![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
With any radiographic finding, you need to be able to explain it in terms of 4 different things. What are these categories?
|
bone appearance, pathology, internal appearance, effect of lesion on surrounding tissue
|
|
|
The mandible is overall (RL/RO) compared to the maxilla
|
RL
|
|
|
The maxilla has (larger/smaller) and (rounder/more irregular) spaces then the mandible
|
smaller, rounder
|
|
|
Most abnormal conditions are (bilateral/unilateral)
|
unilateral
|
|
|
What are the 7 steps to analyze an osseous lesion?
|
1.Position & Distribution
2.Size & shape 3.Internal structure (RO/RL/Mixed) 4.Borders 5.Effects of the lesion on surrounding structures like bone & teeth 6.Periosteal reactions 7.Differential diagnosis |
|
|
A lesion may be in one area or spread out... what are the technical terms for these?
|
localized and generalized
|
|
|
We need to be sure to look at what portion of the root to diagnose periapical lesions?
|
apical 1/3
|
|
|
The point of origin of a lesion is also known as the ___
|
epicenter
|
|
|
If the epicenter is coronal to the tooth, it is probably ___
|
odontogenic
|
|
|
If the epicenter is above the mandibular canal, it is probably ___
|
odontogenic
|
|
|
If the epicenter is below the mandibular canal, it is probably ___
|
NOT odontogenic
|
|
|
If the epicenter is within the mandibular canal, it is probably ___
|
neural or vascular in nature
|
|
|
If the epicenter is in the condylar region, it is probably ___
|
cartilaginous lesion
|
|
|
If the epicenter is within the maxillary sinus or antrum, it is probably ___
|
non-odontogenic
|
|
|
Which of these are likely to be odontogenic?
Epicenter is: A. within max sinus B. coronal to tooth C. above mandibular canal D. below mandibular canal |
B and C
coronal to tooth above mandibular canal |
|
|
If a lesion has a thin RO line around a RL area, we say that this lesion is ___
|
corticated
|
|
|
If a lesion grows rapidly, or causes bone destruction, it tends to be ___ shaped
|
scalloped
|
|
|
Cysts tend to be (circular/scalloped) shaped
|
circular
|
|
|
The trabeculae become (thinner/thicker) in response to inflammation
|
thicker
|
|
|
Cysts tend to have a (corticated/non-corticated) border
|
corticated
|
|
|
A punched out lesion has (no/mild/severe) bone reaction
|
no
|
|
|
What does the bone surrounding a punched out lesion look like?
|
normal, up until the lesion edge
|
|
|
Wide radiopaque margin of reactive bone that is not uniform in width (not well defined) and may indicate SLOW growth of potential for lesion to stimulate the production of surrounding bone is known as what?
|
sclerotic border
|
|
|
What type of border is frequently seen with chronic periapical lesions?
|
sclerotic border
|
|
|
When you have a gradual transition between normal and abnormal bone trabeculae of a lesion, we call this a ____ border
|
undemarcated (or poorly defined)
|
|
|
Cystic lesions will be relatively (RL/RO)
|
RL
|
|
|
Calcified material will be relatively (RL/RO)
|
RO (best seen against a RL background)
|
|
|
If a tooth is ankylosed, it has:
A. A 50% larger PDL space B. A 50% smaller PDL space C. No PDL space D. Ankylosed teeth cannot be identified based on PDL |
C. No PDL space
|
|
|
Which of the following would be likely if a person has GENERALIZED and WIDE PDL spaces:
A. Perio disease B. Malignant growth like bone sarcoma C. orthodontic tooth movement D. severe bruxism |
A, C, and D are all indicated with a wide generalized PDL space.
(Yes, I get that if any of these were in a small area, it would suddenly become 'localized'. I guess these are just more commonly seen with generalized wide PDL. See page 7, slide 6) |
|
|
(No/Wide) lamina dura indicates periodontal disease
|
No
|
|
|
Generalized wide lamina dura may indicate what?
|
osteopetrosis (yes, osteopeTrosis!)
|
|
|
Traumatic occlusion is indicated by a (wider/thinner) lamina dura
|
wider
|
|
|
Orthodontic movement will give the patient a (wider/thinner/no change) PDL and a (wider/thinner/no change) lamina dura
|
wider, no change
|
|
|
A person with uncontrolled diabetes will have a(n) (loss/enlargement) of alveolar bone
|
loss
|
|
|
What bone disease has a 'sun-burst' appearance?
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
What is subpontic hyperostosis?
|
When alveolar crestal bone thickens below a bridge in a patient's mouth
|
|
|
"Onion-skin" type of appearance in periosteal bone indicates what?
|
This is an inflammatory response (like osteomyelitis)
|
|
|
Match:
1. osteomyelitis 2. osteosarcoma A. onion-skin type B. sunburst |
1=A
2=B |
|
|
True or False, inflammatory diseases only cause bone to be resorbed
|
False, it can cause resorption OR formation
|
|
|
Which type of lesion damages the cortical plate bone?
A. Fast moving B. Slow moving C. Both D. Neither, cortical bone is never damaged |
A. fast moving
|
|
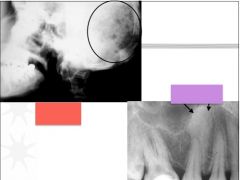
Which is generalized RL and which is localized RO?
|
Red - general RL
Purple - localized RO |
|
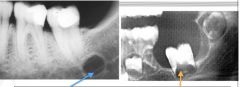
Which is periapical? Pericoronal?
|
blue - periapical
orange - pericoronal |
|
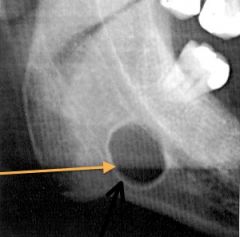
What is this?
|
salivary gland depression (not a cyst)
|
|
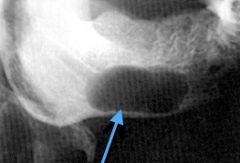
What is this lesion?
|
Neural lesion (because the canal is expanded)
|
|
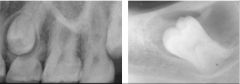
Which is fully and which is partially corticated?
|
left - fully
right - partially |
|
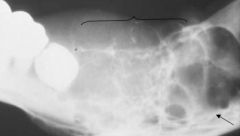
This is considered (uni/multi)locular
|
multi
|
|
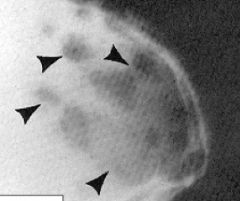
This is considered ___-corticated
|
non (or punched out)
|
|
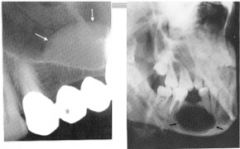
The image on the left is considered __-corticated. The image on the right has bone (resorption/deposition)
|
non-corticated, resorption
|
|
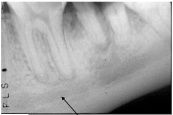
This type of bone forms in response to inflammation, what is it called?
|
sclerotic bone (also, it has an undemarcated border)
|
|
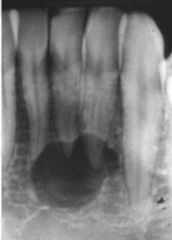
This lesion is ___-corticated
|
partially corticated
|
|
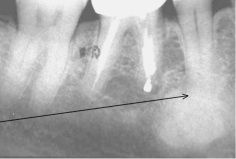
What is wrong with the LD and PDL space here?
|
They are indistinct
|
|
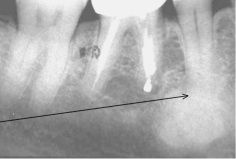
What is wrong with the LD and PDL space here?
|
They are indistinct
|
|
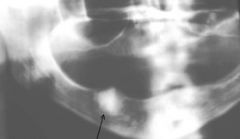
Describe this lesion in terms of its RL and/or RO
|
It is a well defined RO lesion with some cortication and a RL halo
|
|
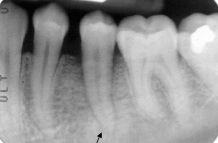
Describe the PDL space and LD
|
PDL is wider, LD indistinct (also, there is sclerotic bone)
|
|
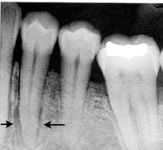
This irregularly wide PDL space is indicative of malignant ____
|
lymphoma
|
|
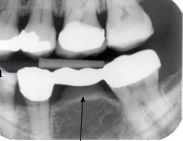
This mass of bone is called what?
|
Subpontic hyperosteosis
|
|
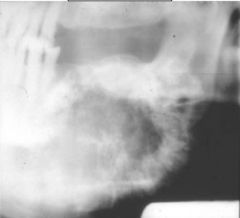
This sun-burst appearance is indicative of what?
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
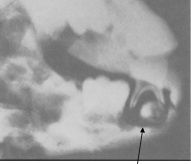
This tooth is called a ___ tooth
|
ghost
|
|
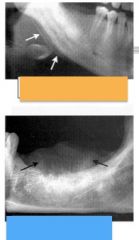
Which is onion skinned and which is sunburst?
|
orange - onion
blue - sunburst |
|
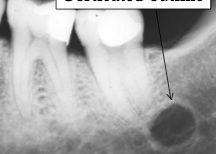
Is this lesions corticated?
|
yes
|
|

This is a ___ cyst
|
periapical
|
|
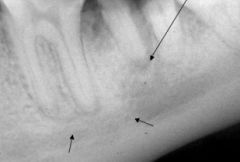
Name the 3 things evident in this picture (PDL, LD, bone)
|
wide PDL
indistinct LD sclerotic border |
|
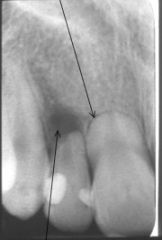
Is this internal or external root resorption?
|
external
|
|
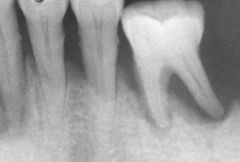
What is wrong with the left canal in the far right tooth?
|
calcified
|
|
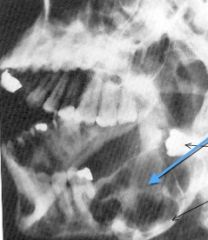
The blue line indicates a __locular lesion (bi, uni, multi, etc.)
|
multilocular
|

