![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is at the centre of an atom?
|
A nucleaus
|
|
|
What is is the nucleus?
|
protons and neutrons
|
|
|
What makes up most of the mass of an atom?
|
The nucleus.
BUT IT IS TINY AND TAKES UP VIRTUALLY NO SPACE |
|
|
What surrounds an atom
|
Electrons. They whiz around the outside. Their paths take up a lot of space.
|
|
|
What takes up most of the space in an atom
|
The electrons. Their paths take up a lot of space, giving the overall size, but it's mostly empty space.
|
|
|
What is the atomic number of an atom?
|
The number of protons in the nucleus.
|
|
|
What is the mass number of an atom?
|
The number of protons and neutrons in nucleus
|
|
|
What are isotopes?
|
Atoms with different numbers of neutrons.
They have the same atomic number, but different mass number. |
|
|
What is the difference between carbon-14 and carbon-12?
|
They are isotopes of carbon. carbon-14 has two extra neutrons than carbon-12.
|
|
|
What makes an element?
|
The number of protons or its atomic number.
|
|
|
How many stable isotopes does an element usually have?
|
One or two. carbon-12 is stable. carbon-14 is unstable and decays (breaks down) and emits radiation.
|
|
|
What is the smallest mass in an atom
|
The electron. carries a single negative charge -1.
|
|
|
How much heavier is a proton than electron?
|
2000 times. carries single positive charge +1
|
|
|
How much mass does a neutron have compared to a proton?
|
About the same. NO CHARGE THOUGH
|
|
|
Show the structure of a carbon-12 and carbon-14 atom
A = atomic mass X = chemical symbol for element Z = atomic number |
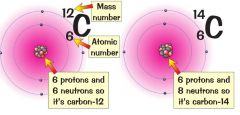
12 and 14
C C 6 6 |
|
|
What is radioactive decay?
|
When the nuclei of UNSTABLE isotopes break down and emit radiation.
|
|
|
What sort of process is radioactive decay?
|
The nuclei of unstable isotopes, like carbon-14, break down at RANDOM.
1000 unstable nuclei will not decay at same time and you can't predict or do anything to make it happen. |
|
|
Does anything natural influence decay?
|
NO!! It's completely unaffected by physical conditions like temp or chemical bonding
|
|
|
What happens when a nucleus decays?
|
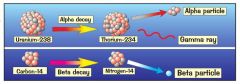
It spits out one or more of three types of radiation: alpha, beta, gamma.
IN THE PROCESS THE NUCLEUS OFTEN CHANGES TO A NEW ELEMENT |
|
|
What sort of background radiation do we have?
|
substances on Earth - food, rocks, soil
cosmic rays - radiation from space - solar flares living things - radiation from plants eaten etc. human activity - nuclear waste etc. (though tiny compared to others) |
|
|
What decides what an element is
|
Number of protons
|
|
|
What decides what an isotope is?
|
Number of neutrons
|
|
|
What sort of isotopes decay
|
unstable ones
|
|
|
If there are 6 protons in an atom, how many electrons are there?
|
6. number of electrons same as protons.
|

