![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MRI stands for what?
|
magnetic resonance imaging
|
|
|
Conventional tomography is also called __ __ radiography
|
body section
|
|
|
True or False, cross sectional imaging allows viewing of an object without overlapping of structures
|
True
|
|
|
In conventional tomography, objects outside the place of interest appear how?
|
blurred out
|
|
|
What two things are commonly analyzed with conventional tomography in the mouth?
|
TMJ and a section of bone for implant analysis
|
|
|
In conventional tomography, the tube and film move in (the same/opposite) directions
|
opposite
|
|
|
The thickness of tissue in the focal plane is called ___
|
tomographic layer
|
|
|
T or F, panoramic technique is a form of tomography
|
T
|
|
|
Looking at the TMJ from the side is in the ___ plane
|
sagittal
|
|
|
Looking at the TMJ from the front of a patient's face is called a ___ plane
|
coronal
|
|
|
True or False, tomographs tend to be 99% stable with magnification
|
False, they will magnify an object
|
|
|
Which has a higher radiation dose, panos or tomography?
|
tomography
|
|
|
A patient with gagging problems would be (super pissed/probably fine) with a tomograph
|
probably fine
|
|
|
Which has higher radiation, tomography or medical CT?
|
medical CT
|
|
|
Tomography is (hard/easy) to use
|
easy
|
|
|
If you inject contrast material into the TMJ and view it with tomography, you are performing a TMJ ____
|
arthrography
|
|
|
What might you use a TMJ arthrography for?
|
disk position assessment, morphology, document something prior to surgery
|
|
|
True or False, TMJ arthrography is minimally invasive
|
false, very invasive
|
|
|
A CT will take cross sectional data and then do what with it?
|
reconstruct it
|
|
|
T or F, with CT technology, x-rays are used just like any conventional intraoral or extraoral radiographic technique
|
T
|
|
|
Computed Tomography uses (a single shot/many rotations) to capture an image
|
many rotations
|
|
|
Computed Tomography have (higher/lower) radiation than conventional tomography
|
higher
|
|
|
Other than cost and radiation dose, what is the other main disadvantage of computed tomography?
|
streak artifacts from metals
|
|
|
Computed tomography produces (2/3) dimensional images
|
3
|
|
|
True or False, computed tomography shows harsh superimposition of structures
|
False, none!
|
|
|
What do CBCT and CBVT stand for?
|
cone bean computed tomography
cone beam volumetric tomography |
|
|
CBCT uses how many 360degree rotations around the patient's head?
|
1
|
|
|
In a CBCT, the beam is shaped like what object?
|
cone
|
|
|
CBCT is limited to what region of the head?
|
maxillofacial
|
|
|
True or False, in most machines, the scan time for CBCT is 40 sec or less
|
True
|
|
|
CBCT allows for 2 and 3-D, T or F?
|
T
|
|
|
Compared to medical CT, a CBCT has (higher/lower) cost and radiation dosage
|
lower
|
|
|
CBCT only works on head and neck, T or F?
|
T
|
|
|
MRIs give (good/poor) soft tissue contrast
|
good
|
|
|
What types of waves are used in an MRI?
|
radiowaves
|
|
|
Which of these cannot be taken into an MRI room?
A. cotton shirt B. cardiac pacemaker C. credit cards D. plastic GI Joe toys E. watches |
B C and E cannot be taken in
|
|
|
Which is best for soft tissue eval of the disk?
A. Conventional tomography B. MRI C. CBCT |
MRI
|
|
|
What system uses vibration frequencies in the range of 1 to 20 MHz?
|
ultrasonography or sonography
|
|
|
The transducer in ultrasonography is made of ___ crystal
|
piezoelectric
|
|
|
What does the transducer do in ultrasonography?
|
converts electrical impulses to high-frequency sounds waves
|
|
|
True or False, human disease can exist without any specific anatomical change
|
True
|
|
|
What is the only means of assessing physical changes that are a direct results of biochemical alterations?
|
nuclear medicine
|
|
|
What are the radioactive materials that are injected into a patient called?
|
radiotracers (or radionuclide-labeled tracers)
|
|
|
signals from patient are recorded with ___ cameras in nuclear medicine
|
gamma
|
|
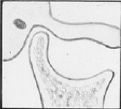
This is a cross section through what structure?
|
TMJ
|
|
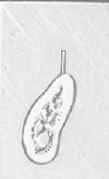
This is a cross section through what structure?
|
Jaw at location of a tooth of interest
|
|
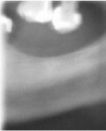
What view is this?
|
Sagittal
|
|
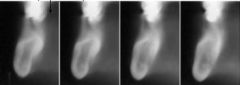
These cross sections are in the ___ view
|
buccal-lingual
|
|
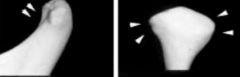
Which image is sagittal and which is coronal?
|
left, sagittal
right, coronal |
|
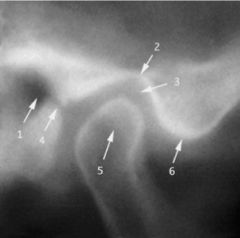
Is this patient's mouth open or closed?
|
closed
|
|
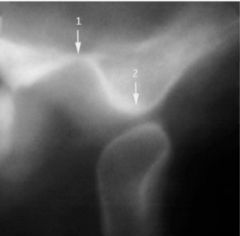
Is this patient's mouth open or closed?
|
open
|
|
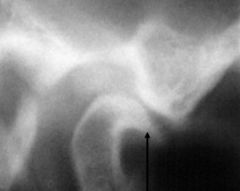
What is wrong with this TMJ?
|
the condylar head has degenerated a bit
|
|
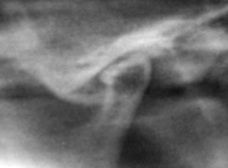
True or False, this condylar head appears too flat and thus is not normal
|
True
|
|
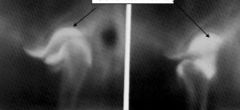
The RO fluid is contrast media, used in a TMJ ____
|
arthrography
|
|
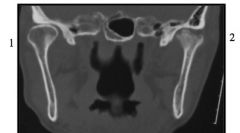
This image was taken with what technology?
|
Computed Tomography
|
|
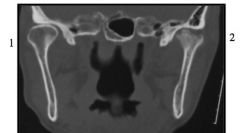
What view is this?
|
coronal
|
|
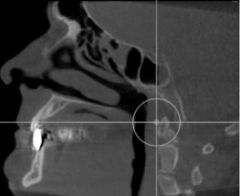
What view is this?
|
sagittal
|
|
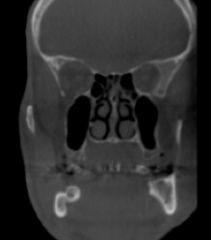
What view is this?
|
coronal
|
|
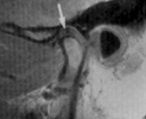
This image was taken with what technology?
|
MRI
|
|
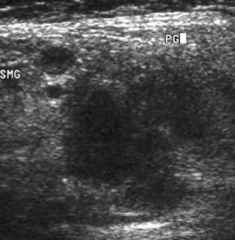
This image was taken with what technology?
|
Ultrasonography
|
|
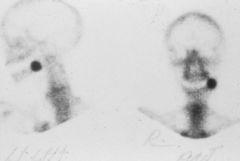
This image is generated using what technique?
|
nuclear medicine
|

