![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the seven step approach to determining sellar pathology
|
-First identify the pituitary gland and sella turcica.
-Then determine the epicenter of the lesion and whether it is in the sella or above, below or lateral to the sella. -If it is in the sella, determine whether or not the sella is enlarged. -Once the location of the mass is clear, analyze the signal intensity patterns: is the lesion cystic or solid? - Determine if it contain any abnormal vessels? -Determine if there is any calcifications? |
|
|
So basically you want to find determine the epicenter of the lesion, if it is enlarging the sella, and if it has fat, cystic changes, a solid component, calcificaitons and any vessels
|
yes
|
|
|
What bony structure does the pituitary gland lie within
|
the sella turcica
|
|
|
Do females tend to have a convex superior margin of the sella turcica
|
yes, it appears to be bulging out and this is normal. Males will be concave
|
|
|
What are the 3 most common abnormalities that arise from the pituitary gland
|
pituitary adenoma, Rathke's cleft cyst and craniopharyngioma
|
|
|
What are the common pathology that arise from the pituitary stalk
|
rathkes cleft cyst
craniopharyngioma germinoma eosinophilic granuloma mets |
|
|
Can a rathkes cleft cyst and a craniopharyngioma both arise from the stalk or the pituitary gland its self
|
yes
|
|
|
What demographic tends to get germinoma and eosinophilic granulomas of the pituitary stalk
|
children
|
|
|
Can mets and lymphoma also be found in the pituitary stalk
|
yes
|
|
|
Is the optic chiasm technically in the suprasellar cistern
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the MC tumor to arise from the optic chiasm
|
gliomas
|
|
|
What demylinating disease commonly affects the optic chiasm
|
MS
|
|
|
How can you tell if the optic chiasm is effected by MS
|
it will be swollen
|
|
|
What is just above the optic chiasm
|
the hypothalamus
|
|
|
What ventricle does the hypothalamus help make up the walls of
|
3rd ventricle. Anatomically the hypothalamus forms the lateral walls and floor of the third ventricle.
|
|
|
What pathology may occur in the hypothalamus of children
|
hamartomas, germinomas and eosinophilic granuloma.
|
|
|
What does the supracavernous segement of the ICA bifurcate into
|
anterior cerebral artery, which passes cranially to the optic chiasm, and the middle cerebral artery, which runs laterally.
|
|
|
What pathology may involve the ICA
|
aneurysm
|
|
|
What nerves run through the cavernous sinus
|
nerve III (oculomotorius), IV (trochlearis), V1 and V2 (trigeminus).
The sixth cranial nerve (abducens) runs more medially and is located caudal to the carotid artery. |
|
|
What are some examples of common pathology that
|
schwannoma
thrombosis C-C fistula |
|
|
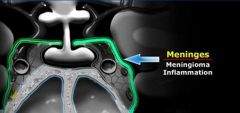
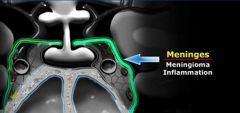
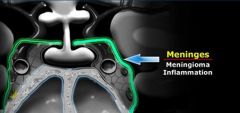
Do meninges cover the cavernous sinus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What 2 pathology may arise from the meninges
|
meningioma
mets meningitis |
|
|
Where is the sphenoid in relation to the the pituitary gland
|
bellow the sella turcica
|
|
|
What are the 2 bony boundaries of the pituitar
|
the area it lies in is the sella turcica
Front-tuberculum sella Back-Dorsum sella |
|
|
What pathology may arise from the sphenoid
|
SCC and adenoid cystic carcinoma
chordoma, chondrosarcoma, and osteosarcoma from the clivus bacterial and infections can also occur here. |
|
|
What is the size criteria for a pituitary microadenoma
|
less than 10mm
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a pituitary microadenoma
|
a rathkes cleft cyst
|
|
|
What is the treatment if a pt has excessive hormone production from a suspected pituitary adenoma
|
an MR without contrast. It doesnt matter if it is negative the only thing that the ordering physician is concerned about is if there is a large mass. Pt will be treated symptomacally no matter if it is negative or if there is a small microadenoma
|
|
|
What if the pt fails conservative therapy then is contrast necessary
|
yes, you want to see the small lesion as accurately as possible
|
|
|
What percent of pituitary microadenomas are detected by non-contrasst MR
|
70%
|
|
|
What percent of microadenomas are detected with MR with gad
|
85%
|
|
|
What is the size definition of a macroadenoma
|
>10mm
|
|
|
Describe the appearance of a macroadenoma
|
They tend to be soft, solid lesions, often with areas of necrosis or hemorrhage as they get bigge
|
|
|
Why do macroadenomas get the snowman appearance
|
Because they are soft tumors, they usually indent at the diaphragma sellae, giving them a 'snowman' configuration.
|
|
|
What are 2 ways to differentiate a meningioma from a macroadenoma
|
a meningioma will not compress in at the diphragma sella and it will not expand the sella turcica
|
|
|
Does a pituitary macroadenoma expand the sella turcica
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the covering of the sella turcica
|
diphragma sella
|
|
|
Do meningiomas typically have uniform enhancement
|
yes
|
|
|
How is the sella turcica violated for surgery of a macroadenoma
|
through the floor of the sella turcica and the macroadenoma is taken out via the sphenoid sinus
|
|
|
What is the most common tumor of the skull base
|
pituitary adenoma
|
|
|
Pathologically what does a Rathkes cleft cyst look like
|
The cyst is fluid-filled and has very thin walls with a thickness of only one or two cell layers
|
|
|
Can a rathkes cleft cyst occur in or above the sella turcica
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the main ddx of a suprasellar cystic structure
|
craniopharyngioma
Rathkes cleft cyst |
|
|
What is a similarity of a ratkes cleft cyst an a pituitary adenoma
|
they both will not enhance with contrast
|
|
|
Since all extracellular masses enhance, what is the ddx of a non-enhancing extracellar mass
|
Rapid arterial flow (eg. large blood vessel).
No cellular tissue (eg. cyst). No blood supply (eg. infarcted mass). pituitary adenoma |
|
|
Is a major difference between a rathkes cleft cyst and a craniopharyngioma
|
Technically these are benign tumors, but unlike Rathke's cleft cysts, they have thick walls and are locally invasive
|
|
|
What is the common appearance of a craniopharyngioma
|
A large intrasellar and suprasellar mass with cystic and enhancing components as well as calcifications.
|
|
|
Can a cranipharyngioma be both intrasellar and extrasellar
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the main ddx of a craniopharyngioma
|
teratoma
|
|
|
What percent of meningiomas occur at the skull base
|
The most common intracranial tumor in adults is the meningioma with 20% of occurring at the skull base
|
|
|
Are meningiomas generally solid tumors that can have occasional peripheral cystic change
|
yes
|
|
|
What suprasellar lesion must always be ruled out first
|
aneurysm
|
|
|
What tends to happen to pituitary adenomas as they enlarge in size
|
When pituitary macroadenomas get this size they usually have areas of hemorrhage or necrosis - in mengiomas this is less often the case.
|
|
|
What 3 lesions can be partially in the sella turcica and partially suprasellar
|
aneurysm
menigioma adenoma |
|
|
What are 3 things that are black on MRI
|
air
bone rapid blood flow |
|
|
Can a mass compressing upon the pituitary cause increased hormone release
|
yes, even an aneurysm
|
|
|
What is the stalk section effect
|
The pituitary stalk connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland and hormones produced in the hypothalamus are transported to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland via portal veins running along the stalk.
Most of these hormones stimulate the production of other hormones in the pituitary gland (such as TRH, GnRH, GHRH and CRH), but the release of dopamine inhibits the production of prolactin by the anterior lobe of the pituitary. Therefore when the stalk is compressed by a mass or is transected, the level of prolactin rises while all the other hormone levels decrease. This is known as the 'Stalk Section Effect'. It is the reason why masses other than adenomas can cause hyperprolactinemia. |
|
|
What are suprasellar hamartomas
|
Hamartomas masses of dysplastic tissue found almost exclusively in young children.
|
|
|
What demographic typically gets suprasella hamartomas
|
children
|
|
|
Do hamartomas enhance
|
no
|
|
|
Where do suprasellar hamartoma typically arise
|
they hang down from the floor of the third ventricle. The best images to see hamartomas on are enhanced sagittal T1-weighted MR images.
Here you can see the non-enhancing hamartoma attached to the tuber cinereum between the pituitary stalk and mamillary body. |
|
|
Why is it important to know what the tuber cinereum is
|
it is the portion of the between the mamillary body and the stalk where hamartomas arises.
|
|
|
If you see a non-enhancing mass attached to the tuber cinereum in a child what is the ddx
|
there is non ddx. Its a hamartoma
|
|
|
What hereditary disease predisposes patients to optic gliomas
|
NF1
|
|
|
Do optic gliomas typically enhance
|
yes, but not all of them
|
|
|
Do 25% of optic gliomas not enhance
|
yes, only 75% show the typical enhancement pattern
|
|
|
What is a good way to determine if a lesion is an optic glioma
|
look at the optic nerve and if there is enlargement of the optic nerve as it moves into the orbit it is likely an optic glioma
|
|
|
What demographic will typically get germinomas
|
children and adolescents
|
|
|
Do germinomas typically enhance
|
yes
|
|
|
Where do germinomas typcially occur
|
these are midline by the hypothalamus but also will occur in the pineal gland area
|
|
|
Can a germinoma show restricted diffusion
|
yes
|
|
|
Do germinomas typically crawl along the floor of the 3rd ventricle
|
yes
|
|
|
What are 3 lesions that will typically occur in the clivus
|
chordoma
chondrosarcoma mets |
|
|
What is a good general rule of thumb for a chordoma Vs a chondrosarcoma
|
chordomas tend to occur midline
chondrosarcomas will tend to occur off midline |
|
|
Can a chordoma and chondrosarcoma both have calcifications
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the signal intensity of the clivus normally on T1
|
high signal intensity but if infiltrated by tumor it may be dark.
|

