![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 basic tenets of radiation safety?
|
1. Decrease time spent near a source
2. Increase distance from a source 3. Use shielding |
|
|
What does ALARA stand for?
|
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
|
|
|
Exposure has a _____ relation to length of time.
|
Linear relation
|
|
|
The intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the distance from a point source.
If distance is doubled, the intensity is quartered |
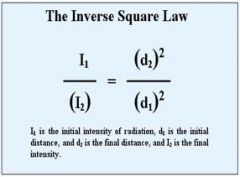
Inverse Square Law |
|
|
The exposure rate at a standard distance from a unit of radioactivity of a specific radionuclide
Units are in R⋅cm^2 / mCi⋅hr |

Specific exposure rate constant or gamma constant
|
|
|
What is the dose rate (DR) formula?
|
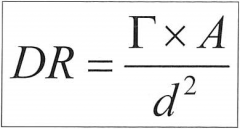
Gamma constant (R⋅cm^2 / mCi⋅hr)
Activity (mCi) Distance (cm) |
|

A specific exposure rate constant that neglects the contribution from low energy photons is indicated by a subscript for the energy cutoff in keV. How would you interpret this?
|
Any photons with energies below 20 keV we are ignored
|
|
|
What are the 3 ways that energy is lost?
|
1. Photo electric - photons hit something hard
2. Compton - Low energy protons hit outer orbital electrons and scatter 3. Pair production |
|
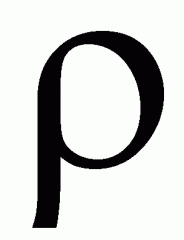
Density
|
ρ = gram/cm^3
|
|
|
Density thickness
|
ρ thickness = gram/cm^2
|
|
|
The fraction of the number of photons removed from the radiation field per cm of absorber.
It is specific for the energy of photon and the type of absorber |
The linear attenuation coefficient (μ)
|
|
|
What are the units for linear attenuation coefficient?
|
1/cm (thickness of shield is put in denominator)
|
|
|
The fraction of the number of photons removed from a radiation field per unit of mass of absorber
|
Mass attenuation coefficient
μ / ρ = cm^2/gram |
|
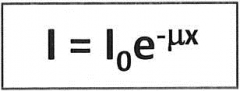
I = intensity after shielding
Io = initial intensity e = 2.718 μ = linear attenuation coefficient in cm^-1 x = thickness of shield in cm |
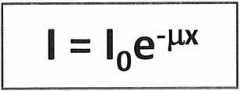
Shielding formula |
|
|
The thickness of a shielding material necessary to reduce the incident radiation intensity by 1/2.
It is specific to energy and absorber |
Half value layer (HVL)
|
|
|
How is the half value layer related to the linear attenuation coefficient?
|
HVL = 0.693 / μ
|
|
|
Thickness required to reduce exposure to 1/10th its original value
|
Tenth Value Layer
|

