![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
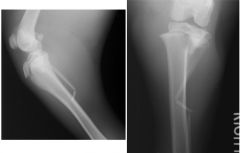
|
-Salter Harris Fracture of the Proximal Tibia
|
|
|
What should you do when you don't know what the normal anatomy for a breed/species looks like?
|
-compare it to the other limb
|
|
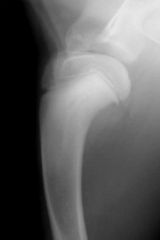
|
-osteochondrosis of the humeral head
|
|

|
-Panosteitis
|
|
|
How to use a systemic approach in radiographic interpretation
|
-Evaluate quality of the films: properly exposed and positioned, includes all areas of interest, enough views are made in order to diagnose
-Evaluate soft tissues: swelling? mass? mineralization? -Always include the joint proximal and distal to the long bone |
|
|
5 parameters of bone to evaluate
|
-site
-shape -size -number -presence/absence |
|
|
Monostotic
-definition |
-affects 1 bone
|
|
|
Polyostic
-definition |
-affects more than 1 bone
|
|
|
Cortical bone
|
-compact bone on the outside of the bone
|
|
|
Medullary bone
|
-cancellous bone on the inside of the bone
|
|
|
Periosteum
|
-outside surface of the cortical bone
|
|
|
Endosteum
|
-inside surface of the cortical bone
|
|
|
What is necessary to know in order to understand the disease processes of bone?
|
-modeling and remodeling processes of bone
|
|
|
What happens to articular cartilage as an animal gets older?
|
-the articular cartilage mineralizes and shrinks
|
|
|
Bone responses to insults
|
-production of new bone
-destruction of existing bone (combination is usually present with one predominating) |
|
|
How long does it take to radiographically appreciate change in bone?
|
-10-14 days
|
|
|
An area of bone resorption is called
|
-lysis/osteolysis
|
|
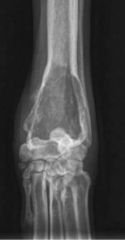
What is occuring in this image?
|
-there is an area of increased opacity, indicative of bone lysis
|
|
|
How can aggressive bone lesions be characterized?
|
-destruction
-production -zone of transition -location -rate of change |
|
|
How can you differentiate and lesion of severe aggressive bone lysis from a lesion of mild bone lysis?
|
-mild = smooth margin
-severe = irregular margin |
|
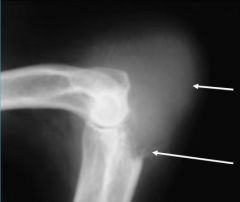
What is this?
-describe why |
Geographic lysis
-irregular margin -soft tissue swelling -missing a large lucent area of bone |
|
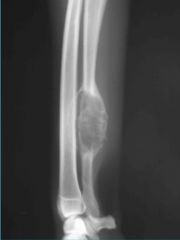
What is this?
|
-geographic lysis that probably began in the medullary cavity
|
|
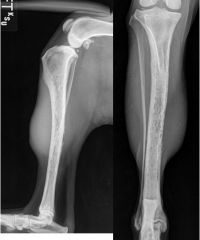
What is this?
-describe it |
Lysis hemangiosarcoma
-permeative lysis -long zone of transition -soft tissue mass is present |
|
|
How do you know there is new bone formation?
|
-area of increased opacity
|
|
|
How do you know if new bone production is benign or malignant?
|
-benign: smooth contour and uniform opaque
-aggressive: opacity is not uniform |
|
|
Different ways to describe a periosteal reaction
|
-focal, smooth (tendon attachment)
-periosteal buttressing (callus) -thin smooth periosteal proliferation -palisading -multiple layers -spiculation |
|
|
What are the only 2 aggressive reactions that occur in bone?
|
-inflammation
-neoplasia |
|
|
Types of Periosteal margins
|
-active/aggressive = fluffy
-less active/non-aggressive = sharp (chronic) |
|
|
Enthesophyte
|
-reaction of bone to abnormal forces
|
|
|
Panosteitis
|
-endosteal and periosteal new bone
- |
|
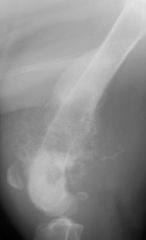
Describe
|
Panosteitis
-Spiculated -amorphous |
|
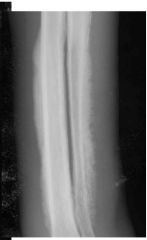
What is this?
|
Pallisading periostial growth
|
|
|
A pallisading growth lesion
-aka |
-Hypertrophic osteodystrophy
|
|
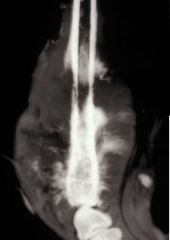
What is this?
-describe it |
Liposarcoma
-spiculated -sunburst pattern |
|
|
Codman's Triangle
|
-a triangular area of subperiosteum that separates the periosteum from bone
-almost always associated with aggressive lesions |
|
|
Effect of a degloving injury
|
-osteomyelitis
|
|
|
What occurs in a degloving injury?
|
injury is so bad that tissue has been ripped off of the bone
|
|
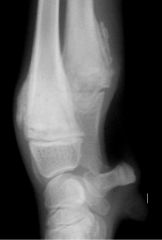
What is this?
|
Chronic HOD metaphyseal cuffing
|
|
|
Animals that Chronic HOD metaphyseal cuffing occurs in
|
-young dogs
|
|
|
Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy
-secondary condition to |
-neoplasms or infectious masses in the thoracic or abdominal cavities
|
|
|
Hypertrophic osteodystrophy
-treatment |
thoracic or abdominal surgery
|
|
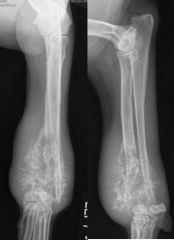
Describe the lesion.
|
-mixed lesion
-hair-like periosteal new bone |
|
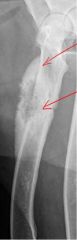
What type of bony response exicts
|
-mixed lesion
|
|
|
Short vs. Long Zone of Transition
-characteristics |
Long:
-about themajority of the cortical bone Short: less aggressive |
|
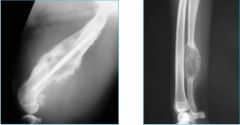
Which has the longest/shortest zone of transition
|
-shortest = right
-longest = left |
|
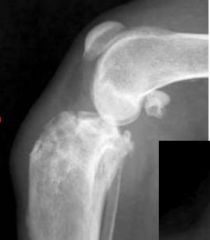
What is this disease?
|
-Polyostotic disease
|

