![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
well-defined unilocular
|
one cavity
border is well-defined, most benign lesions are unilocular |
|
|
well-defined multilocular
|
border is well defined with several cavities
|
|
|
well defined honeycomb or soap bubble
|
multilocular
|
|
|
diffuce radiolucency
|
cannot follow the border of the radiolucency, 90 % of the time is is cancer
|
|
|
first diagnosis if there is a loss of cortical plate
|
cancer
|
|
|
hamular process
|
bony projection that arises from the sphenoid bone and extends downward and slightly posteriorly
|
|
|
hamular process on radiograph
|
proximity to the posterior surface of the maxillary tuberosity,
varies greatly in length, width and shape among patients usually has a bulbous point, but sometimes tapered |
|
|
coronoid process on radiographs
|
the image of the mandible on maxillary pa's
its tapered or triangular radiopacity below the molar teeth and maxilla |
|
|
superior gray scale resolution in digital photography
|
the human eye can only appreciate 32 shades of gray, the traditional radiograph differentiates 16-25 shades of gray, while the digital image uses up 256 shades of gray
|
|
|
storage phosphor imaging system
|
uses reversible imaging plate rather than a sensor (more flexible)
|
|
|
direct digital imaging system
|
uses an intraoral sensor attached to a fiberoptic cable
|
|
|
indirect digital imaging system
|
scans an existing radiograph and digitizes the image
|
|
|
charge-coupled device (ccd)
|
the most common digital image receptor
solid state detector with silicon chip embedded in it the circuit in the chip is sensitive to the X-rays |
|
|
primary radiation
|
the radiation produced at the anode of the X-ray tube that is attenuated by the filter and object
|
|
|
secondary radiation
(scatter) |
interactions of the primary beam with the atoms in the object being imaged
it is a major source of image degredation |
|
|
when x-radiation passes thorough a patient, what three interactions can happen
|
coherent scatter
photo electric absorption compton scattering |
|
|
most scattered x rays in diagnostic xray imaging arises from:
|
compton scattering
|
|
|
what reduces the amount of scatter radiation?
|
leaded rectangular done (reduces the size of the beam)
|
|
|
collmination
|
the control of the size and shape of the X-ray beam
|
|
|
how big can the diameter of a circular beam be
|
2.75 inches
|
|
|
short wavelength xrays
|
great penetrating power,
produced at higher kilovoltage form the image on the film |
|
|
long wavelength xrays
|
produced at lower kilovoltages
lower penetrating power are useless rays |
|
|
what filters out long wavelength rays?
|
aluminum discs
|
|
|
filtration
|
removal of parts of the X-ray spectrum using absorbing materials in the X-ray beam
reduces patient does, contrast and film density |
|
|
inherent filtration
|
filtration by any parts of the X-ray tube through which the beam must pass
parts include the glass envelope, and oil |
|
|
added filtration
|
obtained by placing thin sheets of aluminum in the conn to filter the beam further
|
|
|
total filtration
|
inherent + added filtration
|
|
|
recommended total filtration
|
equivalent of 0.5 mm (below 50 kvp) and 2.5 mm (over 70 kvp) of aluminum
|
|
|
how far should the operator stand from the patient when taking xrays
|
6 feet
|
|
|
where should the operator stand to avoid the primary beam when taking xrays
|
90-135 degree angle to the beam
|
|
|
EKTA speed film
|
provides the most effective way to reduce exposure time, amount of radiation reaching the patient and amount of scatter radiation to the operator
|
|
|
what is the max dose of radiation for someone who works near radiation
|
5 rem (.1rem per week)
|
|
|
what is the max dose for normal people
|
.5 rem
|
|
|
what can too much radiation exposure cause?
|
carcinomas, genetic mutations, different leukemias, cataracts
|
|
|
mechanisms that cause carcinogenesis and genetic mutations
|
frame shift mutations
synergism with checimal carcinogens altered dna repair enzymes |
|
|
radiosensitive cells
|
small lymphocytes
bone marrow reproductive cells prostate gland hemopoietic tissue |
|
|
what is the most sensitive to radiation?
|
hemopoietic tissue
|
|
|
radioresistant cells
|
mature bone
muscle nerve |
|
|
what is the most resistant to radiation?
|
muscle
|
|
|
radiation absorbed dose (rad)
|
a measure of the energy imparted any any type of ionizing radiation to a mass of any type of matter
|
|
|
equivelant dose
|
the correct unit of measurement used by the dentist to compare the biologic-risk effects/estimates of different radiation damage to a tissue or organ
|
|
|
effective dose
|
used to estimate the risk in humans
|
|
|
exposure
|
a measure of radiation quantity
|
|
|
roetgen (R)
|
traditional unit of radiation exposure measured in air
only applies to X-rays and gamma rays |
|
|
what has more energy?
X-rays or light |
X-rays
|
|
|
cephalometrics
|
(lateral head radiograph) radiographs used to study craniofacial growth, diagnosis, planning ortho, and evaluation of treated cases
assess tooth to tooth, bone to bone and tooth to bone relationships |
|
|
serial cephalometric films show what?
|
amount and direction of growth
|
|
|
submental vertical view
|
diagnose basilar skull fractures
provides diagnostic info about zygoma, zygomatic arches and mandible taken from below mandible and film above the head |
|
|
water's view
|
showing anterior view of paranasal sinuses and mid face and orbits
film is against patients face and source is behind patients head |
|
|
towne's view
|
visualize condyles and neck of mandible
film is under head with source from the front at 30 degrees from frankfort plane-directed right at the condyles |
|
|
conventional tmj radiographs
|
show the condyles in the glenoid fossa, range of the condyles antero-posterior movement and areas of bone destruction of the condylar heads
|
|
|
developer solution
|
converts invisible image into visible image
reduces silver halide crystals to black metallic silver |
|
|
4 chemicals that are in developing solution
|
developing agent (hydroquinone
antioxadant preservative (sodium sulfite) accelerator (sodium carbonate) restrainer (potassium bromide) |
|
|
developing agent
|
Hydroquinone
changes exposed silver halide crystals to black metallic silver gives detail to the X-ray |
|
|
antioxidant preservative
|
sodium sulfite
prevents developer solution from oxidizing int the presence of air |
|
|
accelerator
|
sodium carbonate
alkali that activates the developing agents and maintains the alkalinity of the developer softens gelatin of emulsion |
|
|
restrainer
|
potassium bromide
control the action of the developing agent so it does not develop the unexposed silver halide crystals to produce fog |
|
|
xray fixing solution
|
fixer
stops development and remove remaining unexposed crystals |
|
|
what four chemicals are in fixer?
|
clearing agent (sodium or ammonium thiosulfate)
antioxidant preservative (sodium sulfite) acidifier (acetic acid) hardner (potassium alum |
|
|
clearing agent
|
sodium or ammonium thiosulfate
commonly called hypo dissolves and removes underdeveloped silver halide crystals |
|
|
antioxidant preservative
|
sodium sulfite
prevents decomposition of the fixer chemical |
|
|
acidifier
|
acetic acid
necessary for the correct action of the other chemicals neutralizes any alkaline developer still on the film |
|
|
hardner
|
potassium alum
shrinks and hardens the gelatin in the emulsion shortens drying time protects the emulsion from abrasion |
|
|
brown film
|
not fixed long enough
|
|
|
advantages of bisecting angle technique
|
decreased exposure time
|
|
|
disadvantages of bisecting angle technique
|
image may be distorted
|
|
|
buccal object rule
slob rule |
same lingual opposite buccal
|
|
|
inverse square law
|
original intensity= new distance2
new intensity original distance2 |
|
|
focal spot
|
small area of tungston on the anode from which emanates and receives the impact of the speeding electrons
|
|
|
target
tungston target |
a tungsten wafer embedded in the anode face at the point of electron bombardment
|
|
|
target film distance
|
distance from the xray source (focal spot) to the film (dertimined by the length of the cone)
|
|
|
two sizes of cones
|
20 cm - 8 inches
41 cm - 16 inches |
|
|
half value layer (HVL)
|
the amount of material required to reduce the intensity of an X-ray beam to half
normaly aluminum or copper thickness, may also be other materials or media |
|
|
what does hvl incicate
|
quality of an X-ray beam
|
|
|
what does the focal spot influence
|
image sharpness/definition
|
|
|
intensifying screens
|
devices used in extra oral radiography (pano, ceph)the convert X-ray energy into light which exposes the screen film
reduces amount of radiation exposure |
|
|
what does the operator control?
|
kvp kilovoltage
mA miliamperage exposure time |
|
|
kVp
|
the quality oor penetrating power of the X-ray beam that controls the speed of electrons
suitable range of kVp 64-100 |
|
|
how does kVp influence the X-ray beam and radiograph
|
contrast and determines the penetrating ability of the X-ray beam
|
|
|
what affect does increasing or decreasing kvp have?
|
increasing kvp reduces subject contrast
decreasing kvp increases subject contrast |
|
|
miliamperage mA
|
controls the number of X-rays produced
suitable ranges 7-15 controlled by the temperature of the tungsten target |
|
|
exposure time
|
the length of time X-rays are produced
|
|
|
density
|
overall darkness of a radiograph
|
|
|
how to affect density
|
increases as mA, kVp, or exposure time increase
decreases as mA, kVp, or exposure time decrease |
|
|
contrast
|
difference in the degree of blackness between adjacent areas on a radiograph
affected by kVp only higher kvp produces low contrast |
|
|
5 rules to create accurate images
|
1. use smallest focal spot
2. use longest source-film distance 3. place film as close to structure as possible 4. direct central ray at right angle to film 5. keep film parallel to structure |
|
|
what does a long cone do?
|
minimizes image magnification
|
|
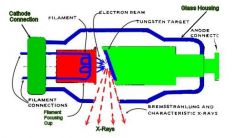
X-rays are generated when a stream of electrons (produced by the filament) travels from the cathode anode and is suddenly stopped by its impact on the tungsten target
|
filament
molybdenum cup electron stream tungsten target focal spot copper sleeve vaccum xray beam leaded glass housing |
|
|
occult diseases
|
includes small carious lesions, cysts and tumors that don't have signs or symptoms
X-rays should not be done to look for these |

