![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Survival Curve
|
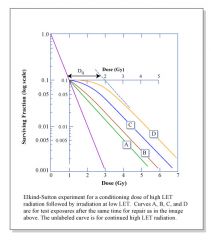
|
|
|
Cellular Damage from radiation can be divided into three categories:
|
-lethal damage
-sub-lethal damage - potentially lethal damage |
|
|
Lethal Damage
|
Kills the cell, irreversible and is not repairable.
|
|
|
Sublethal Damage
- repairable damage has the potential to repair |
Repairable damage, does not kill the cell unless further damage occurs.
Evident from split does experiments, Applies to X and gamma radiation only. No evidence from for repair from densely ionizing radiations. |
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage
|
Component of radiation damage that can be altered by the post irradiation environmental conditions.
|
|
|
For mitotic cell deaths caused by radiation the chromosomes lethal aberrations can be placed into two groups:
|
those caused by when a single photon creates two defects in a chromosome, and those caused by when two photons create two defects in a chromosome.
|
|
|
According to theory, it takes
|
2 strands to kill a cell.
|
|
|
The defects caused by the single photon when graphed on a survival curve make up the linear portion.
|
The defects caused by two photons make up the quadratic portion of the survival curve. ** See P.P
|
|
|
Damage which can be repaired (causes survival curve to bend), causes the quadratic portion of the survival curve.
|
In theory, when the first dose is given, a single strand breaks occurs. When dose is broken up over time, you increase the odds of a cell surviving.
|
|
|
During the time period doses, some of these single strand breaks can be repaired before
|
a second lethal strand break from another photon can occur.
- Can't give caner patient radiation all at once, radiation therapy over a 5 week span time. |
|
|
The more we _____________ the does, the more chance for repair
|
fractionate
|
|
|
Repair of sublethal damage is only significant for cellular damage caused by
|
photons.
- Neutrons and other high LET radiations ( alpha particles & neutrons) show little repair of damage ( as indicated by the survival rate) when the dose is fractionated. |
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (3rd Type)
- Cells need time to repair radiation damage. - Cells that replicate often are more prone to damage vs. cells that don't replicate often. |
That damage which is repairable to by the cell only if the cell is removed to an environment which puts it in stasis. For a cell, this type of environment is one which is absent of nutrients, causing a hault in division.
|
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (PLD)
-This is most likely be it delays the next mitosis. |
During mitosis, damage to the chromosomes is actually expressed. Deprived of nutrients, the cell cannot grow or progress through the cell cycle. The delay in mitosis increases the surviving fraction of cells exposed to X or gamma rays.
|
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (PLD)
cont. |
Damage done by densely ionizing/high LET radiation shows no PLD repair. This includes damage done by neutrons.
|
|
|
Potentially lethal damage (PLD)
cont. b |
Repair of PLD has been proved to occur in vitro. If cells are irradiated in vivo and then excised to an environment which stops their growth, repair also occurs.
|
|
|
Repair of sublethal damage is only significant for cellular damage caused by
|
photons.
- Neutrons and other high LET radiations ( alpha particles & neutrons) show little repair of damage ( as indicated by the survival rate) when the dose is fractionated. |
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (3rd Type)
- Cells need time to repair radiation damage. - Cells that replicate often are more prone to damage vs. cells that don't replicate often. |
That damage which is repairable to by the cell only if the cell is removed to an environment which puts it in stasis. For a cell, this type of environment is one which is absent of nutrients, causing a hault in division.
|
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (PLD)
-This is most likely be it delays the next mitosis. |
During mitosis, damage to the chromosomes is actually expressed. Deprived of nutrients, the cell cannot grow or progress through the cell cycle. The delay in mitosis increases the surviving fraction of cells exposed to X or gamma rays.
|
|
|
Potentially Lethal Damage (PLD)
cont. |
Damage done by densely ionizing/high LET radiation shows no PLD repair. This includes damage done by neutrons.
|
|
|
Potentially lethal damage (PLD)
cont. b |
Repair of PLD has been proved to occur in vitro. If cells are irradiated in vivo and then excised to an environment which stops their growth, repair also occurs.
|
|
|
Potentially lethal damage (PLD)
cont. b |
Whether this has any bearing on repair of radiation damage to humans is a matter of debate.
|
|
|
Different asynchronous cell populations exhibit different amounts of repairable damage:
|
Example: Intenstinal jejunum cells exhibit a large shoulder on a survival curve, indicating a large amount of repair.
- Bone marrow stem cells have a narrow shoulder and exhibit a little repair. |
|
|
However, different cell types are almost equally
|
radiosensitive when they are in mitosis.
|
|
|
If all cells are radiosensitive during mitosis, it implies
|
that differences in cell type radiosensitivity occur mostly during interphase.
|
|
|
Death by apoptosis also varies with cell type. Radioresistant cells show little death by apoptosis, whereas,
|
radiosensitive cells, like WBC's show a large amount of apopptic death.
|
|
|
Fractionating dosage
|
Breaking up the doses over time.
|
|
|
Sublethal Damage and Split Dose experiments
|
If we fractionate the dose given to a population of cells, that is divide one large dose into two or more smaller doses, the % of cells surviving increases.
- This is due to the repair by the cell of sub-lethal damage |
|
|
Repair of sublethal damage chart....
|
4 Gy + give more time, you will see more and more repair.
|
|
|
The % of cells surviving for a growing population is effected by
|
the time between doses of radiation.
|
|
|
However, there is a limit to this effect.
|
After a few hours delay, there is no appreciable increase in surviving fraction.
-All repair that occurs will happen during first few hours |
|
|
Normally, a population is asynchronous. A dose of radiation to a cell population will partially synchronize the cells as more cells are killed which are in sensitive phases of the cell cycle.
|
The surviving fraction change is affected by synchrony in the cell population.
|
|
|
Radio sensitivity and the Cell Cycle
G1+G2 = resting phase |
In a synchronous cell population it is found that there is greater amount of cell killing if radiation is given during (Mitosis and in G2) = very sensitive to radiation.
|
|
|
Radio sensitivity and the Cell Cycle cont.
|
For most cell types, S phase is the most radio-resistant phase of the cell cycle.
|
|
|
The Four R's of radiobiology
|
1. Repair
2. Reassortment 3. Repopulation 4. Re-oxygenation |
|
|
Reassortment
|
Redistribution of a cell population as to their place in the cell cycle.
|
|
|
Repopulation
|
When the dose is split, or given at a low dose rate, cellular survival increases due to cellular division. (Simply giving cells more time to grow, good for normal tissues not good for cancer cells.)
|
|
|
Mammalian Cells on average experience
|
100,000 plus DNA lesions per day.
However, mammalian mutation is very low due to repair mechanisms. |
|
|
Stop Breathing so Much
|
It is calculated that endogenously generated oxygen free radicals makes about 10,000 oxidative interactions with DNA per human cell per day.
|
|
|
Antioxidants
|
Antioxidants are chemicals which neutralize free radicals by donating one of their own electrons.
|
|
|
Antioxidants (2)
|
Vitamin's C and E are good at doing this and may protect against cellular damage.
|
|
|
Antioxidants (3)
|
Phytochemical found in fruits and vegetables also do this; free radicals scavengers.
|
|
|
Dose Rate Effect
|
In general, the lower dose rate the greater the surviving fraction. Dose rate shows the greatest effects between the rates of 0.001 Gy/min and 1 Gy/min, beyond or below this rate, there is little change in repair of damage or cell survival.
|
|
|
Dose Rate Effect cont.
|
Human cells show a great variation in the sensitivity to dose rate. This would indicate that some human cell types are good at repairing damage and others are poor.
|
|
|
Survival vs. Dose Rate
|
See. P.P Chart
|
|
|
The Oxygen Effect & Re-oxygenation
Oxygen is a _____________ |
radiosensitizer. It must be present during irradiation or immediately after to effect cell sensitivity.
|
|
|
Oxygen Enhancement Ratio
OER = |
The ratio of doses of hypoxic ( low oxygen) vs. aerated cells required to give the same biological effect.
|
|
|
OER =
|
Do for hypoxic cells/ Do for oxygenated cells
|
|
|
For photon exposure ( X + gamma) most cells have an OER of
|
2.5 to 3.0
|
|
|
OER is unity for ___________________ ie alpha's neutrons
|
Ionizing Radiations
|
|
|
Oxygen is believed to make
|
permanent the damage from indirectly ionizing radiations.
|
|
|
OH- is very damaging
|
Smalls amounts of oxygen are sufficient to significantly increase cell killing.
|
|
|
Hypooxic
|
low oxygen
|
|
|
anoxic
|
no oxygen
|
|
|
necrotic
|
dead
|
|
|
At 2% oxygen concentration, cell killing is about the same as it would be from normal aeration. Increasing.....
|
oxygen concentration beyond that of air even to 100% oxygen, doe not significantly increase the biological effect
|
|
|
Tumors larger then 200 microns (small) have necrotic centers.
|
Oxygen can diffuse about 150 microns from a capillary into a tissue.
10-15 % ( not sensitive to radiation, bad for cancer patients) hypoxic cells in tumors is typical. |
|
|
Brachytherapy
|
Is a method of using radioactive isotope to treat tumors and cancerous tissues.
- The sources are either implanted interstitially into the tumor volume or temporally inserted into the body cavities to place then in close proximity to the tumor. |
|
|
Treat by killing cancer cells and sparing good tissues
|
I-125 = half life of 60 days, this is why this is a great therapy.
|
|
|
Cs-137,Radium, I-125,Ir-192
|
are some isotopes which have been used for brachytherapy.
|
|
|
Cs-125 implants are used in prostate cancer.
|
Prostate cancer is slow growing tumor, cells have a long cycle, they do not reproduce quickly.
|
|
|
In quickly growing tumor types, tumor cell repopulation will make up
|
for what has been killed by the implant.
|
|
|
Dose Rate for interstitial therapy depends upon the amount of isotope implanted.
|
This is obvious, more isotope = greater dose.
|
|
|
Total prescribed dose to prostate is about
|
16 Gray
|
|
|
External Beam Therapy
- most common cancer treatment |
The most common method of cancer treatment utilities a linear accelerator. The linac emits high energy X-Rays which are well collimated to the tumor site. A high energy beam is necessary to penetrate deep into the body.
|
|
|
Treatment Plans
- All 4 of the R's of radiotheraphy come into play here |
A normal treatment plan is 5 days of therapy with 2 days off. Treatment continues for 5 weeks.
|

