D imaging is built on a gradient echo framework and is thus prone to artifact.
|
|
|
The "line of stabily" is located where there are equal numbers of protons and neutrons at low Z numbers. Where is it located at higher Z numbers?
|
Where there are more neutrons than protons.
|
|
|
Where are atoms with excess neutrons created?
|
In a nuclear reactor
|
|
|
Where are atoms with excess protons created?
|
Particle accelerators (including linear accelerators and cyclotrons)
|
|
|
What is the radioactive decay equation? What is it similar to?
|

Similar to the equation related how many photons pass through a given mass, except "time" is replaced with "thickness"
|
|
|
What is the decay constant equal to?
|
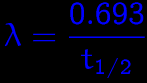
|
|
|
What is the SI unit of radioactivity? What is the old unit? How are they converted?
|
SI- Becquerel = 1 dps
Old- Curie 1.0 Curie- 3.7 x 10^10 dps |
|
|
For which atoms does Beta minus decay occur? To what do these excess nucleons decay?
|
Atoms with excess neutrons.
Neutron -> Proton + electron (beta) + antineutrino |
|
|
For which atoms does electron capture (K capture) occur? What is the basic process? What is emitted after?
|
Those with excess protons. The proton grabs a K shell electron and they combine to form a neutron. The empty K shell is filled, releasing a characteristic x-ray.
|
|
|
For which atoms does positron decay occur? What are the output products?
|
Atoms with excess protons. 1.02 MeV of energy is used to create an electron and positron, which combine with a proton in the nucleus. Final output is a neutron, positron, and neutrino.
|
|
|
What is a gamma ray?
|
A photon that originates in the nucleus. The same as an x-ray, but from a different location.
|
|
|
What is internal conversion?
|
Process in which the exiting gamma ray interacts with and ejects an inner shell orbital electron (called an internal conversion electron). Electrons then fall, emitting a characteristic x-ray. The characteristic x-ray can then be ejected, or interact with an outer shell electron, emitting an Auger electron.
|
|
|
What are the three possible outcomes for internal conversion?
|
1) gamma ray
2) internal conversion electron + characteristic x-ray 3) internal conversion electron + Auger electron |
|
|
In regards to Radionuclide generators, what is breakthrough?
|
Contamination of the eluant by parent nuclide (i.e. Molybdenum showing up in a Technecium eluant)
|
|
|
What is the "generator" principle?
|
At equilibrium, the activities of the parent and daughter are almost the same.
|
|
|
For charged particles and nonpenetrating photons (i.e. E<30 keV), what is the effect of increasing each of the following on organ dose:
1) Concentration 2) Activity 3) Effective half-life 4) Energy 5) Organ mass |
All except organ mass increase dose.
Organ mass is inversely proportional to dose (little baby organs get more dose for the same injected radioactivity) |
|
|
What is the effective half life equation?
|
1 1 1
--- = ---- + ----- eff phys bio |
|
|
How is gamma ray radiation calculated?
|
Very complex... most estimations based on Monte Carlo calculations in a simulated human.
|
|
|
What is geometric efficiency of nuc med detectors?
|
The fraction of all emitted radiation that hits the detector.
|
|
|
What is intrinsic efficiency of nuc med detectors?
|
The fraction of incident radiation that is actually measured by the detector.
|
|
|
What is the equation for overall efficiency in a nuc med detector?
|
Overall efficiency = Geometric efficiency x intrinsic efficiency.
|
|
|
What is detector "dead time"?
|
The time after a detected event in which the detector cannot register another interaction.
|
|
|
With _____ detectors, additional events occurring during dead time extend the duration of dead time.
|
Paralyzable
|
|
|
With _____ detectors, additional events occurring during dead time do not extend the dead time (although they are still not measured).
|
Nonparalyzable
|
|
|
In which gas detector voltage region can damage occur because of ongoing spontaneous discharges without radioactivity?
|
Avalanche, region 5.
|
|
|
In which gas detector voltage region can exposure (in mR or R) actually be measured?
|
Ionization region, region 2.
|
|
|
What is FWHM of a gamma detector?
|
Full width half maximum. Width in energy of the photopeak at half its maximum counts. Is a measure of the energy resolution of a detector.
|
|
|
What is the function of the NaI crystal in a gamma camera?
|
Scintillation material, converts gamma rays into light which is directed toward the photomultiplier tube through light pipes.
|
|
|
What occurs in photomultiplier tubes?
|
Light from scintillation crystal is converted to electrons by a photocathode. Electrons then "cascade" across high voltage between Dynodes. Each interaction with a dynode multiplies the number of electrons. The resulting electrons are much greater in signal but proportional to the initial gamma rays. Signal is then detected by pulse height analyzer/multichannel analyzer.
|
|
|
How does the thickness of NaI crystal in gamma camera relate to screens in film-screen radiography?
|
The same. Thicker ones are more efficient at detecting gamma rays but offer worse spatial resolution.
|
|
|
Do pinhole collimators minify or magnify?
|
They can do both, depending on if they are closer than the focal length (L), in which case they magnfiy, or farther than the focal length, in which case they minify.
|
|
|
How is the efficiency of gamma camera collimators related to the following parameters?
1) Thickness of the lead septa 2) Length of holes 3) Diameter of holes |
Thicker septa, longer holes, and smaller holes decrease efficiency. However, these same changes result in better spatial resolution.
|
|
|
Without correction, gamma camera uniformity should be better than ____ %.
With correction, this number falls to ____ %. |
10% without correction.
5% with correction. |
|
|
Describe sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value.
|
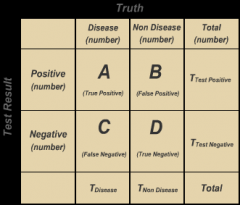
Sensitivity = true positive/all with disease (a/(a+c))
Specifivity = true negatives/all without disease (d/(b+d)) PPV = true positive/all test positive (a/(a+b)) NPV = true negative/all test negative (d/(c+d)) |
|
|
Describe the properties of a point source when used for gamma camera uniformity check?
|
Smaller than 0.5 mL, 0.5 to 1.0 mCi activity, and located at least at a length than is 3x the detector diameter away.
|
|
|
What is the limit for lifetime effective dose of an occupational worker?
|
10 mSv x age
|
|
|
What is the risk of cancer per Sv for low dose radiology applications estimated to be?
|
5.5%/Sv
|
|
|
What is CTDI proportional to?
|
kV^2 x mAs x 1/pitch
|
|
|
What is the typical entrance skin exposure in CT?
|
30 mGy
|
|
|
What is the estimated fetal dose from a mother's ab/pel CT?
|
10 to 50 mGy
|
|
|
What is ultrasound axial resolution equal to?
|
Axial resolution = spatial pulse length/2
|
|
|
What is spatial pulse length in ultrasound?
|
# of cycles in the pulse x wavelength
|
|
|
What equation relates HVL to linear attenuation coefficient?
|
HVL=0.693/u
|
|
|
How accurate is CTDI for pediatric dose?
|
Usually underestimates (smaller child = greater underestimation)
|
|
|
Relationship of scatter to primary ratio to kVp?
|
Scatter to primary ratio increases with higher kVp.
|
|
|
What parameters of TE and TR produce the most signal to noise?
|
Long TR (allows time for full T1 recovery)
Short TE (gather signal before it decays) |

