![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does SLOB stand for in the SLOB rule?
|
Same Lingual; Opposite Buccal
|
|
|
What are the three different names for the rule dictating how object appear to move when the angle of an X-ray is changed?
|
Buccal Object Rule; Tube-shift technique Clark's Rule; SLOB rule
|
|
|
In the Buccal Object Rule, if you have two objects that are superimposed and move the X-ray beam to the LEFT, what should happen to the object CLOSEST to you?
|
It will move AWAY.
|
|
|
The object closest to you moves in the (same/opposite) direction?
|
opposite
|
|
|
For the Buccal Object Rule to work, you need one of two things. What are they?
|
2 films at slightly different position; Image of object from two different angles
|
|
|
The object closest to the buccal surface appears to move (towards/away from) the direction of the tubehead.
|
away from
|
|
|
What if you take 2 images and the object does NOT move?
|
It is centrally located
|
|
|
Horizontal beam angulation is changed when locating (vertically/horizontally) aligned objects
|
vertically
|
|
|
Vertical beam angulation is changed when locating (vertically/horizontally) aligned objects
|
horizontally
|
|
|
The Right-angle technique is also called what?
|
Miller's Technique
|
|
|
Miller's Technique is also called what?
|
Right-angle technique
|
|
|
What is the method for determining the facial/lingual position of objects?
|
Miller's technique (aka right-angle technique)
|
|
|
The first radiograph in a Right-angle technique is a ___ or ___ while the 2nd one is a ____
|
PA, BW; Occlusal
|
|
|
True or False, Miller's technique (right-angle technique) uses two images to create an artificial 3-D view of a certain area
|
True
|
|
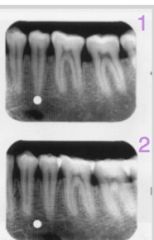
What side (buccal or lingual) is the white dot on based on these two images?
|
Lingual (The 2nd slide is more anteriorly located and the dot moved towards the anterior as well. "Same Lingual")
|
|
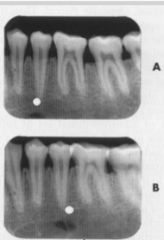
Which side (lingual or buccal) is the white dot on?
|
Buccal (film B is more anterior but the dot is more posterior... opposite buccal)
|
|
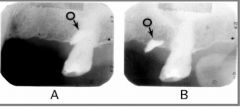
Based on these two films, where (buccal or lingual) is the foreign object [indicated by the black arrow] located?
|
Buccal (Film B is more posterior than A [note the coronoid process in the lower right, indicating a more posterior position] yet the object has moved anteriorly. "Opposite Buccal")
|
|
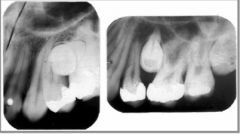
Where is the crown of the tooth located? (buccal or lingual?)
|
Lingual (Film on right is more distal and the crown is more distal as well. Same Lingual)
|
|
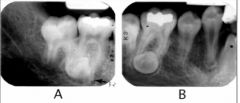
What side is crown of this impacted tooth located? (buccal or lingual)
|
Lingual (film B is more mesial and crown is more mesial, same lingual)
|
|
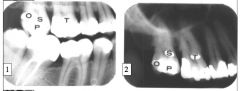
Is point O on the lingual or buccal surface?
|
Buccal (The film is shifted UP and O has shifted DOWN so it is opposite buccal)
|
|
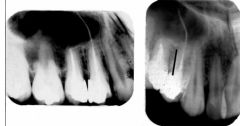
The very long white canal is on which side? (buccal or lingual)
|
Lingual (film more mesial, long canal is mesial, same lingual)
|
|
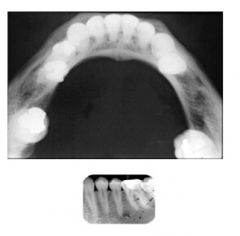
These two images are used in conjunction for which type of analysis?
|
right-angle technique (aka Miller's Technique)
|

